The development of technologies served as an engine for the transformation of macroeconomics. The key segment in the development of financial markets has become the introduction of new financial technology that appears as a result of conservative financial management when using digital technologies.
Over the past few years, financial inclusion has developed at a significant pace, but despite the rapid development of this phenomenon, the exact definition of fintech has not yet been derived.
Changing dynamics of financial services
FinTech (financial technologies) is a business direction that uses emerging technologies and innovations in the financial services market. It includes such areas as digital, mobile digital payments and money transfers, personal financial management, mobile wallets, online lending, P2P platforms, crowdfunding, online funds, online insurance, etc.
These technological advancements demonstrate how FinTech impacts banks by enabling them to offer seamless, technology-driven solutions that cater to a digital-first clientele. For example, omnichannel banking combines convenience with robust customer service, further illustrating how FinTech helps banks improve customer loyalty and operational efficiency.
The first meaning of FinTech is presented as a new branch of the economy, consisting of young companies that provide improved products and services to the financial market.
The second meaning of this concept is expressed in the aggregate of new technology companies that, on the basis of their own funds, are developing mechanisms for introducing innovative technologies into the traditional financial sector of the economy.
The third understanding of the essence of fintech lies in the practical activity based on the use of software to meet the demand for products in the financial market.
Having decided on an understanding of the essence of FinTech, it is advisable to study the history of its development for a deeper analysis of this phenomenon. The evolution of FinTech development can be conditionally divided into 3 stages, which are clearly shown in the image below..
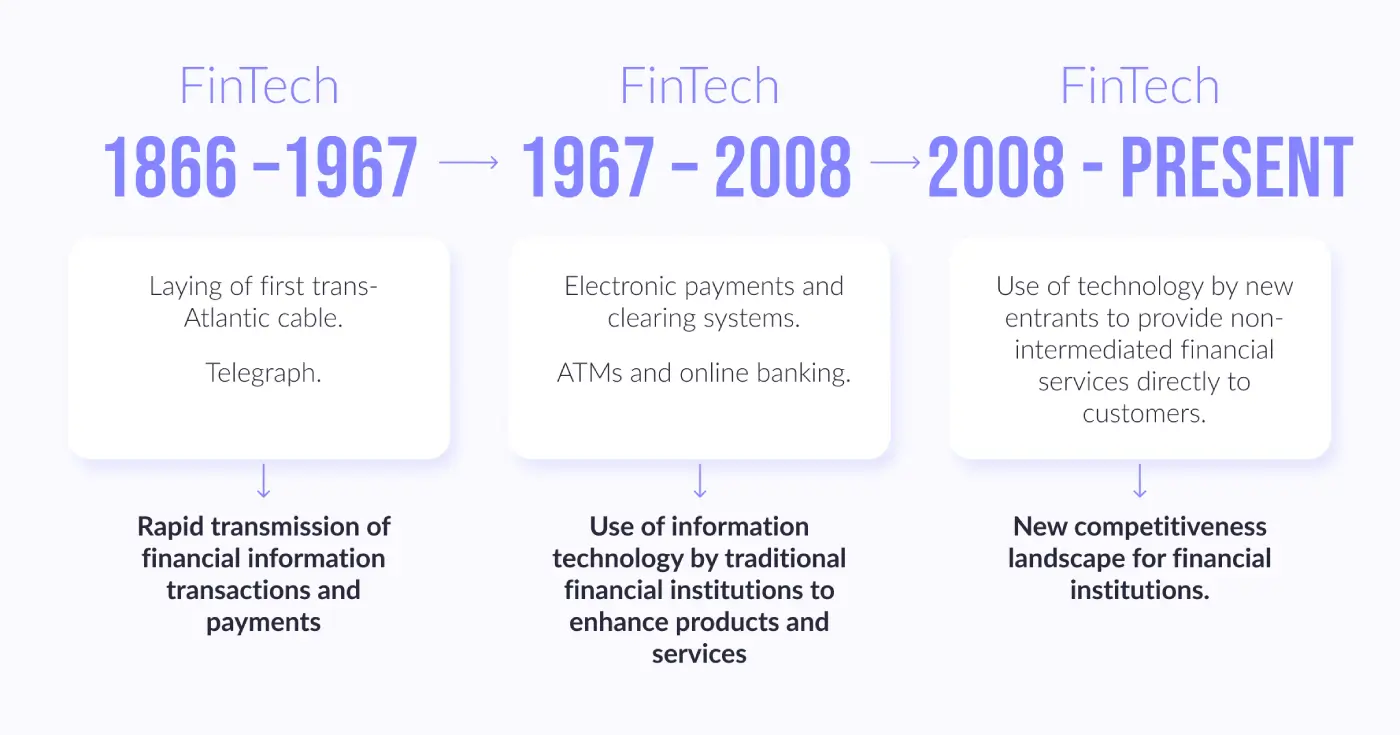
It should be noted that the FinTech revolution was provoked by the global financial crisis of 2008 and was caused by the transition of financial market participants to low-capital-intensive business models, modernized in accordance with modern market realities. Subsequently, the equalization of market conditions contributed to the emergence of innovative participants in the financial services market – FinTech companies. The current state of FinTech is characterized by rapid digital transformations based on the proliferation of robotization, artificial intelligence, and other innovative technologies.
Thus, we can say that FinTech has grown beyond simply introducing technology into traditional industries. It has become a powerful mechanism that shapes user expectations.
FinTech service providers are no longer seen just as start-ups. They are now professionally managed companies with extensive operations, diverse product portfolios, and global reach.
FinTech is changing the way the traditional financial market operates and is one of the fastest-growing segments at the intersection of financial services and innovative technologies. In this segment, technology startups and new market participants are applying innovative approaches to products and services, shaping preconditions for the effective development of fintech.
In this article, we will look at how FinTech affects banks and the financial system, the main effects of FinTech on the banking industry, and FinTech impact on financial services.
How fintech affects the financial system
The global financial crises have exposed serious problems and weaknesses in financial regulation and supervision. As a result, the Financial Stability Board is undertaking a comprehensive and ongoing review of the global financial regulatory architecture to set standards. One of the weaknesses identified by the crisis was poor risk data collection and reporting in banks. This led to the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision publishing its Principles for Risk Aggregation and Risk Reporting in 2013.
This was a key development as the principles set minimum standards for data collection and management, which may require additional investment in technology and organization restructuring. The increasing complexity of the global regulatory framework, growing regulatory requirements and the risk of costly penalties as a result of tightening post-crisis standards have contributed to higher compliance costs for financial institutions. This has become especially important for international banks faced with formidable and sometimes conflicting regulations.
The global regulatory framework is becoming increasingly complex, with stricter standards introduced after the financial crisis. This has led to growing regulatory requirements and higher risks of costly penalties for financial institutions. As a result, compliance costs for these institutions have risen significantly.
The concept of “financial innovation” is much broader than FinTech, and, accordingly, not all financial innovations are financial technologies (for example, the creation of a new derivative, etc.). At the same time, the concept of financial innovation can be partially included in the concept of “digital economy” (FinTech completely, since its functioning without digital technologies is almost impossible).
FinTech today is often viewed as a unique segment of financial services and information technology. However, the relationship between finance and technology has a long-standing relationship, typically complementing and reinforcing each other. As we wrote above, the global financial crisis of 2008 was a turning point and the reason FinTech is turning into a new paradigm. This evolution creates challenges for regulators and market participants, especially in balancing the potential benefits of innovation with the potential risks.
Currently, FinTech includes numerous technology startups, as well as large organizations trying to improve and optimize the financial services provided. At the end of 2014, investments in this segment reached 157 billion dollars. After that, the term began to refer to a large and rapidly growing industry.
Most of the banking software development is modernizing traditional financial services and products in several areas:
Payments and Transfers: Online payment operations, online transfer services, P2P currency exchange (transfers between individuals), B2B payment and transfer services (transfers between legal entities), cloud cash desks and smart terminals, mass payment services;
Financing: P2P consumer lending, P2P business lending, crowdfunding;
Capital management: Robo-advisers, programs, and mobile applications for financial planning, social trading, algorithmic exchange trading, and money-saving services.
The new wave of FinTech over the past 10 years tends to develop from the bottom up, i.e. it is born mainly in agile startups that seek to break traditional rules, do business, compete, or are acquired by existing financial institutions. This new startup trend has a lot of advantages and coupled with post-crisis regulatory reforms that have spurred structural change in the financial industry, is pushing incumbent financial institutions to increasingly focus on technology to compete against the threat posed by new FinTech startups.

Read next
AI In Fintech: Use Cases of Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning in Fintech
Explore transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) on the FinTech industry.
Take a lookFintech can influence the financial market in several main areas
1. By increasing competition, empowering consumers, increasing financial inclusion, democratizing access to financial services, especially in developing countries and, as a consequence, stimulating further innovation. Innovation creates new product/service opportunities, new strategies, and commercialization channels;
2. By improving efficiency through innovation in:
- Relevant infrastructures such as payment system infrastructure, credit information systems, and public registries. One example is the know-your-customer utility. That is, these are funds that can be used by several financial service providers and that optimize the collection and exchange of customer identification data;
- Back-office and frontline procedures in traditional financial institutions, as well as in their decision-making process. This includes improving risk management and regulatory compliance. More often than not, institutional innovation relies on partnerships with FinTech companies that take on specialized roles such as providing credit scoring, insurance pricing tools, managing prepaid accounts, and automating communications.
3. By creating new investment opportunities for existing financial institutions. Banks and insurance companies are increasingly investing and buying out financial technology companies as part of their (broader) investment portfolio, and some are also sponsoring FinTech incubators to create investment opportunities;
4. By improving financial supervision;
5. By improving and optimizing the risk management process.
In the realm of how FinTech impacts the financial market, two factors have recently gained significant prominence:
- the level of acceptance of basic technologies by society;
- degree and prevalence of technological know-how among the general population.
Effects of fintech on the finance industry
FinTech and mobile banking sector includes the following technological trends:
Cloud computing and big data
Cloud computing provides access to data without installing special payment apps on the device, which allows banks to offer their FinTech products anywhere in the world by centralizing banking services on the network.
Big data, in turn, provides customers with personal target offers based on the analysis of heterogeneous and fast-moving digital information, the sources of which are the Internet, corporate document archives, readings of sensors, devices, etc.;
APIs
An API is a collection of classes, procedures, functions, structures, and constants that are provided by an application, service, or operating system for use in external software products.
Social media and mobile communication
Integration of the banking business with social networks allows for the obtaining of customer information preferences when proposing new financial products, establishing trusting relationships with each bank's client, and accelerating the implementation of Blockchain technology in relationships with customers. Examples of successful implementation of such relationships in retail are Amazon and Deutsche Bank.
Omnichannel banking
The main advantage of omnichannel banking is that customers' troubles can be resolved very fast. Using the Internet and TV devices, they can avoid in-person interactions in bank branches and get to their point quickly and efficiently. Delegating a part of the tasks to digital tools such as chatbots will save operational costs and provide customers with more personalized service through the digital world of banking services. This approach is flexible and adapted to customers' unique needs. As an extra advantage, you can find the opportunity to improve your bank experience and get much higher loyalty from your customers, leading to fewer drop-offs and better conversions.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
Payment systems are adjusted with tools with artificial intelligence & machine learning, defining the future of digital payments globally and on any device. By analyzing customers' operation history, spending habits, and behavior, we can predict their activity in the future and suggest payment methods with reduced fees.
One of the most significant trends is voice-activated transactions. They require special approaches to security and verifications, which now are one more substantial area for growth. The most valuable resource now is financial data. Integrating FinTech solutions, like payment tools, with other systems can help understand shopping behavior deliver relevant recommendations, increase retention, and deliver better customer experiences.
More on the topic
Core Open APIs For Banking & Payments
Find out how open banking relies on open APIs to promote collaboration and innovation, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Read the articleOpen banking
Open banking is the ability for third-party providers to access customers' financial information securely. There is a standard format for the process, specified by open banking, available only with the customer's consent. It can help major companies get an accurate picture of their consumers' financial situation to offer their services. Also, it allows consumers to get a clear picture of their finances.
E-wallets
E-wallets have had a transformative FinTech impact on the banking industry. These digital wallets have streamlined the way individuals and businesses manage their finances, offering unparalleled convenience and accessibility.
Based on Global Payment Report 2023 – digital wallets comprise 49% of worldwide e-commerce transactions, while credit cards make up 21% of the total.
Traditional banks have had to adapt to this changing landscape, either by integrating e-wallet services into their offerings or facing the risk of losing customers to standalone FinTech companies. The rise of E-wallets like Cash App has also spurred innovation in payment processing, ushering in an era of faster and more secure transactions.
As the banking industry continues to grapple with these changes, collaboration and competition between banks and FinTech firms will shape the banking services ecosystem of the future.
Smart chip technology
Smart chip technology has played a pivotal role in reshaping the banking industry in the age of financial technology. The introduction of EMV chips in credit and debit cards has been a game-changer, dramatically reducing instances of card fraud and enhancing the security of transactions. This technology has been instrumental in establishing trust among customers, who now expect their financial institutions to provide them with safer and more secure payment methods.
Traditional banks have been compelled to adopt smart chip technology to keep unprecedented pace with the evolving landscape and remain competitive, ultimately reshaping the way they approach security in FinTech services.
Biometric sensors
Biometric sensors represent a breakthrough in authentication methods within the financial industry, contributing significantly to the FinTech-driven transformation of mobile banking. These sensors, capable of recognizing unique physical attributes like fingerprints, facial features, and even voice patterns, have not only enhanced the security of financial transactions but have also made the customer experience more convenient and efficient.
The adoption of biometric sensors has created a shift towards seamless and hassle-free customer authentication, reducing the reliance on traditional passwords and PINs. As a result, financial technology companies have to adapt to meet customer expectations for improved security and user-friendly experiences, redefining their approach to authentication in the digital age.
Reasons and prerequisites for the development of financial technologies in the banking sector
The development of financial products, especially noticeable in the last five years, was caused by the following circumstances:
1. Loss of customer confidence in the traditional banking sector during the 2008 global financial crisis and stricter regulation. Trust is an absolutely necessary category for the successful functioning of the financial system, and its loss has accelerated the process of development of financial technologies, which is inevitable in any case. Against this background, there is a demand for services provided by FinTech startups, as well as for the optimization of services caused by a decrease in their profitability due to stricter regulation.
2. Raising the level of expectations for the services provided, including financial. The consumer becomes more and more focused on constant updating and acceleration of processes, greater availability of technologies and greater convenience of services in the conditions of obsolescence and limitations of traditional financial services both in form and in essence. The development of information processing technologies has determined the development of such FinTech segments as blockchain, peer-to-peer lending, online scoring, algorithmic trading, etc.
3. The spread of the mobile Internet, leading to the fact that the focus of the bank's customer acquisition strategy is shifting from opening another branch to creating online services and supporting the mobile version of the site.
4. The desire for innovation, increased requirements for ease of use of services, quality, and speed of obtaining information, characteristic of the largest generation of millennials in world history (born in the period from 1980 to the early 2000s), is a powerful catalyst for changes in the financial sector.

Sharing some insights
Recent Trends In Investment Banking Technology
Learn more about the swift recent changes in banking caused by IT spending and digital innovation.
Dive Deeper5. Banking legislation, for which consumer rights are always a priority, but their protection does not impede the implementation of financial technology innovations and flexibly adapts the rules to the requirements of the financial industry (in the UK, Singapore, and Australia). On the contrary, in other countries, the financial sector is highly regulated, which hinders the development of the financial services industry.
6. The success of tech companies in other sectors of the economy (retail, entertainment, etc.). The emergence of successful companies that have significantly changed their markets and offered more competitive products and services has sparked the interest of entrepreneurs, including in the financial sector.
How does FinTech affect banks? Consulting experts from McKinsey & Co. predict that over the next ten years, commercial banks may lose up to 60% of profits in favor of new financial companies. Among the areas of banking activities that can primarily be replaced by FinTech startups are consumer finance, microloans, and payment services.
Why fintech and banks should work together:
The way people use financial services and banking has evolved. Technological changes of recent times provoked changes in people's banking behavior, and now we already see the changes, which indicate the significant FinTech applications impact on the finance industry. Let's list several of them:
- The use of mobile devices has increased a lot. According to Pew Research Center, 81% of adults in the U.S. own a smartphone, and more than 50% own a tablet. So, any business that wants to have a good connection with its customers should consider developing its products and offering mobile-friendly products. That means that we can reach any information quickly from a device that has an Internet connection. Same with the banking details, which bank clients can access from pretty much anywhere. A great advantage is that nowadays, the updates of information don't need to settle overnight: transactions are speedier, and the information is the most up-to-date.
- More services are available online. Some people still prefer visiting a physical bank branch to maintain financial services. Others are already used to transferring money between their accounts, depositing checks, and tracking their transactions online. In the beginning, the banks offered some perks to get their customers to use online services primarily. Now lots of customers consider online services more convenient as they can take place at any time.
- Great attention to security issues in FinTech is called to emphasize that this new approach to banking is safe, this cooperation is reliable, and customers' private financial data is protected. Traditional banking at the time might not have invested a lot of money and resources into focusing on data protection and raising attention to making customers aware of the necessity to decrease vulnerability.


Thank you for Subscription!
Impact of fintech on banks
According to a Marketforce LIVE expert, UK banks see FinTech startups as a major threat to the business models of traditional financial companies and institutions. About 600 representatives of the financial sector were interviewed to find out the attitude of banks toward fintechs.
According to 81% of respondents, quality of service outpaces customer trust in a brand in the race to acquire and retain users.
79% of participants believe that FinTech startups have the most attractive brands.
59% see fintechs as a global competitor to banks that can replace traditional forms of providing financial services.
At the same time, 46% of the respondents see a big threat in fintechs, since in order to compete with them, it is necessary to optimize the business model in the near future.
Banks are inferior to fintechs in terms of speed of service provision, convenience, and simplicity, as stated by 71% of survey participants.
30% of respondents believe that fintechs will run banks, and 31% believe that FinTech will benefit traditional financial institutions.
What does fintech mean for banks? In general, the financial services industry has seen various forms of collaboration between classic banks and Fintech. If, some time ago, fintech was viewed as a potential threat to banks and the banking industry in general, now they talk about cooperation and mutual benefit. FinTech companies can provide financial support for banks via specific services and solutions, such as risk analysis services or wealth management. Baltic International Bank also uses FinTech companies as service providers. The Bank is currently in a process of change, successfully implementing a new business model, so many new ideas and methods need to be adapted.
Here is one example of how a classic bank can partner with Fintech. Baltic International Bank is a client of the American rating agency Sigma Ratings, which uses an advanced technological approach to assess the management efficiency and risk of financial crimes at the organizational level. In early 2020, the company also carried out an independent assessment of Baltic International Bank, assessing the risks of organizations related to the prevention of financial crimes, governance, sanctions, corruption, and reputation. All of this was done online by the company using a methodology based on industry best practices.
How does fintech affect banks? FinTech perfectly complements classical banking, helping, for example, to use the available data more intelligently and offer data analysis services since data is more valuable than gold and oil today. An increasingly popular term is the Insight Driven Organization (IDO), or knowledge-based organization that uses data analytics and the input it makes to all decision-making processes.
Impact of fintech on financial services
New technologies are changing the way people use FinTech banking and financial services. Unlike previous historical episodes of heightened competition in the banking market, alternatives are now evolving too quickly.
The banking industry has existed for centuries, and during this time it was predicted an imminent end more than once. For example, in the middle of the XX century. in the United States, the threat to traditional banking came from alternative credit institutions in the 1970s. mutual funds offered an alternative to deposits and in the early 2000s. banks faced competition from large trading and industrial companies, which began to obtain banking licenses and offer services in addition to their core business.
But what is happening now differs from the periods of aggravation of competition in past years in scale, speed and global nature. The scale of FinTech innovation is unprecedented, they are introduced at an unprecedented rate and spread with ease around the world, ignoring boundaries. This changes not only banking business models, but also the principles of financial services.
Regulatory implications
Impact of technology on financial services is testing not only the existing banking business model, but also the traditional scheme of financial regulation. Regulators need to balance many forces to ensure financial stability, a competitive and efficient environment, and proper data handling.
For example, it is not yet clear to what extent financial stability is sensitive to technology as such. The “ungrouping” of services traditionally united by one bank, inherent in the current technological breakthrough, can lead to the formation of a new type of risk. For example, some activities will fall outside the perimeter of prudential regulation and supervision. In addition, FinTech projects using wholesale funding may be vulnerable to liquidity shocks.
It is also unclear how artificial intelligence and algorithmic provision of financial services based on new types of data will behave in a disrupting time of crisis. At the same time, the growing dependence on digital processes and systems increases operational and cyber risks. Now, they are perceived and regulated as specific, but the digitalization of financial services turns them into systemic ones, which may lead to the need to revise the regulatory approach.
Our experience
The Geniusee team has extensive experience in FinTech consulting & developing FinTech solutions. Below we will provide some examples of our work.
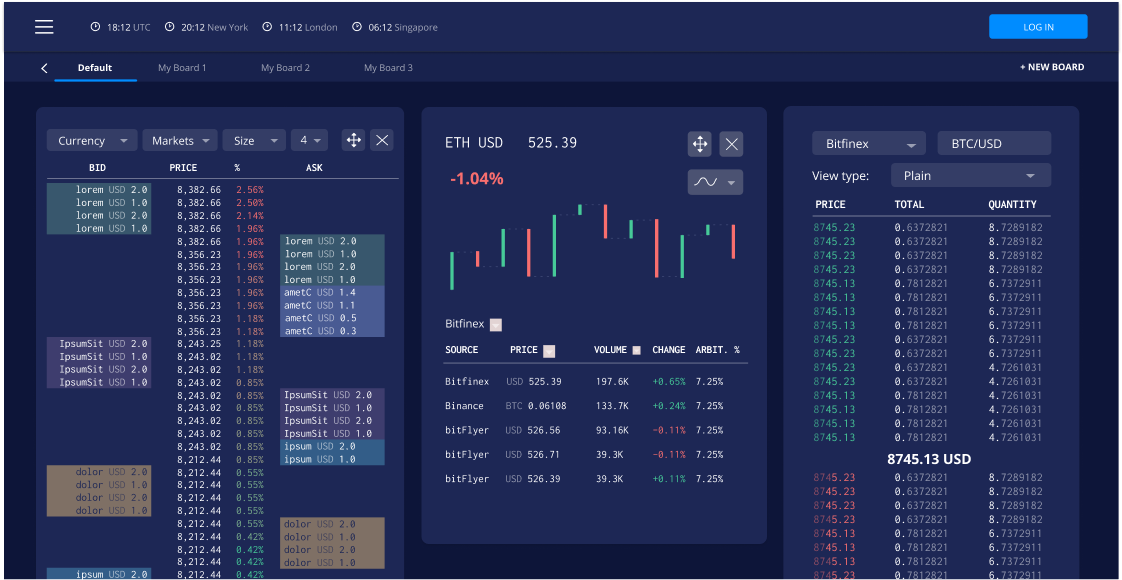
1. Crypto Data Analytics
Due to the high volatility of the cryptocurrency market, a trading company was faced with the issue of traders needing to analyze cryptocurrency market information quickly.
We were faced with the following tasks:
- Financial dashboard for traders allowing to analyze cryptocurrency exchange rates on different platforms.
- Visualization of such information in a more user-friendly way, allowing to quickly conduct buy/sell decisions.
- Possibility to purchase cryptocurrency on this platform.
- Visualization of such information in a more user-friendly way allowed quick conduct of buy/sell decisions.
- Possibility to purchase cryptocurrency on this platform.
Result:
2. DigitalBits Crypto Wallet
DigitalBits is an open-source project supporting the adoption of blockchain technology by enterprises. The technology enables enterprises to tokenize assets on the decentralized DigitalBits blockchain; transfer & trade those tokenized assets on-chain; and enables fast payments & remittances.
We were faced with the following tasks:
- Development of the Web/mobile wallet prototype allowing the transfer of money through an internal wallet.
- Development of the financial dashboard allows the tracking of financial performance and the history of the wallet.
- DevOps services on AWS for blockchain infrastructure.
- Automation quality control.
Result:
3. TradeSmarter
Tradesmarter is leading in providing white-label trading FinTech solutions, offering a web-responsive trading platform that enables top financial companies to unleash a new era of competition, FinTech revolution, and user experience.
We were faced with the following tasks:
- Сreating the necessary conditions in the infrastructure for the normal functioning of software.
- Organizing environment for making changes.
- Process automation.
Result:
Conclusion
FinTech blends new technologies with financial services, reshaping how industries operate. It’s not just about banks; FinTech touches retail, insurance, investments, real estate, and even agriculture. Governments and regulators are paying close attention, working to address legal and security challenges while making financial services more accessible.
For banks, FinTech is both a competitor and an opportunity. Features like online banking and instant payments are now standard, but FinTech keeps pushing boundaries with faster innovations. While some ideas will thrive and others fade, collaboration between banks and FinTech can unlock big benefits. Banks bring experience, and fintech brings fresh ideas — together, they’re transforming the financial industry.





















