The pandemic, the economic upheavals associated with it, the war between Russia and Ukraine, and other events in 2021-2022 gave impetus to the emergence of technological innovations, including large-scale breakthroughs in the areas of cloud and edge systems. Long-established companies are reshaping their business modesl and turning them into completely contactless online services. According to Radware's "The State of Web Application and API Protection" report, 70% of production web applications are currently running in the cloud. Moving workloads to the cloud and the edge at scale is becoming a new source of work for hackers. In this article, we will talk about the most popular vulnerabilities of 2022.
In this Article:
Cyber Security Analytics 2021
The annual losses from cybercrime in the world already amount to trillions of dollars. The pandemic has accelerated digital transformation and exacerbated the problem, exposing the vulnerabilities of IT systems. As a result, cybersecurity has become the most important economic factor that directly determines the company's profit. The scale of the problem is only growing, and no one will be able to leave cybersecurity risks unattended. However, work in this direction requires investment, process restructuring, and adaptation to new threats.
According to the data provided by Cyber Polygon, in 2021, the classic attacks were dominant — coronavirus-themed phishing sites, issuance of supposedly genuine vaccination documents, fraudulent transactions with services, and advertising of projects that bring instant income. Such malicious acts accounted for more than 85% of attacks. Approximately 10% of attacks recorded in 2021 were ransomware that targeted corporations. The most famous example is the attack on the Colonial Pipeline, which paralyzed the giant gas station network in the United States. And the least attacks were, no more than 5%, of a targeted nature, extremely well organized, aimed at government structures in different countries. They have not yet been fully explored.
Online security trends 2022
No one could have imagined that the cybersecurity industry would experience absolute chaos in 2021: Record-breaking ransomware attacks, multiple supply chain disruptions, data privacy battles, and endless leaks. A year ago, all of this might have seemed too bold a scenario to be true. What awaits us next?

1. Government Influence
Government interest and influence in cybersecurity will grow. SolarWinds, the attack on the Colonial Pipeline, spyware, and privacy concerns have all the attention of world governments on the industry. Experts agree that the coming year will be full of new rules and investments.
The US election drew attention to the spread of disinformation to influence the outcome, but after massive cyberattacks on critical infrastructure, the focus has shifted to new national security urgency.Researchers predict that these immediate cyber threats will remain the focus of government attention throughout 2022.
According to Jonathan Reiber, senior director of cybersecurity strategy and policy at AttackIQ, the US government is already actively working to strengthen the nation's cybersecurity. Zero Trust Architecture recommendations will be rolled out and operational across all important government entities in the first half of 2022.
''As the federal government implements this practice, more private entities will follow suit by building higher walls around high-value assets,'' Reiber said.
According to Trevor Hughes, President and CEO of the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), in 2022, both state and national laws are expected to protect consumer privacy. The expert believes that private companies will continue to use privacy to build trust and attract customers but will also use their weapons against lagging privacy competitors.

Article
Geniusee Received An ISO 9001:2015 Certificate
Safety and security of our clients is our essential priority.
Read it!2. Social Engineering
Nothing will change, and in 2022 people will still be people, which means that they will still make mistakes, regardless of the consequences for organizations' security. They are what cybercriminals will rely on to make their social engineering scams work.
Mike Wiacek of Stairwell says that social engineering will not give up its positions in the new year. This is one of the most difficult security problems because no amount of security measures can change the fact that people are imperfect and can be deceived. During the workday, otherwise serious people can be incredibly nonchalant, and that's unlikely to change anytime soon. Did Mike really take the flash drive in the parking lot and plug it into his corporate laptop? Did Alan really believe that he could get a free Rolex by clicking on the link? Cybersecurity is an issue for which everyone is responsible, but only a few understand the damage that their individual actions can cause.
In addition to the widely recommended user education, Wiacek suggested that cybersecurity professionals change their approach to internal communications in 2022. In his opinion, security teams should interact directly with their colleagues and be easily accessible. We need to stop carrying on our shoulders the image of strict colleagues who always say ''no.'' Building a strong safety culture requires working on trust and good relationships. To persuade employees to your side is the main task, even if it's Joe from accounting whom you don't really like.
The presentation of information should also be simplified. Instead of ''gamifying,'' try talking to people in their language and presenting everything in a format that is familiar to them, such as, humorous videos. Whatever the cybersecurity professional tries to convey to employees should look and feel exactly like the content they choose to consume on apps like Facebook, TikTok, Instagram, YouTube, etc.
3. The supply chain is a hot target for ransomware
Ian McShane, CTO of Arctic Wolf, believes that the industry will begin to change its view of ransomware this year and understand that the problem is not with the ransomware itself but the entry point. We will focus on predicting and protecting the first line of attack by using data science to model scenarios that can reveal potential weaknesses in the supply chain.
Supply chain ransomware is of particular concern due to the potential of a single attack to affect hundreds or thousands of companies. According to Deepen Desai, CISO and VP of Security Research and Operations at Zscaler, the number of ransomware attacks in the supply chain will not decrease in the next 12 months either. According to Desai, attacks on technology companies increased by 2,300% in 2021. What will happen in 2022 is scary to imagine.
Experts even suggest introducing a small reward for users for proper security behavior. Rewards can encourage them to become more attentive to details and not make mistakes that cost companies dearly. These common users most often interact with common supply chain attack vectors.
According to Troy Gill, Senior Threat Intelligence Manager at Zix | App River, in 2022, email will increasingly be subject to targeted and high-quality spear-phishing attempts, requiring a change in security tactics. Spear-phishing attacks are attacks in which cybercriminals personalize emails. In 2022, organizations will respond to this by prioritizing building more specific email protections.
4. Ransomware as a Service
Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) has helped turn digital ransomware into a thriving business, and 2022 is likely to be another big year for hackers.
Alas, the RaaS model will continue to be popular as it has proven to be an incredibly effective means of maximizing profits. An increased government presence in protecting critical infrastructure will encourage hacker groups to use ransomware to attack small and medium enterprises. This will help them attract less attention but still achieve their goals. Insufficient funding and indifference of staff in small and medium-sized companies only fuel the interest of hackers.
5. Better coordination of the cyber industry
As we can see from the evolution of malware and phishing as a service, hackers are ready to join forces to achieve mutual success. In 2022, we will see cybercriminals form even stronger working relationships that help strengthen the crime market.
According to Ian McShane, as far as the cybersecurity community is concerned, there is a lot of work to be done to strengthen the entire ecosystem. This means that large companies must share tools and talent with small and medium-sized enterprises that do not have the resources to protect themselves.
In his view, the industry must work to democratize security, especially as talent shortages and staff retention continue to drain teams. Digital transformation and the expansion of technology have created great opportunities for attackers, and securing the entire supply chain is the only way to protect us all.
Classifications of cybercriminals
This classification is somewhat conditional but still the result of a process using the implementation of cybercriminals.
1. Cyberbullies
These include hackers with basic training. Often work alone or in small applications. This is mainly because large companies require weak protection, beautify data, demand a ransom, and sell information on the dark web. Their financial resources are limited.
2. Cyber Mercenaries
They prefer to work by order, discovering the possibility of hacking. They are engaged in exceptional preliminary intelligence, searching for employees of companies who are willing to provide data for capture for a fee. Very well technically equipped exclusive toolboxes hacked confidentially. Their main goal is to terminate the company's activities, industrial espionage, the theft of confidential data of top managers, and the spread of reputation. They have the financial resources to carry out attacks.
Types Of Cybercrimes: How To Prevent Cybercrimes
You can prevent your belongings both real ad virtual. Learn to recognize the modern threats.
3. Groups of cybercriminals
Their qualifications are practically not inferior to the special services. They work very secretly, use the most advanced technologies for anonymity, and develop highly sophisticated tools for stealing data that can bypass standard monitoring systems. Their goal is to destroy the infrastructure of corporations, control over CII, and obtain strategically important information. Their level is so high that only special services in cooperation can cope with them.
Some of these groups are supported by states (PRC, DPRK, RF) that provide appropriate cover. Sometimes they are hired by the intelligence services themselves to attack government sites and infrastructure. In fact, such groups have turned into corporations that have all the tools and financial resources for large-scale attacks on any company or country.
During the discussions, the SOS forum and Cyber Polygon participants noted several critical issues that companies or government authorities have not yet resolved.
Critical Security Breaches 2022
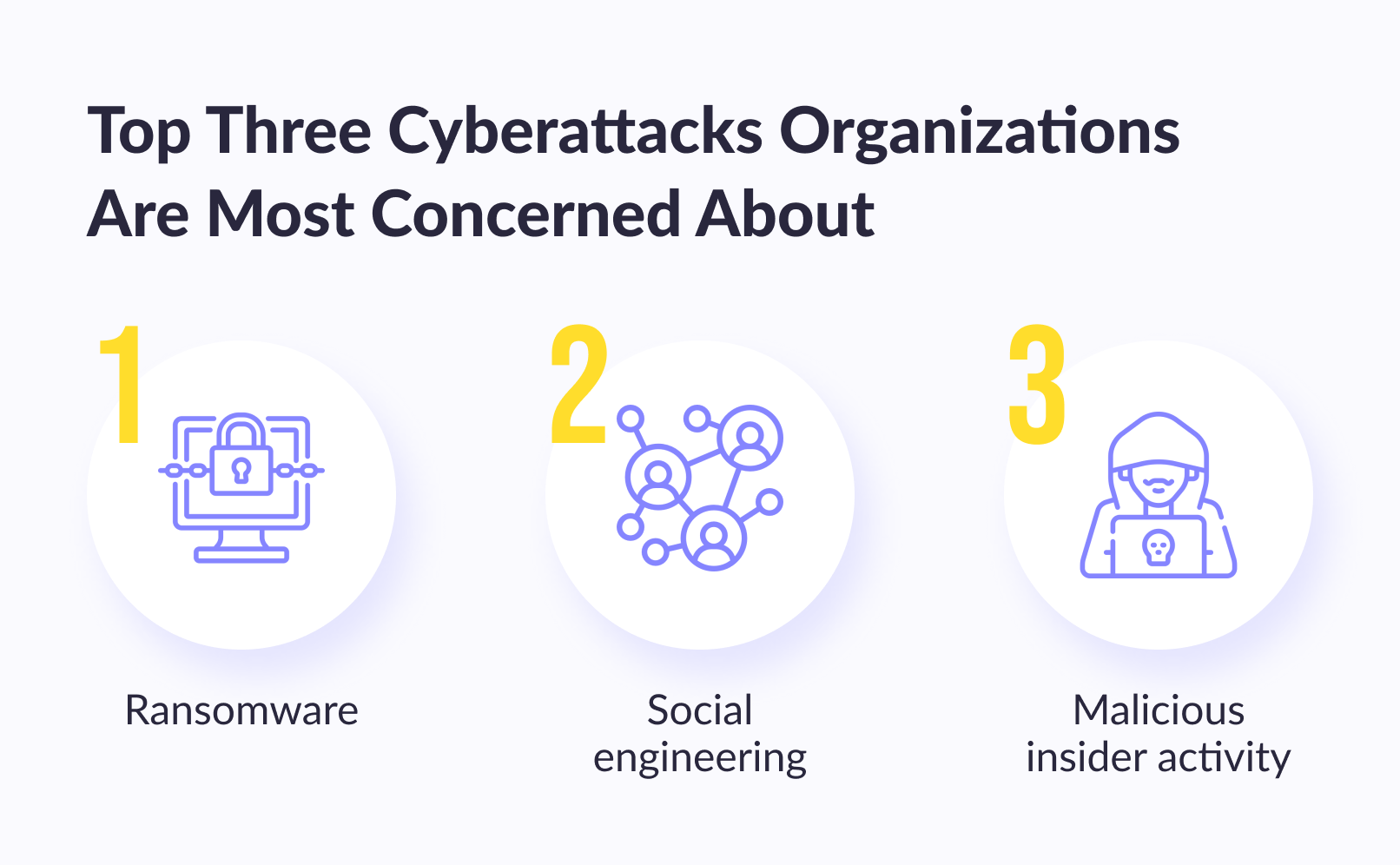
1. Broken Access Control
Access control enforces the policy so that users cannot act beyond their intended permissions. Failures typically result in unauthorized disclosure of information, alteration or destruction of all data, or performance of a business function beyond the user's capability. Common access control vulnerabilities include:
- bypass access control checks by changing the URL, the internal state of the application or HTML page, or simply using a custom API attack tool;
- permission to change the primary key on another user's record, permission to view or edit someone else's account;
- privilege escalation — act as a user without logging in or as an administrator if logged in as a user;
- metadata manipulation, such as reproducing or spoofing a JSON Web Token (JWT) access control token, cookie, or hidden field that is used to elevate privileges or abuse of JWT revocation;
- a misconfigured CORS allows unauthorized access to the API;
- force viewing authenticated pages as an unauthenticated user or privileged pages as a standard user; API access with missing access controls for POST, PUT and DELETE.
2. Cryptographic Failures
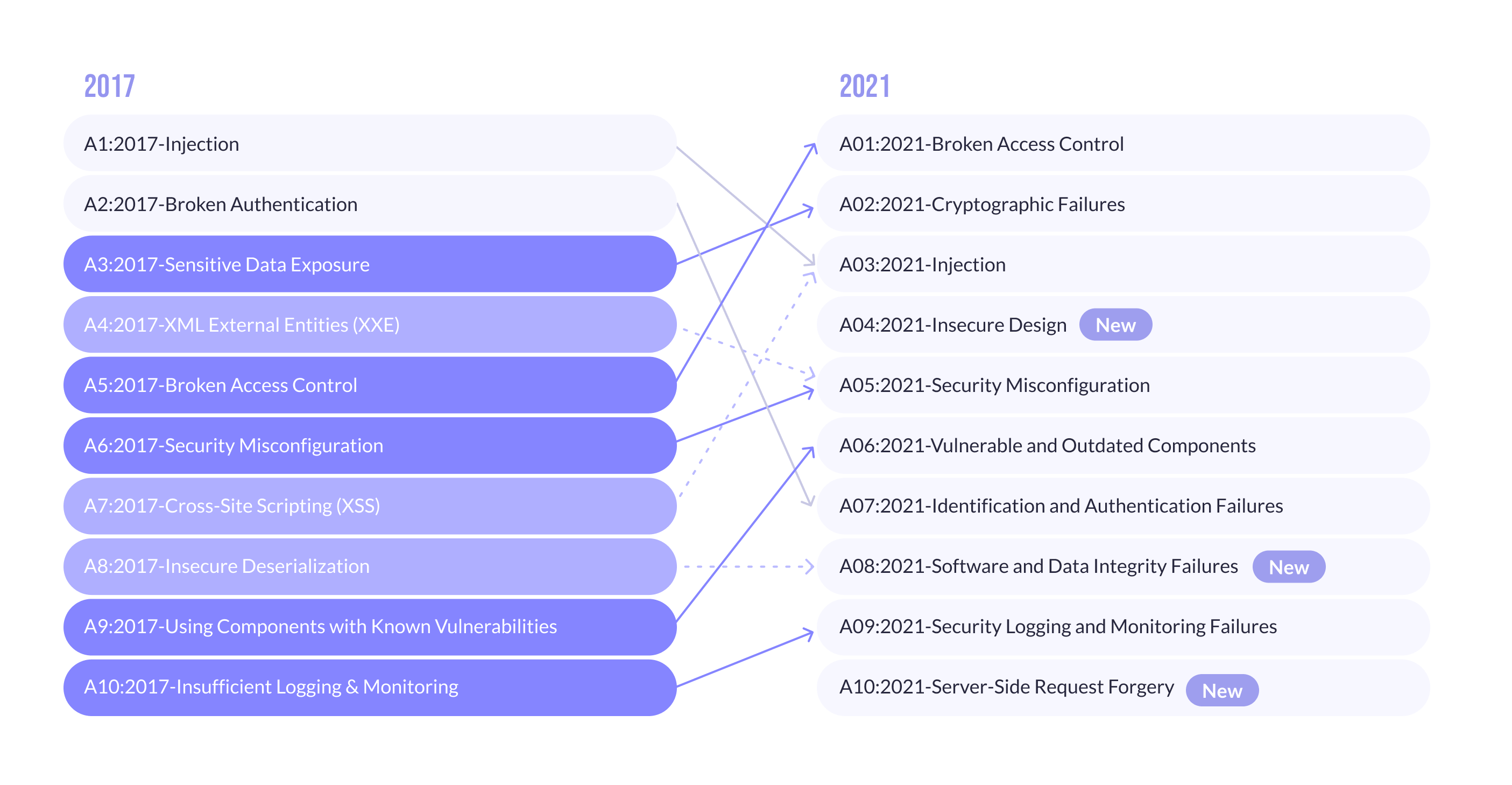
Cryptographic Failures was named a disclosure of sensitive data in the 2017 OWASP Top 10 list. If you notice, the title "Confidential Disclosure" is actually a symptom, not the root cause.
Confidential data can be exposed in many ways, but the description of this vulnerability actually indicates that the cryptography was implemented incorrectly! So I think OWASP did a great job here as they now add the root cause instead of the symptom — a great step in the right direction. Otherwise, everything was at least confusing.
Some of the problems that fall under this category are:
- sensitive data is transmitted (via HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc.) or stored in clear text (in a database, files, etc.);
- use of old or weak cryptographic algorithms;
- using weak or default encryption keys or reusing compromised keys;
- encryption is not enforced, or the server's certificates are not verified when communicating with it.
But I hope you get the basic idea right: if you mess up a cryptocurrency or don't use it at all, you've left an open door leading to this vulnerability!
3. SQL Injection
SQL injection is currently not only a widespread vulnerability but also one of the most dangerous, according to OWASP Top 10 Application Security Risks 2021.
The essence of vulnerability is your execution of an arbitrary query to the database. The request can be anything: for reading, writing, modifying, and deleting any records. Sounds catastrophic, doesn't it? But everything is not limited to these threats since you can get to read/write local files or even code execution under certain circumstances! It all depends on the goals pursued by the attacker, the system used, and how it is configured.
There are several types of SQL injection:
- Classic SQL Injection is simple and easy to use. Allows an attacker to attack the database and immediately see the result of the attack. Rarely seen lately.
- Error-based SQL Injection is a slightly more complex and time-consuming type of attack that allows, based on the displayed DBMS errors, to obtain information about the entire database and its data. Exploited if someone in a hurry forgot to disable error output.
- Boolean-based SQL Injection is one of the "blind" injections. The essence of the attack is to add a special subquery to the vulnerable parameter, to which the database will respond either True or, unexpectedly, False. The attack does not allow the attacker to display all the database data ''on the screen'' immediately. Still, it allows, by sorting through the parameters over and over again, to get the contents of the database. However, this will require a period commensurate with the contents of the database.
- Time-based SQL Injection is the next of the "blind" injections. In this case, the attacker adds a subquery that slows down or pauses the database under certain conditions. Thus, the attacker, comparing the response time to "True" and "False" requests, character by character, can get the entire contents of the database, but it will take more time than in the case of using a Boolean-based attack.
- Out-of-band SQL Injection is a rare type. An attack can only be successful under certain circumstances, for example, if the database server can generate DNS or HTTP requests, which is not common. Also, like Blind SQL, it allows you to collect information about the data stored there character by character.
4. Insecure Design
Insecure Design is a new category for 2021 that focuses on the risks associated with design flaws. It is a broad category representing various deficiencies expressed as ''missing or ineffective control design.'' Unsafe design is not a source for all the other ten major risk categories.
There is a difference between an insecure design and an insecure implementation. We distinguish between design flaws and implementation defects for a specific reason; they have different root causes and solutions. A secure design can still have implementation flaws leading to exploitable vulnerabilities. An insecure design cannot be fixed by a perfect implementation because, by definition, the necessary security controls were never designed to protect against specific attacks. One factor that contributes to insecure design is the lack of profiling of the business risks inherent in the software or system being developed and, therefore, the inability to determine what level of security is required.
5. Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfiguration occurs when security settings are defined, implemented, and maintained as defaults. Good security requires a secure configuration defined and deployed for the application, web server, database server, and platform. It is equally important to keep the software up to date.
6. Vulnerable and Outdated Components
This vulnerability is ranked sixth in the Top 10 in the 2021 Community Survey but also has enough data to be in the Top 10 in our analysis. This category is a known issue that developers have difficulty testing and assessing its risks. This is the only category that does not have Common Vulnerabilities (CWEs) associated with the CWEs included, so their ratings default to an exploit and an impact weight of 5.0. Notable CWEs: CWA-1104: Use of non-serviceable third-party components and two CWEs from the Top 10 2017 and 2021.
You are not protected:
- If you don't know the versions of all the components you use (both client-side and server-side). This includes components that you use directly as well as from outside.
- If the software is unsecured, unsupported, or outdated. This includes the operating system, web/application server, database management system (DBMS), applications, APIs, all components, runtimes, and libraries.
- If you do not regularly check for vulnerabilities and do not subscribe to security bulletins related to the components you use.
- If you do not correct or update the underlying platform, frameworks, and dependencies in a timely manner and without taking into account the risks. This typically occurs in environments where remediation is done monthly or quarterly under change control, leaving organizations open to unnecessary exposure for days or months.
- If software developers do not check the compatibility of updated, upgraded or fixed libraries.
- If there are unsecure component configurations (see A05:2021 — Incorrect security configuration).
Conclusion
The threat landscape is rapidly changing, with groups of state-sponsored actors and professional hackers working in tandem to break systems apart. The 2021 threat thinking process is an excellent step towards an equally evolving security environment, where the focus is shifting from identification (and subsequent mitigation) to proactively preventing security flaws through robust and secure product design with an equal focus on App Sec and Secure alignment. Development in software design and development.





















