Each period of development of our beautiful planet brings its own risks and threats. If 150 years ago the worst the bad guys could scare you with was to steal your horse or set your house on fire, now they have way more exquisite ways to spoil your dolce vitae.
In 2021, we recorded over 1,500 hacker attacks; this is 19% more than in 2020. In 81% of cyberattacks, the victims were legal entities. At the end of the year, the top five most frequently attacked industries included government agencies, industry, medicine, science and education software development services, and the FinTech software development. In each case someone creates and develops, and someone cynically ruins, aiming at an easy catch.
But here's the bright side: now you can prevent your belongings both real ad virtual. Learn to recognize the modern threats in this post.
In this article:
What is cybercrime
Cybercrime is a criminal activity, the purpose of which is the misuse of a computer, computer network or network device. Most (but not all) cybercrime is committed by cybercriminals or hackers who make money from it. Cybercriminal activities are carried out by individuals or organizations.
Some cybercriminals form organized groups, use advanced techniques and are highly technical. Others are novice hackers. Cybercriminals rarely break into computers for reasons unrelated to profit, such as political or personal reasons.
Types of online crimes
Dividing cybercrime into separate categories is not so easy, since there are many suppressions, but in general, we can distinguish the following types of cybercrime.
Financially oriented cybercrime
Cybercriminals use the Internet for commercial gain by carrying out the following types of attacks.
 Phishing
Phishing
As you know, phishing sites are created as fakes of popular web resources that users trust, and almost always the design of phishing sites resembles or even happens to be identical to the design of a popular site (original). Phishing sites are used for lucrative fraud, as most often incompetent and inexperienced users who cannot visually distinguish the original page from a fake one fall for their tricks. Thus, scammers, under the guise of a bank or a brand, ask for registration or motivate them to follow a link in order to receive cash profit or a gift. After the user follows the link, his data is automatically transferred to the attackers. To commit such crimes, cyber scammers mainly use email or social networks.

Cyber Extortion
This method of financially oriented cybercrime is associated with the fact that the user or company, after downloading the malicious code, encrypts files, and then receives an offer to restore in exchange for a monetary reward (usually in the form of bitcoins or other cryptocurrency). Since state banknotes can be tracked, and cryptocurrency is difficult to track. Cyber ransomware mainly uses encryption methods and is currently known as ransomware.

Financial Fraud
Most sophisticated financial fraud schemes involve hacking into retailers' computer systems in order to obtain customer banking data (so-called targeted attacks) or subsequently manipulating the information obtained. Some types of financial fraud are extremely difficult to detect.
Here is an example of cybercrime committed by ransomware that made a splash all over the world: WannaCry, NotPetya and BadRabbit. The cybercriminals gained access to the files on the system, encrypted them, and at the end of the attack showed the user a ransom demand on the monitor screen in exchange for the safe return of their data.
This situation has made thousands of companies nervous, who have clearly seen how they can lose their data if they do not pay the required amount of dollars.
Methods of protection against financially oriented cybercrime
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability tests to clearly know the points of entry into your systems.
- Use adequate protection tools such as firewalls and next generation antivirus/antimalware solutions.
- Keep your PC up to date! Remember that if the affected computers had been updated in a timely manner, they would not have been attacked. This is very important for improving system security, improving performance and eliminating errors in operation. Also note that companies that are forced to use computers with legacy operating systems (such as Windows XP) should adequately protect them and isolate them where possible.
- Do not open files, attachments, or links from unknown or untrusted emails, and do not reply to such emails.
- Be careful when opening links in letters, instant messages and social networks, even if they come from contacts you know.
- Back up periodically, especially the most important and sensitive information, to avoid data loss.
Cybercrimes related to invasion of privacy
Every Internet user should be aware of the risks of confidential data theft, malware threats, and how to mitigate such risks and threats. Hacking and theft of personal data most often affect social network accounts and mail accounts, online payment systems and Internet banking. As a rule, this happens due to the installation of malicious software on the computer, the targeted actions of intruders, as well as negligence and non-compliance with data confidentiality rules. Device malfunction implies both the absolute impossibility of turning it on and working (for example, if a Trojan blocker occupied the entire monitor with a banner asking to transfer money to the specified number), and deterioration of its normal operation (for example, a decrease in data transfer speed).
Personal information that you post on the Internet can fall into the hands of fraudsters, after which they have ample opportunities for committing illegal actions: sending spam among the friends of the user whose account was hacked, as well as distributing commercial or other information among them, etc. .P. That is why every social media user needs to seriously think about how to protect their account from hacking and comply with social media security rules.
Today, many people store personal information on a personal computer, and this information (a set of passwords and records) will allow for greater access to users' personal data, such as personal financial accounts. By running a malicious program on the victim's computer, you can access the files. There are programs that an attacker can use to gain access to your PC.
Theft of personal data.
Theft of personal information usually occurs with the aim of subsequent substitution of the identity of a person or group of people. While some attackers steal passports or other forms of identification to physically impersonate identities, the majority of identity theft takes place exclusively online. For example, someone seeking a bank loan could steal the personal information of a person with a good credit history.
Espionage.
The purpose of espionage, ranging from hacking individual computers or devices to illegal mass surveillance, is to covertly monitor your private life. It can be both physical espionage (for example, using web or CCTV cameras to monitor individuals or a group of people), and mass monitoring of various kinds of communications (reading mail, text messages, instant messengers, SMS, and so on).

Hot topic
Top 6 Security Breaches
Do you know what are the most common breaches nowadays? Find out to protect your company.
Show meSocial and politically motivated cybercrime
Some types of cybercrime are aimed at changing the mood in the political environment or intentionally harming or reducing the influence of individuals or groups of people. Hate crimes against an individual or a group of people are usually committed on the basis of gender, race, religion, nationality, sexual orientation, and other characteristics. Examples: harassment and sending offensive messages and spreading false news about a specific group of people. The anonymity and easy accessibility of the Internet makes it very difficult to combat hate crimes.
Extremist and terrorist groups are increasingly using cyberspace to intimidate, spread propaganda and sometimes harm IT infrastructures.
The main methods of identity theft
Keystroke tracking
Keystroke trackers are programs that record what you type. Keystroke tracking is commonly used to discover passwords to financial information.
Selection of passwords
You can determine the password through a series of guesses or through the use of an algorithm.
Let's say for example that you were born in 1999 and that you have a pet dog named Sharik, so you decide to make your password Sharik1999. Let's assume that you also have a VKontakte account that lists your birthday and a photo description tagging you and Sharik. Any intruder will be able to try to brute-force passwords with exactly this exemplary combination.
Backdoor access
If an attacker wants to get into your computer to steal passwords and files, or remotely monitor your activities, they can install a "backdoor". Backdoor programs take full advantage of weaknesses in network security and allow an attacker to enter and exit the system as they please without your knowledge or permission.
Many backdoors are created when unsuspecting computer users download "Trojan horses" that appear to be useful. Trojans are just one of several ways an attacker can get into a system. As we can see, there are actually numerous access routes, many of which are easy to overlook.
Wireless network attack
Attackers may be outside your home and try to identify your wireless network. If you have Wireless Protected Setup (WPS). Once inside the network, attackers can do a lot. This includes stealing your sensitive information, installing a backdoor connection, or simply implanting any other virus program.
Online deception
Attackers often trick their victims into signing up for wireless networks in public places. For example, an attacker could wait for their target in a cafe, create a network called "Coffee Shop and Free Wi-Fi", and thereby trick the target into logging in. Once the connection is established, the attacker will be able to control what you do on the Internet, view your computer's files, or install a virus.
Malicious email
By now, even the most inexperienced computer user is well aware not to open suspicious emails from mysterious strangers with offers, as it's too good to be true - but attackers know this, and there are creative ways to work.
Malicious websites
Attackers can also get what they want from you by creating malicious websites. Links to such websites can be created on various topics and in numbers. The malicious website may also use Trojan technology and pose as a site that offers free software. Software may be advertised as useful, such as a PC tuner or even an antivirus suite. Such software will actually be a disguise, a kind of virus, for example, to intercept information entered from the keyboard or a backdoor.
Malicious equipment
One of the most creative and seemingly innocuous approaches to identity theft is the use of malicious hardware, such as an infected flash drive. This method is mainly used when identity theft has a specific purpose. If an attacker has done their investigation and found out where you live or work, they can simply download their malware onto a flash drive and place it where you are likely to find it out of curiosity and plug it into a PC. If that doesn't work, they could just go to where you work and wait for the right moment to "borrow a printer" under the pretext that they have to "print a resume" for an interview.
Secure software development
According to a 2019 study by Positive Technologies, most of the vulnerabilities are caused by weak application protection and require serious code changes to fix them. Such shortcomings were found: in 74% of iOS applications, 57% of Android applications, 42% of server parts. InfoWatch declares about the leakage of more than 14 billion personal records from mobile applications.
Personal profiles, payment details and other confidential information (including parts of the code) must remain protected. If you don't want your application to be compromised, turn to secure development.

By the way...
Cyber Security Trends
In this article, we will tell you about the most important cybersecurity trends. Consider implementing them with Geniusee!
Need itThreat Modeling
Threat modeling helps you understand and identify the most likely threats and vulnerabilities specific to a particular application or application use case.
Threat modeling is performed to identify when and where more resources may be required to mitigate risks. There are many vulnerabilities, threats, attacks, and the likelihood that the application being created will collide with them all at the same time is very low. It is also unlikely that a company will need to address all potential security issues. Threat modeling is a tool that allows you to determine exactly where you need to focus your efforts.
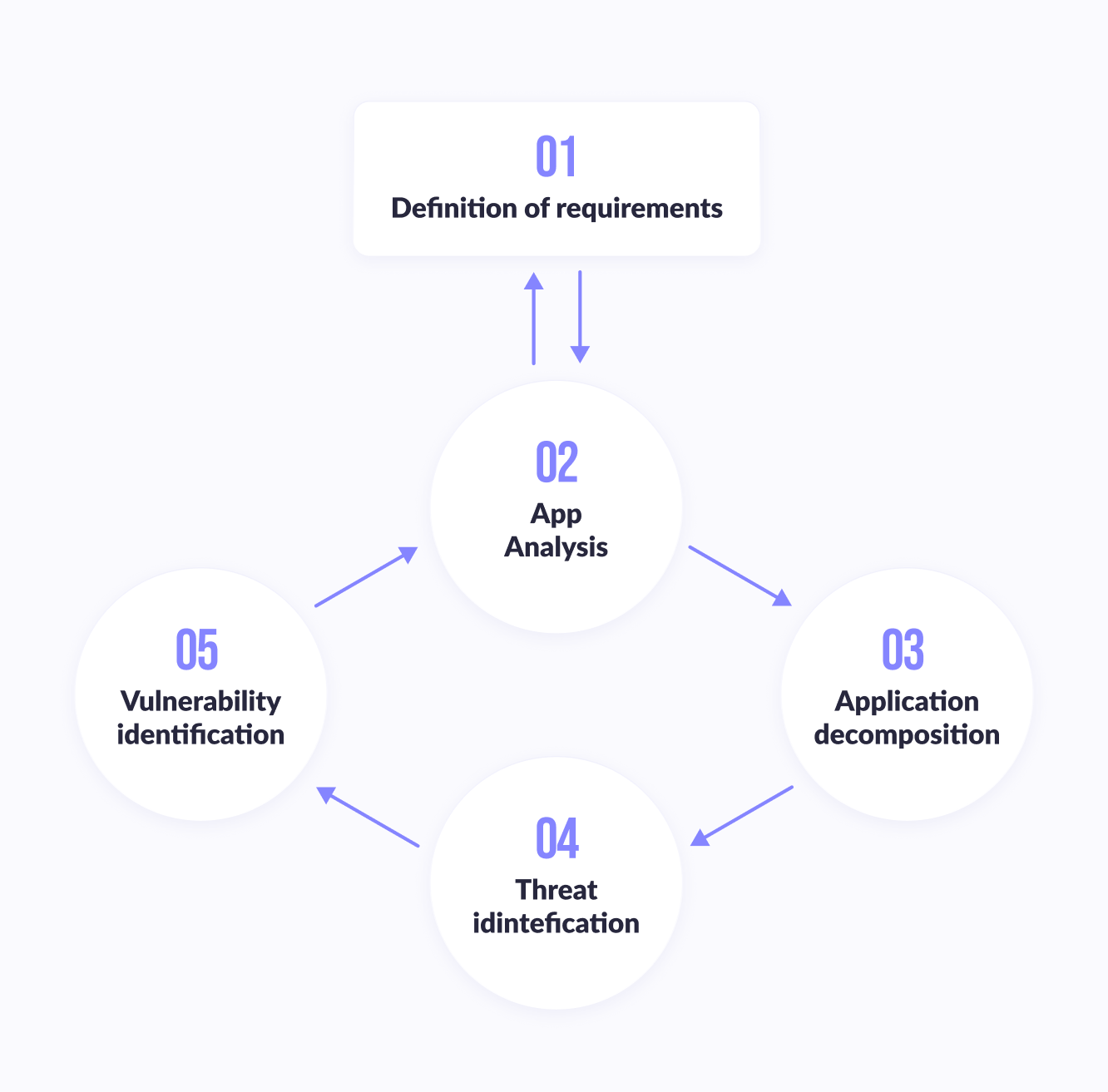
Threat modeling begins in the application architecture and design phase. Before creating a threat model, it is necessary to unambiguously formulate the application security requirements. As we move from the application architecture and design phase to the development phase, new threats identified during the project work are added to the threat model - that is, threat modeling is an iterative process that must be repeated periodically. Threat modeling consists of five main steps.
Step 1
Defining application security requirements. Well-defined requirements help not only complete this step, but also determine the amount of effort required to complete the next steps.
Step 2
Create a general view of the application. Cataloging the main characteristics of the application and the main types of users (“actors”) will help identify significant threats.
Step 3
Application decomposition. Understanding the mechanics of the analyzed application will help in detecting the most significant threats with the appropriate level of detail.
Step 4
Threat identification. Using the information collected in steps 2 and 3, you can identify the threats that are relevant to the application, possible scenarios for its use, and the context in which it will be executed.
Step 5
Vulnerability identification. Analyzing application links to identify vulnerabilities in the context of identified threats can help focus on areas where implementation errors are most likely to occur.
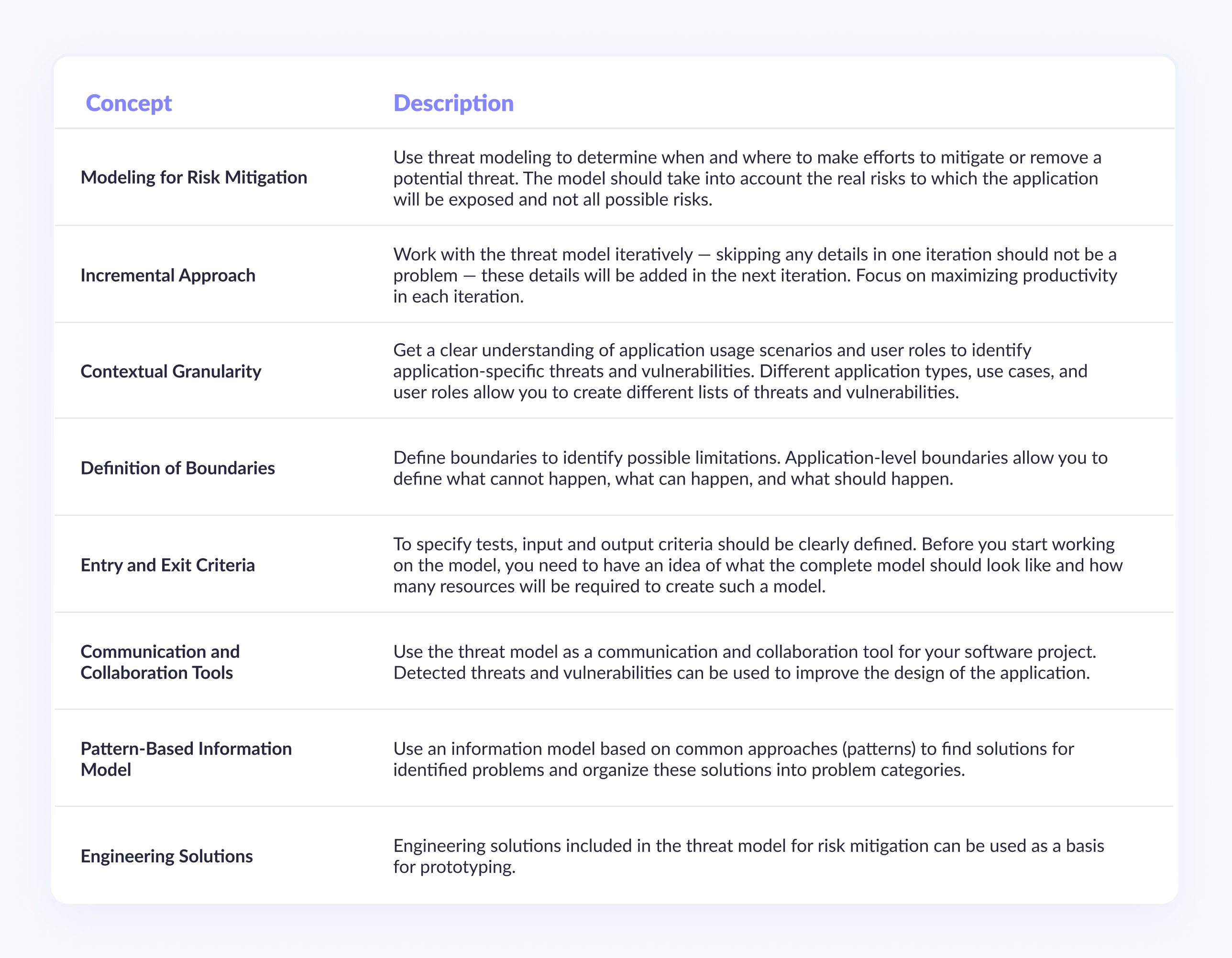
Key Threat Model Concepts
The threat modeling process has been optimized to help identify vulnerabilities in the applications you build. The table below summarizes key concepts and recommendations based on experience with projects of varying complexity.
Checking architecture and design for compliance with security requirements
Checking the architecture and design of the application will allow you to analyze them for compliance with security requirements. This review should include consideration of issues related to deployment, infrastructure, the overall architecture of the application, its design, and the architecture and design of each physical and logical layer of the application.
There are three main aspects to reviewing the architecture and design of an application for security compliance:

- Consideration of the application architecture should take place in accordance with the infrastructure and deployment scenarios;
- Consideration of the design of the application should take place in accordance with all categories of vulnerabilities identified in the previous phases of the project;
- Component analysis of the application must include consideration of the security mechanisms in each of the key components of the system, including the presentation layer, the business logic layer, and the data access layer.
A question-and-answer approach should be used when performing security validation of the architecture and design. The approaches described below will help you navigate the process of analyzing the architecture and design of an application:
1. Deployment and Infrastructure - Analyze the design of the application in terms of the environment in which it will be deployed. Review the relevant standards and support requirements. Consider the limitations imposed by the infrastructure and existing security mechanisms;
2. Security Patterns - analyze in detail the various critical components of the application, including mechanisms for authentication, authorization, input validation, exception management, etc. Use vulnerability classes as a guide for analyzing key application components;
3. Tier Analysis - analyze in detail all the links and layers of the application, study how to implement security mechanisms for the presentation layer, business logic layer and data access layer.

Important issue
How To Implement Zero Trust Security: Practical Steps
Zero Trust security model is one of the best ways to start with if you want to build a well-protected system.
Tell me moreChecking code for compliance with security requirements
All application code must be checked for possible vulnerabilities. This activity should be iteratively performed during the development and testing phases of the software product.
Correctly conducted code analysis, like no other activity, can make the application code as safe as possible. A lot of bugs can be eliminated at the verification stage, before the code gets to the testing team. In addition, the results of code review can serve as an excellent mechanism for transferring knowledge to all members of the project team.
For code analysis to be effective, it is necessary to determine what constitutes bad code and what is the result of the review. You can use the security requirements for the software product you are developing to guide the verification process. Depending on these requirements, identified vulnerabilities and potential threats should be ranked. For a more specific code analysis, you should use the previously created threat models. Analyzing code to determine exposure to certain threats will help you find many more bugs than any general analysis.
Code analysis consists of four steps, shown in Figure 1. 3, and their essence is described below:

Determination of the goals of code analysis for security. This step defines the goals and limitations for code analysis.
Performing primary analysis. Use primary static analysis to discover the initial set of bugs and identify where bugs are most likely to be found in the next iterations.
Search for security-related issues. This step performs a more thorough code review to detect security vulnerabilities that are most common in applications. It is recommended to use the results from step 2.
Search for security issues unique to the application's architecture. The final analysis should be devoted to finding errors specific to the architecture of the given application. This step is most important when using proprietary security mechanisms or security risk mitigation mechanisms.
Checking the deployment process for security compliance
When reviewing the deployment process, use the server security categories described below, break down the deployment process into separate steps for a more detailed analysis of potential vulnerabilities, and use an iterative approach. In the table below, we list the server security categories that should be used as a basis for reviewing the deployment process.
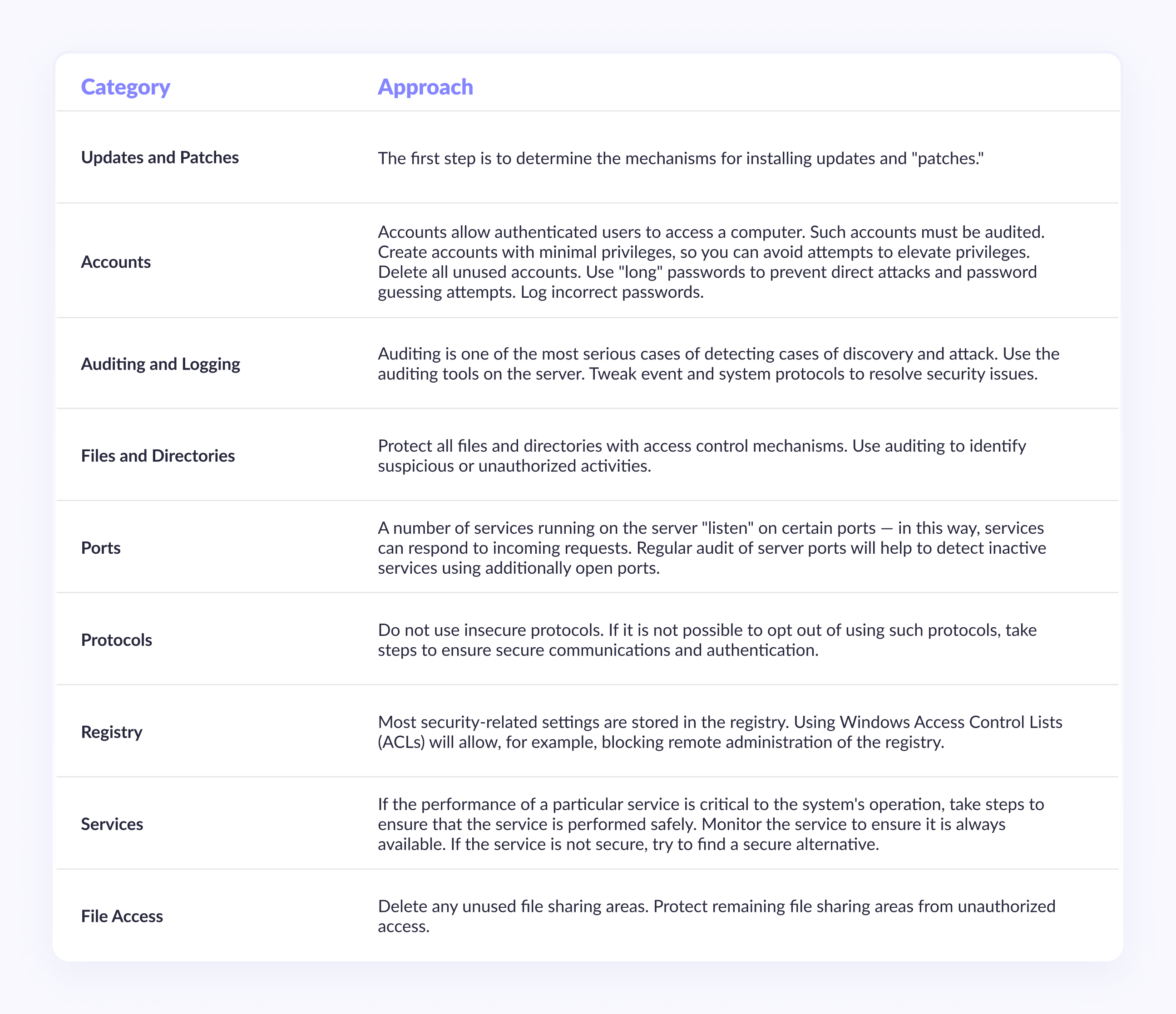
Reviewing the deployment process will ensure that the measures taken to secure the application will not be compromised by misconfiguration of the infrastructure on which the application will run. A systematic analysis based on the above categories will help you identify and fix vulnerabilities in all components of the server that is designed to run the software product.
Conclusion
News about data leaks has become especially loud in recent years, also because attackers manage to use leaks from previous years. This gives them a more complete digital dossier of a huge number of users. We should expect this trend to continue.
The share of targeted attacks is growing: in each quarter we observed more targeted attacks than in the previous one. In Q4 2021, less than half of the attacks (47%) were targeted, and at the end of the year their share was already 67%. We should expect further growth of APT attacks.
In order to keep up with new threats, protection technologies must also be actively developed. However, it will not be possible to achieve a high level of security using only tools to counter and detect attacks. We recommend that companies regularly conduct penetration testing and employee training — this will allow them to detect and promptly eliminate potential attack vectors on critical resources and debug service interactions in the event of a cyber attack.





















