Generative AI-based apps are gradually replacing traditional menu-driven business functions because of their smoother, more natural style of interaction. The AI tool adoption is growing lightning-fast: only in the US, it already tops 45% of adults. This guide explains eight design principles of GenAI, shows live products like Duolingo Max and Zillow’s AI search, and gives an architecture checklist for product teams.
The last several years of generative AI's booming adoption have flipped everything we thought we knew about in-app user experience.
For many years, it was about application interfaces becoming more intuitive within the same general principles: menus, buttons, and multi-step interaction logic. Today, we are speaking about the swift switch from navigation to direct, intent-based communication.
This might sound futuristic. But based on a 2024 Salesforce's survey, 45% of U.S. adults are already using generative AI in their daily lives for at least one use case. And this is a tremendous level of adoption for a relatively new technology.
This shift isn’t just about UX —it marks a turning point where software stops being a tool you operate and becomes a partner you collaborate with. In the GenAI era, value moves from features to fluency: how naturally an app understands what the user wants, and how intelligently it delivers.
What exactly does this mean for application product teams?
Based on years of experience and dozens of projects in AI development, we’ll break down the actual shifts happening in UI today, what they mean for business, and how to build GenAI features that actually deliver in real-world apps.
The new generative AI era and user experience
What is generative AI (GenAI)?
Gen AI is artificial intelligence that creates new content, based on user input. This content may be text, graphic, video, or more complex formats like reports or guidelines that combine several types of media at once.
GenAI can appear as tools, agents, or embedded features inside apps, designed to interpret intent, generate relevant outputs, and adapt to user context.
What is called the “GenAI era” isn’t just about doing the usual things faster, like writing messages or drawing charts. It’s about software finally catching up to how humans think — and starting to act accordingly.
Instead of learning where to click, what to select, or how to phrase a query, users now can:
Ask in a natural way — by typing, speaking, or uploading media — and get direct, task-relevant answers from an AI tool that interprets intent and adjusts accordingly.
Set a goal, and almost instantly receive a multi-step response without manual configuration.
Request explanations, not just outputs and receive contextual, situation-aware feedback.
Revise content or actions directly in the flow, without starting over.
Trigger and automate complex workflows in one prompt, even across different tools or services.
Use follow-up prompts with context and memory preserved.
Speak, listen, and interact with systems that operate across text, voice, visuals, sometimes even sensors or ambient data — and much more, thanks to generative AI's ability to handle multiple modalities and preserve context.
Create their own agents — AI entities tailored to specific tasks, personas, or goals, with memory and behavior that evolve over time.
Until now, we people were the ones adapting. We used commands, followed tricky paths, and learned how to fit what computers could understand. Interfaces stood as a shared middle ground between us and the system.
With the use of generative AI, that middle layer begins to disappear, as software starts handling interpretation, memory, and execution on its own.
A modern AI tool remembers, suggests, reroutes, and clarifies when needed, adapting in real time and collaborating, not just responding.


Thank you for Subscription!
Generative AI systems are changing UI principles for business — but how, exactly?
GenAI for business is changing how digital products are built and what users expect. Companies need to revisit their interfaces, workflows, and backend logic to match the shift toward more flexible and context-aware experiences. Otherwise, they’ll gradually lose their market relevance.
Treated with this kind of customer experience, people become less and less tolerant to friction that used to be inevitable before. They begin taking smooth, ChatGPT-like interaction as the new baseline.
So, the bar is no longer set by your competitors. It’s set by ChatGPT, Midjourney, Perplexity, and every GenAI-native product that now feels more responsive and intuitive than most business apps and software.
To align with this shift, you need to stop thinking of generative AI solutions as an interface layer and start designing interaction as a new business value.
That means:
Designing for intent. Stop mapping prompts to features. Start interpreting what the user is trying to achieve, and structure your flows to respond to those goals.
Embedding intelligence into the flow, not just the UI. GenAI shouldn’t sit on top of the application as a chat window or prompt bar. It should reshape how actions are taken by suggesting, completing, or adapting flows based on context, user intent, or historical patterns.
Letting the system take initiative. Don't wait for perfect prompts. The system should propose, autocomplete, disambiguate and guide users forward without being asked.
Supporting multiple input types. People won’t just type. They’ll speak, upload, or act through other tools, so your system needs to process multiple formats.
Embedding persistent memory. Context shouldn’t reset every session. Systems must remember user behavior, past inputs, and ongoing goals — and use that memory in real time.
Redefining ownership inside the team. Traditional teams divide by function: design, backend, data, infrastructure, and others. GenAI introduces a new layer that interprets vague, user input, and decides what the system should do. And this layer should be treated as a core product capability, not a shared responsibility or an afterthought.
Otherwise, if GenAI just sits on top of a traditional product architecture, it’s just a layer of friction. But when it’s designed into the interaction logic itself — aligned with real capabilities and real user goals — it becomes the engine that drives decisions, actions, and outcomes.

More from our blog
Why does every business need AI agents now?
Use AI agents to automate workflows, boost ROI, and cut costs — see how AI empowers smarter, faster business decisions.
Read moreHow to build if you want to enhance your UI with benefits of generative AI?
To build GenAI-enhanced UI, adopt a strategy that structures your interface around intent. Use natural language inputs instead of dropdowns or forms. Connect those inputs to real backend logic, so AI can trigger actions. Support multimodal input (text, voice, image) and let the system adapt dynamically based on context, history, or user feedback.
If we want to understand how to match the evolving user expectations in interfaces, we need to stop treating generative AI for business like a smarter version of what we already had.
What happens if you take your Gen AI applications as just another add-on? You’ll eventually find yourself where many startups and corporate innovations end up — where tons of spent budgets brought little more than a chatbot nobody uses twice, demo flows that only work under ideal conditions, and disconnected AI features that generate output but are practically useless in driving results.
On the other hand, there are tons of great generative AI use cases that generate real product and customer value, for example:
Duolingo Max integrating a roleplay tutor and instant feedback explanations, creating deeper engagement and improving learning outcomes for language students.
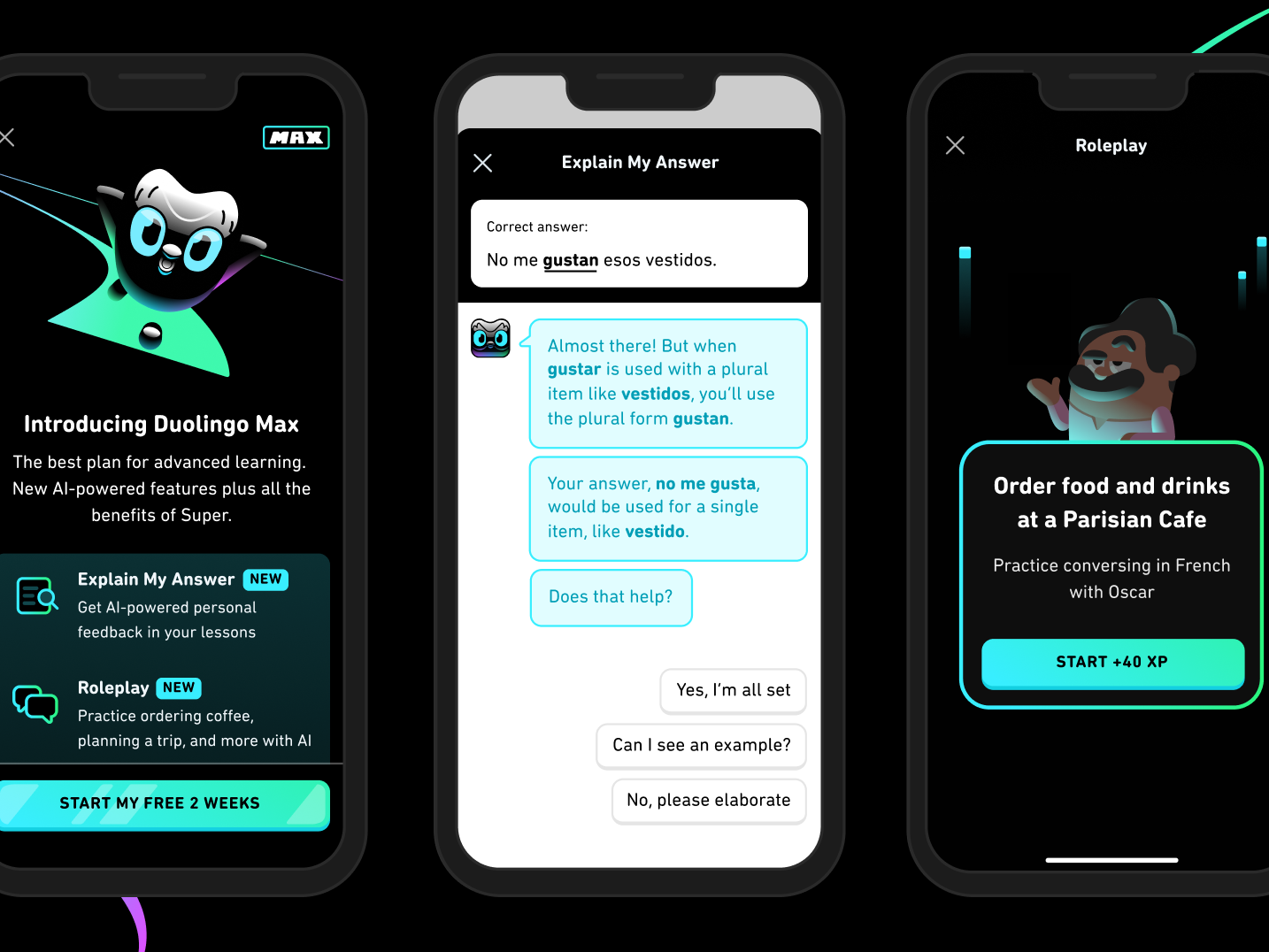
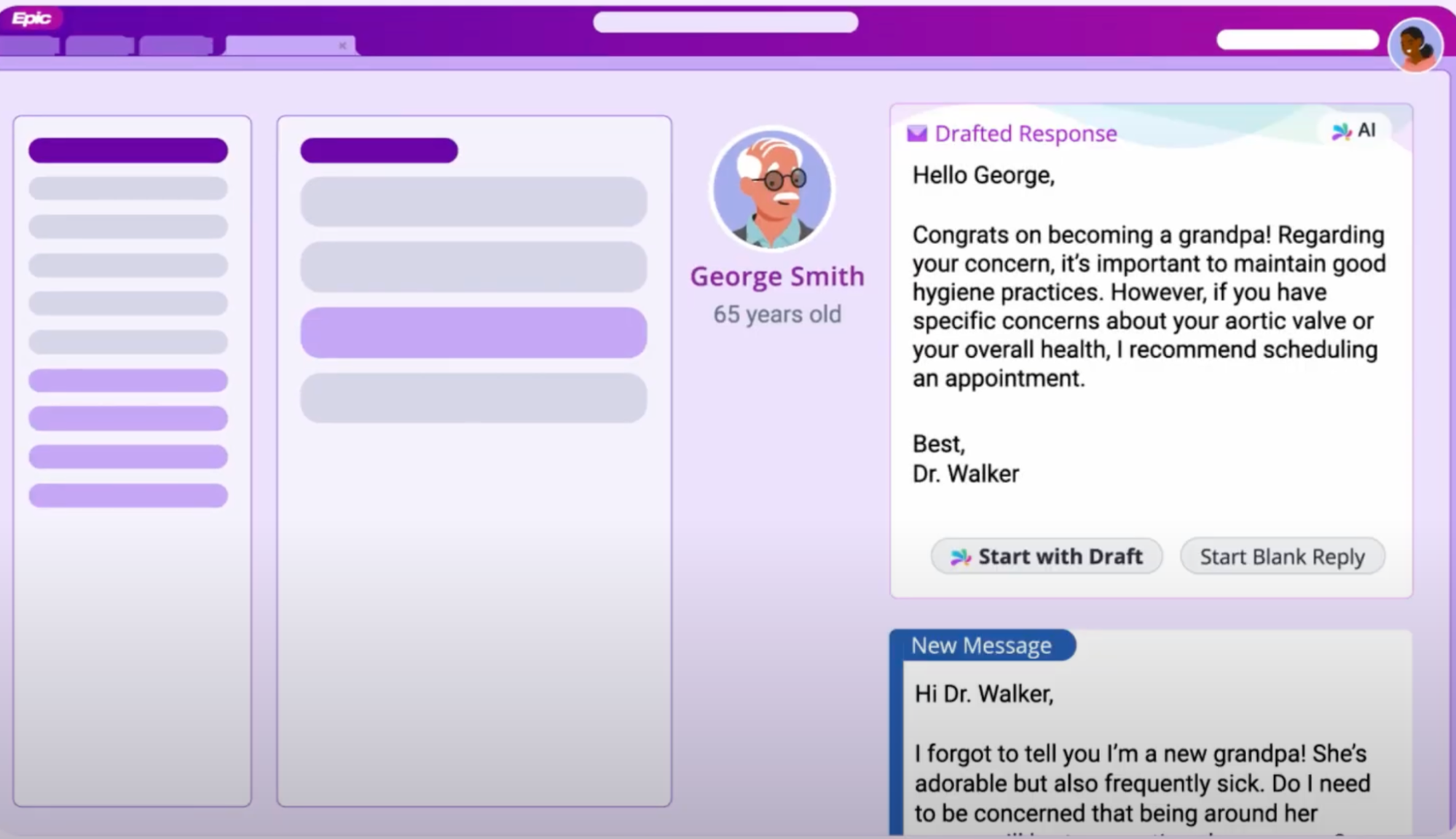
Epic’s ChatGPT plugin allowing clinicians to retrieve records or summaries by asking questions in natural language, driven by the underlying AI model, not by clicking through tabs or remembering query syntax, which significantly improves their productivity.
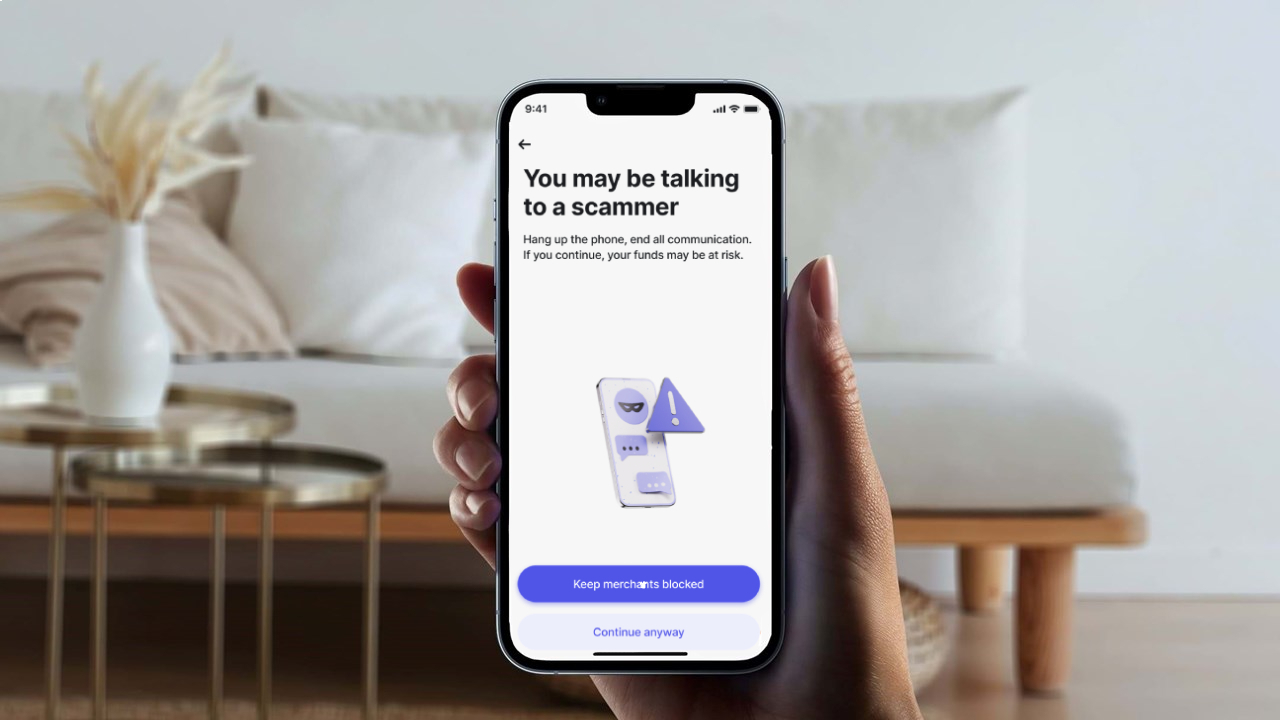
Revolut, launching an AI assistant within their fintech app to help users analyze their finances, understand spending, and automate making smarter decisions.
Here's what makes a difference and lets you develop high-value generative AI technology:
1. Treat user input as intent, not instructions
People don’t think in features. They jump around, mix formats, and refer to something that happened five clicks ago. Your system needs to keep up and turn all that into clear, structured intent.
2. Use negotiation logic
When input is vague or risky, don’t let the system guess. Make it recap what it thinks the user meant, ask the next question, and steer the flow safely. If the next step carries real consequences, simulate it first. Never pull the trigger blindly.
3. Design for native multimodality
Chat is only part of the picture. Users speak, upload, scan, or tap — and input can come from files, sensors, or what’s on screen. Your system should handle it all natively, reacting to real context, not just typed text.
4. Ground every output in system logic
The AI model should never suggest results that the application can’t actually deliver. Every response must be backed by real logic — whether that’s a RAG pipeline, a state machine, or a function call chain that can run or reject the task.
5. Align AI outputs with real execution
When the user needs more than just an answer, wire AI outputs directly into backend orchestrations that kick off real processes, respecting permissions and role limits. If the AI stalls or drifts, instantly switch to rule-based fallback logic to prevent disruptions. Clearly separate casual responses from executable commands, so your system acts only when action is intended.
6. Build shared context memory across layers
Users expect systems to remember the context across questions, sessions, and channels, and that means shared memory across UI, backend, and GenAI. Use persistent storage to track intent and progress, and route multi-step tasks through traceable interaction chains.
7. Prepare the infrastructure, not just the model
The model generates content, and the infrastructure makes it usable. Without the system to manage latency, fallback, and execution, the model output stalls, times out, or triggers the wrong flow. Building GenAI features means designing the full stack that runs them.
8. Test what breaks, not just what works
Edge-case testing looks different in GenAI. It’s not just about unusual input but more about ambiguity, revision, and unclear intent that emerge during AI use. That’s where logic gaps show up. Simulate messy flows to find logic gaps. Make every step traceable, and test how the system recovers without wiping user progress.
The real challenge of GenAI UI isn’t the interface but the architecture behind it.
If you’re still thinking in terms of flows, inputs, and outputs, you’ll miss what actually makes these systems effective.
Freeform prompts, mid-task edits, and multimodal input aren’t UI tricks — they require a full shift in how intent is captured, processed, and executed through machine learning. That means designing for ambiguity, preserving context across layers, and grounding every output in real system logic.
How can Geniusee help you create effective generative AI models?
Every project is unique. You might need end-to-end app development, consulting, or assistance developing specific features while your internal team does the rest.
We can help you with any of that:
Connect GenAI to real business logic. Research deeply how GenAI can deliver real value to your users, what are your capabilities, and how to structure the interaction so that AI doesn’t just generate output but solves something people actually care about.
Design application flows that reflect real behavior. Structure the interaction around how people actually think, switch context, hesitate, get stuck, misread, change priorities, and re-engage.
Implement full-stack GenAI flows built around a large language model that handle ambiguity, execution, and feedback loops. Build the full cycle — from vague input to precise action — and make sure the system knows how to clarify, adapt, reroute, and keep moving forward when the input isn’t clean.
Build memory-enabled, latency-resilient infrastructure, so GenAI works under real conditions. Design the architecture to handle session context, cross-step memory, and degraded performance — so the system keeps delivering even when latency spikes, prompts overlap, or users return mid-flow.
Help your team move from AI experiments to usable, scalable features that deliver measurable productivity gains. Work directly with your team to turn prototypes into product-grade systems — battle-tested, connected to real workflows, and built to scale without falling apart the moment usage spikes or edge cases show up.
Most teams still treat GenAI as a layer on top, not as a strategy, and that’s exactly why so many features that could raise productivity or improve value for users end up unused, disconnected, or impossible to maintain.
If you want to build systems people actually use — and trust — we at Geniusee can work with your team to design and ship GenAI features that solve real application tasks, connect to real logic, and perform under real-world conditions.
FAQ
How does generative AI simplify user interaction?
Generative AI turns a plain-language or image request into the exact workflow steps, so people skip dropdowns and forms and streamline the whole task into a single prompt.
How will AI change user interfaces?
AI is shifting interfaces in business applications from static menus to conversational, context-aware surfaces: models interpret a user’s goal and build the buttons, text, and visuals on the spot—sometimes even carrying out routine steps automatically.
How does generative AI enhance customer interactions?
AI and machine learning enhance interactions by turning each plain request into structured actions, remembering context, and pulling live data to automate routine steps, suggest next options, and hand agents quick summaries—so replies come faster and feel tailored.





















