Over the past few years, AI and LLMs have evolved into strong tools for enterprise use. These models can now support your complex business operations, better engage your customers, and discover valuable insights from your data.
Adoption is accelerating fast. ChatGPT alone reached over 400 million users in a single week. With the anticipated release of ChatGPT-5, OpenAI is set to push the boundaries of natural language understanding and generation even further.
Now is the strategic time to invest in machine learning models. They can simplify your content workflows, personalize customer interactions, and extract meaningful patterns from massive datasets.
In this article, we’ll compare the top LLMs, covering performance metrics, enterprise readiness, and the latest innovations.
LLM landscape overview
Grand View Research reported that the LLM market reached $5.6 billion last year and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 36.9% by 2030.
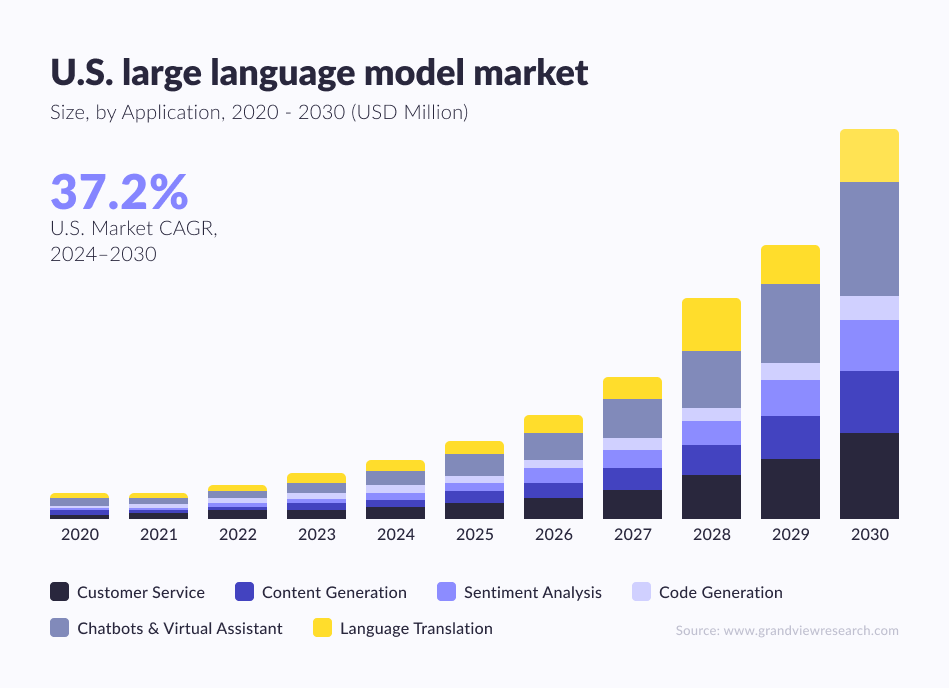
The primary factor behind such rapid growth is the increasing need in sectors such as finance and healthcare, where natural language processing (NLP) features are essential. It is expected that by the beginning of 2026, 750 million apps will use ML. Companies are already investing in LLMs, working on better customer service, streamlining, automating workflows, and increasing data analysis.
From a technical aspect, improvements in self-supervised and transfer learning enable models to achieve new tasks with the aid of pre-trained knowledge. Faster training and inference are possible thanks to progress in GPU and TPU hardware. As a result, LLM adoption is helping companies improve efficiency and gain a competitive edge.
However, the constant emergence of new models makes it harder for businesses to assess their long-term fit. Clear benchmarking and strategic evaluation are now more important than ever.
GPT-4.5 (OpenAI)
Background: Built by OpenAI with significant backing from Microsoft, GPT-4.5 is part of the broader GPT-4 series and an evolution of GPT-4.. OpenAI is the market leader in developing advanced Generative AI models that are highly capable, scalable, and widely adopted across enterprise and developer environments.
Functionalities: GPT-4.5 is multifunctional and can be used in long-form writing, code generation, chat-based interfaces, search, email composition, and other creative tasks. It also enhances context retention and reasoning compared to previous versions. Available via API and ChatGPT (Pro and enterprise plans), it's one of the most widely used LLMs in business today.
Gemini (Google)
Background: Developed by Google DeepMind, Gemini powers intelligent features across the Google ecosystem, including Search, Workspace, and Android. It’s available for LLM developers through Google Cloud’s Vertex AI.
Functionalities: Gemini delivers high-performance results in code completion, text generation, question answering, summarization, and translation. It’s designed for multimodal input (text, image, code) and adapts well to both internal tooling and customer-facing applications.
Claude 4
Background: Anthropic, founded by former OpenAI employees, built Claude 4 as the next step in safety-first AI. Known for its “Constitutional AI” approach, Claude focuses on alignment with ethical standards and minimizing hallucinations.
Functionalities: Claude 4 excels at tasks that require nuance, reliability, and reduced bias, such as legal analysis, policy writing, and structured content generation. It’s also gaining popularity for enterprise use cases where accuracy and transparency are key.
Llama 4 (Meta)
Background: LLaMA 4 (Large Language Model Meta AI) is the latest version of Meta’s open LLM family. It comes in multiple variants: LLaMA 4 8B, 70B, and multimodal versions, designed as open-access alternatives to proprietary models.
Functionalities: LLaMA 4 supports tasks like summarization, translation, multilingual generation, and code synthesis. While still relatively new, it performs competitively with leading commercial models. Its open weights enable full-stack custom deployment, ideal for businesses seeking control over their infrastructure and costs.
Comparison of LLMs
Our LLM model comparison below focuses on critical enterprise requirements to help you prioritize based on use case, risk tolerance, and scalability.
Feature | GPT-4.5 (OpenAI) | Gemini (Google) | Claude 4 (Anthropic) | LLaMA 4 (Meta) |
Primary focus | Advanced text generation, reasoning | General-purpose, multimodal AI | Safety, transparency, alignment | Open-source, flexible deployment |
Strengths | Industry-leading creativity, long context, strong APIs | Easy integration with the Google ecosystem | Emphasis on reliability, reduced bias, safety-first | Customization, multilingual, cost-effective infrastructure |
Limitations | Requires subscription/API access; high cost for scale | May require tuning for specialized workflows | Available in tiers; output tuned for caution and safety by design | Limited public performance data; still maturing |
Performance | High across logic, reasoning, and text tasks | Balance between code, text, and multilingual tasks | Strong in structured, factual, and safety-critical tasks | Strong in academic benchmarks; multimodal support is expanding |
Factual accuracy | Improved over GPT-4, still may hallucinate | Generally high across domains | Prioritizes correctness and ethical filtering | Claimed improvements; real-world benchmarks are still limited |
Scalability | Robust infrastructure, fast deployment at scale | Enterprise-ready with Google Cloud integration | Scalable across tiers; optimized for operational safety | Open weights allow custom infrastructure and on-prem use |
Ethical alignment | Moderate; policy-based guardrails | Developed under Google’s responsible AI guidelines | Core design principle based on the Constitutional AI framework | Limited documentation on alignment and ethical tuning |
Integration examples | Microsoft Copilot, Duolingo, Stripe | Google Workspace, Vertex AI, YouTube | Slack, Notion, Quora, Poe | Meta platforms, custom chatbot deployments |
Accessibility | API access via OpenAI (Pro, Enterprise tiers) | Paid access via Google Cloud | Available via Anthropic with usage tiers | Open source with weights downloadable for local use |
Cost | Higher-end pricing, per-token and subscription fees | Usage-based via Google pricing | Tiered access with pricing based on usage and licensing | Free (self-hosted) or cloud-hosted cost depends on the setup |
Safety/Alignment | Moderate guardrails; user-customizable policies | Responsible development practices by Google DeepMind | Strong focus with built-in safety and transparency | Limited details; alignment optional depending on usage |
LLMs applications
In just a few years, LLMs have transformed nearly every industry, boosting automation, accelerating workflows, and enabling smarter decisions. They deliver consistently high performance across content operations, support systems, and data analysis. Below are the top enterprise use cases gaining traction:
1. Content generation
LLMs like GPT-4.5, Claude 4, and Gemini consistently generate high-quality content at scale. Marketing teams rely on them to automate product descriptions, technical documentation, and multi-channel campaigns without compromising brand voice or consistency.
2. Customer support and chatbots
Customer service LLMs such as Claude 4, Sonnet, and Gemini power intelligent support systems that scale efficiently while maintaining a conversational tone. Trained on extensive datasets, these LLMs understand intent and provide precise, context-aware responses across channels.
3. Code generation
LLMs like DeepSeek Coder and Code LLaMA support multilingual coding tasks, accelerating development cycles and enhancing code quality. In fintech, Python scripts generated by LLMs help teams rapidly prototype data-driven products and shorten time-to-market. Open-source developers also use Mistral Small to automate bug fixes and suggest improvements.
4. Healthcare and scientific research
Models such as GPT-4 and Claude 4 Sonnet process massive datasets, from clinical trial results to medical records and research papers. Their ability to distill and summarize complex information enables faster analysis, supporting diagnostics and scientific discovery.
Here are some examples:
Advanced models like Mistral Large and LLaMA 4 are increasingly used in pharmaceutical research to analyze molecular structures and predict compound efficacy. This helps simplify the identification of viable drug candidates.
Claude 4 also shows strong potential in pharma, helping companies assess the likelihood of success for new compounds and significantly reduce research timelines.
Key enterprise evaluation criteria
When assessing LLMs for enterprise applications, the following criteria help measure readiness and suitability:
Enterprise benchmark data – Look for third-party metrics on accuracy, fluency, and response times across core business use cases.
Specialized knowledge depth – Evaluate how well the model has been trained on domain-specific data, especially in regulated sectors like healthcare, finance, or legal.
Computational efficiency – Consider the cost-to-performance ratio, particularly how well the model processes large-scale enterprise data while staying cost-effective.
Flexible integration – Assess the ease of embedding the model within your existing enterprise architecture, including compatibility with internal workflows and security protocols.
Compliance and governance – Ensure the model meets compliance standards and supports auditable outcomes for highly regulated environments.
Analysis of leading LLMs
Top-performing large language models are evaluated using standardized benchmarks to measure accuracy, reasoning, speed, and adaptability across various enterprise use cases. Below is a condensed leaderboard of the most capable models currently available:
Model | Type | Key strengths | Benchmark score | Use cases |
GPT-4.5 | Proprietary | Exceptional in complex reasoning, creative tasks, and coding | High | Content generation, app development |
Claude 4 | Proprietary | Strong alignment, context retention, and human-like dialogue | High | Enterprise support, legal, and medical insights |
Gemini | Proprietary | Fast response time, multimodal processing, and long context windows | High | Translation, chat, data analysis |
LLaMA 4 | Open-source | Open-access, scalable, with competitive multilingual abilities | Competitive | Creative workflows, internal tooling |
Mistral Large | Open-source | High efficiency in code and language tasks, solid reasoning | Competitive | Code generation, documentation, QA |
How are LLMs used in business?
LLMs are taking a leading role in enterprise AI strategy, delivering quantifiable returns in customer experience, efficiency, and innovation. When implemented effectively, LLMs can generate a strategic edge and unlock organic operational value.
Companies are not only experimenting with these models, but they are also building core solutions around them. Here’s how major corporations utilize LLMs in practice:
Amazon uses LLMs to personalize product recommendations for its vast customer base.
PayPal uses LLMs to identify fraud based on transaction patterns. Such a proactive detection system safeguards both users and the platform against financial risk.
Netflix’s recommendation engine operates based on LLM. It constantly adapts to viewers’ behaviours and presents each subscriber with the most relevant content.
Bank of America created an LLM-based virtual assistant, Erica, who handles daily banking operations, such as transfers and budgeting. This frees up mundane interactions, allowing human advisors to focus on more complex tasks.
Pfizer uses LLMs to digest increasing volumes of scientific research, speeding up drug discovery and making more data-driven clinical decisions.
What are some of the benefits of using LLMs?
Enterprises don’t adopt LLMs just for innovation’s sake — they do it for measurable business value. As noted earlier, these models offer a wide range of advantages that drive adoption across industries.
Here are some of the key benefits LLMs deliver:
Personalized approach
67% of consumers now expect tailored interactions. LLMs can meet this demand by analyzing customer behavior and generating personalized responses and content. The result? More relevant support, higher satisfaction, and stronger brand loyalty.
Increased efficiency
LLMs can automate routine queries through intelligent chatbots that handle FAQs, troubleshoot issues, or route users to the right solution. CX Today reports that automation like this can cut inquiry resolution time by up to 50% without sacrificing quality.
Content creation at scale
Producing consistent, high-quality content at scale is a challenge for any business. LLMs help fill this gap by generating text for blogs, product listings, social media, and more, freeing up marketing teams for strategic work.
New insights
LLMs are proving their value in data analysis as adoption grows. These models can reveal trends, outliers, and new opportunities by scanning large volumes of text or code to power smarter, faster decision-making than traditional methods.
Improved teamwork
LLMs also support internal growth. They enable personalized employee training programs, making onboarding and ongoing education more relevant and effective. That leads to better-informed teams and stronger organizational performance.
Our experience integrating LLMs
AWS Bedrock assessment-driven LLM migration
Challenge
International companies needed to transition away from OpenAI’s public toward secure, compliant infrastructure in AWS Bedrock. The aim was to test which models best fit LLM content generation needs and develop a migration strategy that would not affect operations while providing complete control over the infrastructure and data privacy.
Solution
Geniusee conducted a 3-week Gen AI assessment using the AWS RAPID Discovery framework. During Week 1, we held pain point and use case prioritization workshops as well as established model requirements (Claude, Titan, Llama).
Throughout Week 2, the emphasis was on practical tests. We compared AWS Bedrock foundation models with the actual client prompts based on the output quality, latency, and tone match. We were also assessed for compliance readiness, considering both effort and cost.
During Week 3, we provided a migration plan (with changes in architecture), AWS credit alignment, and a well-established business case. The whole assessment was 100 percent Amazon Web Services financed.
Impact
The client also secured a safe and scalable path forward for deploying LLM content generation on AWS Bedrock. After selecting the optimal model and securing AWS funding, they now have complete control over the infrastructure, enhanced compliance, and a clear implementation path.
The successful examples of implemented projects are related to our clients, including Hospitality Radar (Parasol Trading), Imagine, Supplied, Ness Healthcare, and TechQuarter. We have helped them use GenAI in AWS while meeting specific industry rules and performance standards.
Imagine: AI-Based Resume Parsing
Challenge
Imagine was built to scale the automated processing of resumes and contacts with candidates and managers.
Critical points:
Structuring of unstructured documents.
Filtering candidates to the corresponding hiring managers in a multi-layer process.
Creating AI-written outreach emails on an individual basis.
Managing a quick rise in the size to more than a million candidate records.
Embedding of content generation (job descriptions, tone editing, summaries) to an existing NestJS backend.
Solution
Geniusee provided a modular, AI-based pipeline based on OpenAI and a Python /NestJS backend.
Highlights:
Resume parser: The most important sections extracted by the LLMs were six in number which included employment and education history. Contains resume verification by AI and language detection.
Template engine: Parsed data was rendered to adaptive rendered tested, and branded CV templates in a Jinja-style.
Mailshot system: automatically creates highlighted emails with tone/style reminders.
Candidate-manager matching: SQL and AI location, title, domain, and industry fit based on matching.
Job description writer: with tone/density adjusters.
Interview summarization: The transcription-to-summary provided actionable items and key learning points from interviews.
Infrastructure optimization: Switched containers to Azure Function, which provides scalable, cheap performance.
Impact
Today, Imagine digitally processes the files of millions of candidates in an end-to-end AI pipeline:
A more than 85% accurate resume parsing
Time of CV transformation: less than 3 seconds
70% mailshot time reduction.
6x increase in production managed without issues
The cost of the infrastructure is reduced through serverless migration
This engine is AI-first, which provides unparalleled effectiveness in recruitment processes
Conclusion
Following our hands-on experience with LLM implementation, it’s clear: we’ve moved beyond experimentation. Language models are actively reshaping businesses' operations and interaction with technology.
The momentum isn’t slowing down. As companies continue to push for scalable solutions in content generation, support automation, and data analysis, the role of LLMs will only grow. Advances in model architecture and computing power are setting the stage for the next generation of AI, which will be faster, more accurate, and even more adaptable to specialized enterprise needs.
Want to merge the power of an LLM into your business? Contact our team to develop a custom LLM solution based on your business needs. We'll help you explore the full range of LLMs to automate processes, interact with customers, and uncover new insights!
FAQs about large language models
1. How can enterprises ensure that LLM outputs are GDPR or HIPAA-compliant?
To remain in compliance, businesses implement stringent data procedures for their use of LLM. This includes:
Obfuscation of sensitive input before passing it to the third-party APIs.
The practice of self-hosting, such as LLaMA 4, is to have complete data residency control.
Capturing, recording, and tracking the interactions using AI governance platforms.
Using differential privacy or zero data retention measures to the external APIs such as OpenAI.
2. How is fine-tuning different than prompt engineering when using LLMs in business?
Prompt engineering utilizes a generic model for specific tasks by cleverly phrasing the input. It is fast, no-code, and effective when it comes to an MVP or low-hanging fruit.
Fine-tuning instead refers to re-training the model on domain-specific data (such as financial reports or legal contracts). This requires greater effort but provides greater precision and specificity to meet enterprise demands, particularly in regulated industries.
3. Do LLMs have potential in business prediction like stocks or companies?
Although the task of LLMs is not to make predictions the way time-series models do, they are getting integrated more and more into:
Through the extraction of trends, this can be used in huge blocks of unstructured data (social media, news, reviews).
Chain-of-thought prompting to help thematically review the scenario and analyze potential business actions.
Signal amplification of weak signals hidden in textual data streams using LLMs; e.g., at-risk churn or potential market requirements.
Combined with predictive models or BI tools, LLMs allow adding a qualitative dimension to the classic forecasting pipelines.





















