Today, AI and machine learning improve claims processing, underwriting, and fraud detection. Advanced automation technologies enable insurance leaders to achieve unprecedented results in their operations.
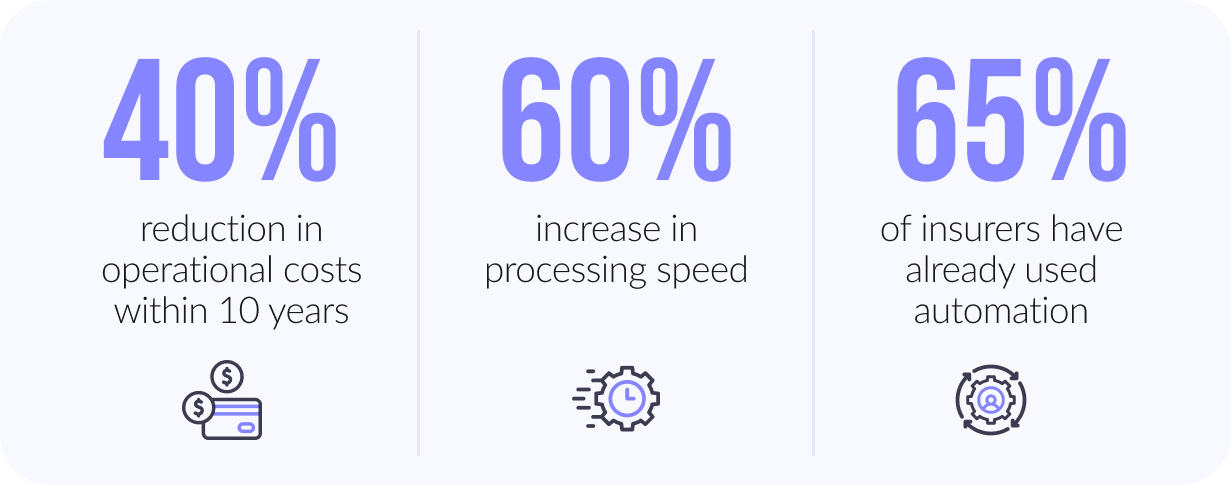
As a result, McKinsey's analysis shows that insurance operation expenses will be cut by 40 % in 10 years and achieve a 60% faster processing speed. Therefore, 65% of insurers already use automation processes, allowing them to stay ahead in this competitive market.
So, what does this mean to the industry? We'll examine how automation is reshaping insurance processes, key use cases, and the main benefits companies gain from successful automation initiatives.
What is the importance of automation for the insurance sector?
Automation gives insurance companies 3 essential advantages: faster processes, enhanced intelligence, and superior customer service. You can leverage automation to optimize operations by processing repetitive tasks, which offers improved service speed and fewer mistakes.
Automation creates the following improvements:
Efficiency and cutting costs
For a long time, standard operations in insurance organizations have relied on lengthy document processing, manual data entry, and intricate negotiations. By automating repetitive tasks, these challenges transform into consistent, high-accuracy performances.
You can benefit from reducing human errors and administrative expenses, allowing your staff to focus on customer service and strategic development activities. AI systems' instant assessment of risks through data analysis allows underwriting to proceed from days to hours. By implementing this process, you achieve better service accuracy and cost reduction.
Enhancing customer experience
Long and slow claims processing and limited customer service availability create major obstacles during the customer experience. Implementing automation technologies delivers both quick processing speed and efficiency to customers. AI chatbots can answer customer inquiries 24/7 by providing fast answers about policies, processing claims, and helping with policy selection.
The main advantage of personalization becomes even more impactful with AI. By analyzing customer behavior and data, AI can offer tailored coverage suggestions, personalized pricing, and relevant add-on products. For example, customers filing a home insurance claim after a storm can automatically receive recommendations for additional coverage options and expedited repair services, creating a faster, more responsive experience.
Key use cases for intelligent automation in insurance
By 2026, AI-based automation solutions will be widely used for claims management, underwriting, and fraud detection, ultimately transforming core insurance operations. Still, because of automation deployment in key operational areas, the insurance sector is experiencing fundamental changes:
Claims processing and management
For example, Insurance Australia Group (IAG) enabled AI technology to automate processes, which sped up claims assessment and delivered personalized deals to clients. The company's strategic decision led to operational improvements and increased customer satisfaction.
AI technologies use self-operating systems that evaluate claim validity and measure damage expenses to approve payments in under 24 hours. The reduced administrative expenses enable insurers to manage more insurance claims without additional resources. Yet, these systems must be free from ethical bias so that no customer receives unfair treatment. Explainable AI (XAI) is the focus here, as it involves using unbiased datasets and transparent decision-making by AI systems.
Underwriting and risk assessment
Basic underwriting operations benefit from automation, resulting in quicker document assessment and more accurate decision-making. The global insurance company AIG, for example, operates an innovation hub in Atlanta focused on advancing digital solutions and AI capabilities. This initiative, involving data engineers and AI specialists, helps develop tools for better policy evaluation and risk analysis.
AI analytical models can review extensive clinical records, driving histories, and credit reports to support continuous assessment and smarter underwriting decisions. System implementation shortens evaluation periods to hours and delivers more precise risk assessments. With faster decision-making, your company can offer better pricing and simplify the customer onboarding process.
Still, to maintain fairness, it’s crucial to minimize potential biases in underwriting models. Explainable AI (XAI) helps by keeping models transparent and accountable.
Fraud detection and prevention
The insurance industry suffers yearly financial losses from fraudulent activities. AI systems enhance business market dominance by identifying fraud patterns and creating effective appeal documents for denied policyholders. For instance, Zurich Insurance AI tracks digital interfaces and detects irregularities in some claims; this decreases the prevalence of fraud and minimizes the number of reviews made.
AI models detect fraudulent activity patterns, which help identify potential cases of insurance fraud before claims are processed. Another benefit is natural language processing (NLP), which can check that customer statements are consistent, further raising fraud detection. Insurers can also integrate facial recognition and behavioral analytics to prevent any fraud.
Additionally, AI systems must include adequate security measures to ensure that customer information is private and protected from unauthorized access.


Thank you for Subscription!
Benefits of automation in insurance
Insurance companies now realize that immense benefits can be achieved across all operations as they embrace intelligent automation. Automation saves costs through risk management, improves customer satisfaction, and enhances a company's competitive value by providing better services to policyholders. We shall explore how the modern insurance sector has benefited from automation.
Cost savings and increased efficiency
Intelligent automation not only eliminates costs associated with human intervention but also helps insurance companies control costs related to a high volume of claims during peak periods. For example, you have automated systems ready to handle flood claims in natural disasters and other unforeseen events. This would help scale quickly without needing additional employees.
The main unrecognized strength of intelligent automation systems is their capability to convert strategic goals into operational actions. Automating core processes, such as underwriting, claims, and customer service operations, enables insurers to make direct operational improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and compliance.
Improved customer satisfaction
The benefit of intelligent automation is a unique and underexplored way of personalizing the customer experience on a large scale. You can offer hyperpersonalized communication and policy suggestions through AI-powered systems using data from customer interactions and social media activity.
For instance, if an AI system detects that a customer is looking towards more eco-friendly living (such as purchasing an electric car), it may offer eco-friendly insurance policies or a discount. A higher level of customer engagement enhances brand loyalty, making the insurance experience more customer-centric.
Challenges in implementing automation in insurance
Although intelligent automation brings numerous advantages, deploying it in the insurance industry presents some challenges. Now, let’s see what the most pressing problems enterprises currently have:
Data privacy and security concerns
You must be ready to adopt AI and automation, primarily to safeguard sensitive customer data. Of course, this raises the problem that modern automation platforms are large at scale, allowing more opportunities for breaches. For example, hackers from India leaked the medical records and personal details of millions of the country's biggest health insurers when they communicated with them via a set of what the company called 'tech support' Telegram chatbots.
Given these risks, insurance companies employ zero-trust security models that continually verify an identity and grant access to data processing only to authorized user roles. You can use homomorphic encryption, which allows for processing encrypted data without revealing sensitive information. Furthermore, blockchain technology leads to tamper-proof policy data audit trails, increasing security and transparency.
Integration with legacy systems
Insurance companies continue to use legacy systems as their primary operational backbone, although these systems were initially installed decades ago. Modern AI automation faces operational barriers due to using traditional legacy systems. The backend IT transformation project, Blueprint II, aimed to revamp business fundamentals, although its delivery schedule now extends to 2030.
To meet this challenge, you can use a microservices-based architecture to exchange real-time data without re-architecting existing systems. For example, your automation infrastructure can be based on a cloud-native microservices framework, which supports quick updates and scaling. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is also beneficial, as it automates human interaction with legacy systems and tasks without modifying the underlying codebase.
Balancing automation with human oversight
However, with the capability to do repetitive tasks efficiently, AI leaves human oversight with complex, high-stakes decisions. AI won’t deny a claim for you, but humans are always required for argued cases or complex liability issues.
As enterprises aim to prevent errors, they are deploying a human-in-the-loop (HITL) framework where human experts review and verify AI recommendations. Today, advanced AI models provide confidence scores and clean, detailed reasoning, helping make informed decisions. The hybrid approach enables this, ensuring that automation speeds up the process without affecting accuracy or customer trust.
More from our blog
AI CRM: Transforming customer relationship management
Discover the best AI CRM software to improve customer relations and automate sales processes.
Read moreHow to successfully implement automation in insurance
To deploy intelligent automation successfully in insurance, you need a targeted and organized approach to ensure the most significant benefits and minimize risks. There is no way to achieve success without a clearly defined strategy, phased implementation, and ethical guidelines.
Assessment and strategy development
First, discover the most painful parts of the customer journey and then automate these pain points. McKinsey’s 2025 report also found that insurers who paired automation with customer needs saw a 30% increase in customer satisfaction and a 25% reduction in processing time. Successful insurers then identify where to implement automation in their claims and policy cycle.
Aviva France applied an intelligent automation system to improve the handling of live insurance claims. Integrating AI with low-code automation tools enabled the company to witness a 7x growth in the Net Promoter Score (NPS), which speaks to a significant leap in the customer satisfaction quotient.
Pilot testing
When your strategy is determined, launch a mini-trial program to test both AI models and automation methods. Identifying problems at this stage prevents major issues from emerging later. The first step should include simple cases with low-risk elements to minimize the potential problems before moving on to more complex tasks.
Before scaling to the more complicated cases, Swiss Re made essential claims processing automation to ensure that models were accurate and fast. Like all else in life, pilots must have control! Controlled pilots reduce the risk of implementation and improve system reliability.
Deployment and monitoring
The gradual scaling of automation across the business helps with real-time tracking and performance analytics, which tell you who and how to identify and resolve issues early. ML models can detect anomalies, curved lines, and performance drops, allowing for quick adjustments.
Allianz has implemented AI-based monitoring that identifies and corrects errors in claims processing in real-time, increasing accuracy and customer satisfaction. A monitored system provides consistent performance and avoids costly system failures.
Ethical AI governance and transparency
The implementation of AI systems requires ethical governance because they possess both bias-creation risks and security vulnerabilities. Establishing regulatory frameworks helps ensure fairness, along with accountability and regulatory compliance. Through LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations), you can clearly present AI decisions for stakeholders to follow.
IBM created an AI Ethics Board to audit automated decisions to ensure unbiased decision-making. This prevents reputational damage and improves customer trust.
Continuous improvement
Store data on performance and customer feedback to refine automation models and processes. To maintain system effectiveness, models should be regularly updated and retrained in response to changing business needs and regulations. Suppose customer service teams report automation issues back to development. In that case, this removes the usual feedback loop, where the customer service team either presents their issue to development or attempts to solve it independently.
Lemonade’s AI-based claims processing system is updated regularly based on customer interactions, efficiency remains high, and customer satisfaction is maintained at its peak. Automation is always meant to improve continuously and stay relevant and practical over time.
Automation tools and solutions for insurance
Automation in the insurance industry utilizes various tools to reduce operational costs, increase speed, and improve service efficiency. These tools handle complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA tools automate rules-based and repeated tasks such as data entry, policy administration, and claim processing. RPA software mimics human actions to process large volumes of work quickly, thereby minimizing manual errors and freeing up human agents to focus on more complex tasks. UiPath and Automation Anywhere are perfect examples of this.
AI and ML
AI and ML use large datasets to analyze and predict outcomes, ensuring the best decision-making. They are applied to risk assessment, fraud detection, and underwriting processes. AI models can evaluate customer profiles, fraud patterns, and approval decisions. The insurance sector commonly uses platforms such as DataRobot and H2O.ai.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
GPT by OpenAI, for example, is a tool that helps us automate customer communication by generating responses that look natural. This allows for handling customer queries, policy updates, and claims information, all of which can be answered immediately, reducing customer service workloads.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
IDP solutions extract information from documents, such as claims forms and policy documents, and process them more efficiently than manual work would without human intervention. Tools like ABBYY FlexiCapture enable insurers to process unstructured documents, improving data accuracy and processing speed.
Genuisee’s success story: ML automation
We created an automatic pipeline for an insurance provider that uses AutoML to enhance its risk assessment process. Scoring models should be constantly retrained when you implement new data or regulations.
Challenges
Dynamic data: As the client adds customer information changes and other variables (such as gender, location, etc.), scoring models have to be retrained often. Manually processing these updates leads to delays and the danger of human errors.
Regulatory changes: The new regulatory requirements necessitated constant updates to scoring models, especially to eliminate biases (including gender or geographical).
Lack of agility: The client had challenges in the fast transformation of scoring models to include these changes.
Solution
We constructed a dynamic AutoML-based scoring pipeline that deployed automatic generation and retraining of models on the occurrence of data or regulatory guide changes.
It is automated to detect data drift and calibrates the models to meet regulations, minimizing bias (e.g., gender, geography).
It automates model retraining with any change in risk factors, eliminating the need for data scientists to monitor the process constantly.
This allows the client provider to roll out new models quicker and more efficiently without human intervention.
Results
The implementation of these solutions resulted in a significant leap forward in operational efficiency and scalability, driving business growth. Notably, some of the results include:
Reduced deployment time: The automated pipeline allowed the production of the updated models much quicker than before, saving the data scientists valuable time in manual efforts.
Improved compliance: The pipeline guaranteed that the models were consistent with regulatory standards, especially on fairness and non-biased decision-making issues.
Operational efficiency: Through automation, the client minimized the data science team's task burden, enabling them to concentrate more on strategic tasks.
Faster risk assessments: A client can now determine risk more quickly, enabling it to commit to decision-making on policy issuance more quickly, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction.
Why choose Geniusee for insurance automation?
With innovative AI, ML, and RPA solutions, Geniusee leads transformation projects across insurance operations. We automate claims processing, risk management, and customer service, focusing on lowering costs, boosting efficiency, and enhancing the customer experience. Our expertise bridges new-age technologies and legacy systems, meeting customer needs without disrupting operations.
Do you want to boost your insurance operations? Contact us today to upgrade your insurance systems.





















