Are you searching for a proper model for your financial startup or service that will enable maximum flexibility and reliability? Are you learning about decentralized vs. centralized finance to weigh your decision?
Here, we will give you a comprehensive overview of both and their pros, cons, and financial industry examples.
Short on time? Check out a comparison table at the end of the article!
In this article:
What Is CeFi?
Centralized finance (CeFi) is a system where financial institutions — governments, banks, investment companies, stock exchanges, and others — have centralized control over the flow of money and specific financial transactions. It relates to all of the traditional financial services.
Main Features of CeFi
Here are the main distinguishing features of CeFi services:
- Centralized control. There is always a single authority that offers the services and controls the flow on local and global markets.
- Regulation. Centralized financial institutions are typically heavily regulated by government bodies to ensure the safety and soundness of the financial system and to protect consumers.
- Policies. Most CeFi companies have policies in place to protect their customers, such as “anti-money laundering” and “know your customer”. However, this type of management is akin to traditional finance, which often leads to downtime while sorting out issues, as well as corruption and fraud.
- Limited access. Access to financial services and opportunities is limited and may be determined by factors such as creditworthiness, location, and income.
- Accountability. CeFi institutions are typically required to disclose information about their financial performance and operations to regulators and the public.
CeFi Examples
Here are a few examples of centralized companies and institutions:
- Traditional banking systems, such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, are the brightest examples of CeFi. They control the flow of money and offer financial services such as deposits, loans, and online banking.
- Investment firms, such as Fidelity Investments and Vanguard, manage investments and provide financial advice to individuals and companies.
- Stock exchanges: the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. They facilitate the buying and selling of stocks and other securities.
- Insurance companies. Some companies like Allstate and Prudential are also examples of CeFi in the insurance industry.
There are some centralized cryptocurrency-related financial services, CeFi exchanges, and crypto trading platforms. For example:
- Coinbase – a US-based lending and borrowing platform that provides cryptocurrency trading.
- BlockFi – a crypto lending platform from New Jersey.
- Binance – one of the biggest centralized exchanges, as well as a lending and borrowing platform for cryptocurrencies.
Centralized financial approaches are the most widespread nowadays, and even with cryptocurrency assets, significant elements of centralization are still present.
CeFi Limitations
All this looks pretty secure and reliable, but centralization also has significant drawbacks, such as:
- Vulnerability. CeFi primarily relies on centralized institutions, such as banks and governments, which can make the whole system vulnerable to failures, fraud, or security attacks on that single unit.
- High costs. Centralized financial operations can be expensive, as they often include fees and other costs associated with intermediaries, regulations, and compliance.
- Limited transparency. The level of CeFi transparency may not be sufficient in many cases. For example, a bank may not be willing to disclose all the details of the loans they gave out, or an investment firm may not disclose the details of their investment strategies or the performance of their funds.
- Limited customization. Centralized financial services may not be tailored to individual needs, as they are often mass-produced and distributed through centralized channels.
- Low efficiency. CeFi systems can be slow, expensive, and overall inefficient due to the intermediaries, regulations, and compliance costs involved.
- Lack of control and autonomy. CeFi's centralized nature means that individuals and institutions have limited control over their financial transactions and assets and rely on the centralized institution for their financial decisions and actions.
The numerous limitations of traditional centralized financial systems have become an impetus for developing decentralized finance (DeFi).

On the topic
Banking As A Service Disrupts The Value Chain Of Traditional Banks
The BaaS business model offers many advantages. Do you know all of them?
Find out moreWhat Is DeFi?
As opposed to banking services and centralized financial services, decentralized finance (DeFi) is a system that doesn't have a central authority and implies using blockchain platforms and smart contracts.
With DeFi platforms, people can get a loan or pay for a product or service or do margin trading without the need for intermediaries such as a bank, an insurance company, or even the government.
Main Features of DeFi
The following main features identify decentralized finance services:
- Decentralization. The DeFi ecosystem operates on a decentralized, open-source platform that is not controlled by any centralized authority or intermediary. This is the main difference between DeFi and CeFi.
- Transparency. Unlike CeFi, transactions on decentralized platforms are recorded on a public blockchain, making them transparent and easily auditable.
- Accessibility. Decentralization allows for the creation of financial products and services that can be accessed by anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location or credit history.
- Interoperability. DeFi systems are built to work with other protocols, allowing for the creation of a wide range of financial products and services that can be easily integrated and granting better customer experience as a result.
- Automation. DeFi uses smart contracts to automate the execution of financial transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
DeFi Examples
Here are a few examples of DeFi products and services:
- Totle – an aggregator that connects DeFi users to different decentralized exchanges and asset providers. You can use it to find the best token prices and swap coins.
- Augur – a decentralized predictions market and a peer-to-peer exchange with unlimited sports betting. You can use the platform to track different sports and global markets for crypto.
- Kyber – a decentralized exchange, another multi-chain cryptocurrency market that allows monitoring the best rates for tokens and performing swaps.
And also, there are examples of traditional centralized institutions exploring and implementing decentralized technologies:
- JPMorgan Chase's Quorum blockchain platform (acquired by ConsenSys), which is based on the Ethereum blockchain and is used for a variety of financial applications, including supply chain financing and securities settlement.
- R3's Corda platform, a blockchain platform designed for the financial industry, is used by many major banks and financial institutions for various use cases such as trade finance, digital identity, and more.
- Fidelity Digital Assets, a unit of the asset manager Fidelity, has launched a new platform called Fidelity Digital Asset Services that allows institutional investors to access bitcoin and ether in a fully regulated, enterprise-grade custody solution.
DeFi Limitations
Decentralized finance is often called the future of financial institutions, but there are still some significant drawbacks of DeFi services that are important to consider:
- Complexity. Using decentralized technologies and smart contracts can make DeFi more complex to implement.
- Lack of regulation. DeFi operates outside of traditional financial regulatory frameworks, which can make it more risky for users and can also make it more difficult for regulators to protect consumers.
- Volatility. DeFi assets can be highly volatile, making it hard for users to predict the future value of their investments and making it more difficult for DeFi platforms to maintain stability.
- Security risks. The decentralized nature of DeFi can make it more vulnerable to hacking and other security threats.
- Lack of insurance. Many DeFi protocols don't have insurance to protect users against loss of funds due to smart contract bugs, hacking, or other issues.


Thank you for Subscription!
DeFi vs. CeFi in Services
Now that you have a basic understanding of the technology, let's compare decentralized vs. centralized finance based on several aspects.
Main Services
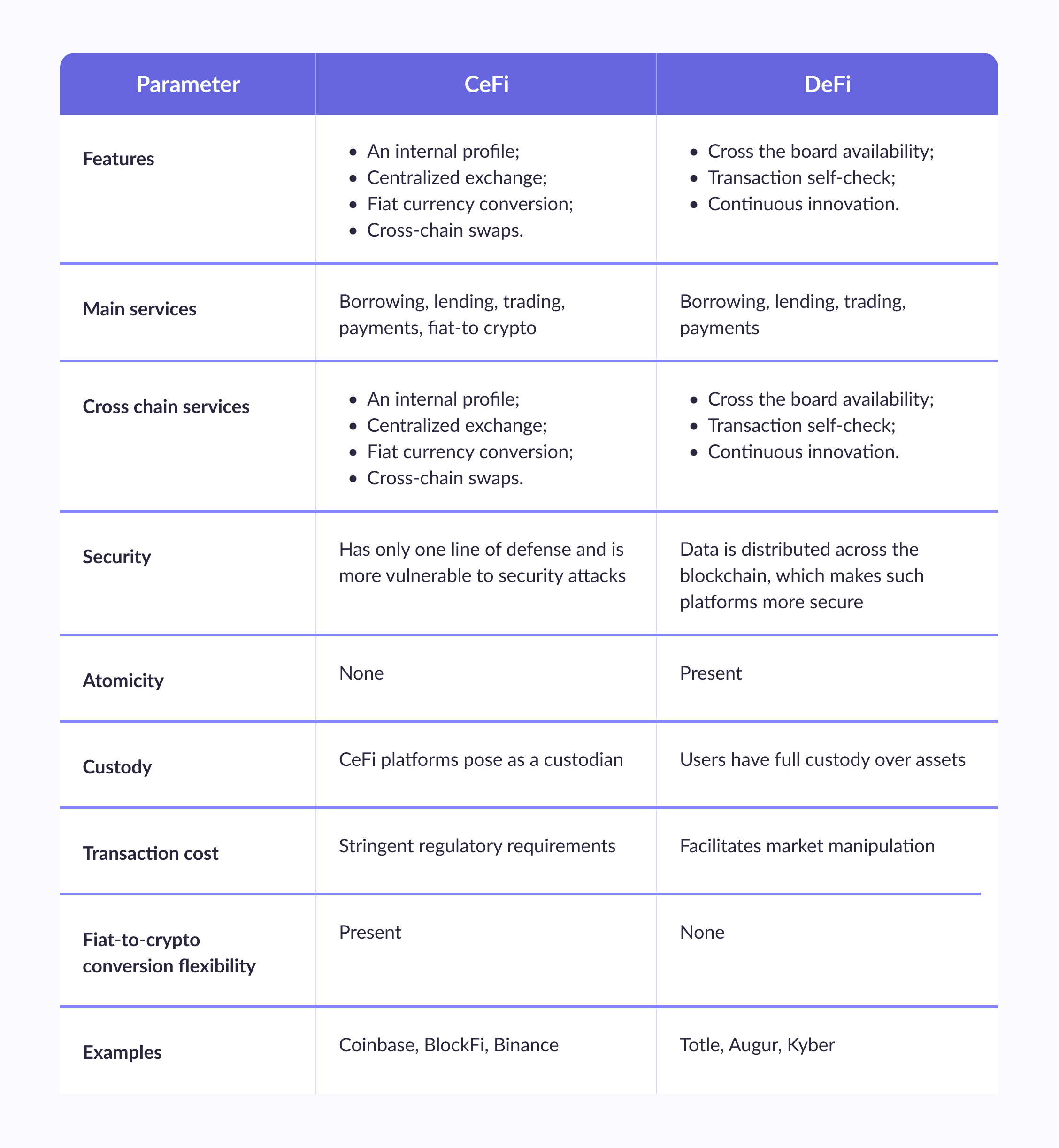
Both CeFi and DeFi protocols enable almost the same services, though centralized finance platforms can offer a bit more at the moment.
- CeFi – borrowing, lending, trading, payments, fiat-to-crypto exchange.
- DeFi – borrowing, lending, trading, payments.
Cross-Chain Services
Both DeFi and CeFi enable services via smart contracts — an immutable and irreversible piece of code baked into the blockchain — that remove unnecessary paperwork and intermediaries. The key difference here is that DeFi smart contracts don't support complex tokens that centralized exchanges do.
- CeFi – Provides a platform for trading the majority of cryptocurrencies.
- DeFi – Complex tokens cause a delay in completing the cross-chain exchange.
Security
DeFi vs. CeFi security depends on the data distribution model. This is where DeFi projects take the lead because data is distributed across a blockchain and doesn't depend on only one defense system. Centralized finance provides more possibilities for altering information.
- CeFi – Is heavily regulated by governments and financial institutions, which can provide a level of oversight and protection for consumers. On the other hand, centralization means that the whole system shares the vulnerability of its central unit.
- DeFi – Is built on blockchain technology, which is designed to be secure and tamper-proof.
If you're interested in secure financial software development solutions, Geniusee has sufficient experience building such projects.
Complete FinTech guide
Dive into all industry insights from our leading experts
Atomicity Element
An atomicity element, by the principle of a regular transaction, either completes all the activities or fails altogether if, for example, the internet connection is broken. So you don't get failed transactions that were completed anyway.
- CeFi – Not present.
- DeFi – Has an atomicity element.
Custody
Custody is the control over digital assets, which also means you need technical skills to complete transactions.
- CeFi – Platforms act as a custodian, taking the burden of any possible technical issues during transactions.
- DeFi – Gives customers complete custody, along with the technical hazards that may arise during use.
Malleability of Execution Order
Malleability depends on the regulatory requirements placed on the order in which a transaction must be executed. If they are strict, there’s little possibility of manipulating the market. If not, transactions can be conducted on a peer-to-peer basis, which makes the platforms more malleable and prone to innovation.
- CeFi – Stringent regulatory requirements leave no scope for market manipulation since there is a predefined sequence in which a transaction must be executed.
- DeFi – Users don't conform to any regulations and don't need permission to use DeFi platforms, which provides more avenues for market manipulation.
Transaction Costs
Blockchain transaction fees are very common since they are often the only source of financial support for a platform. The fees depend on the type of crypto assets you're exchanging. For example, ether fees are always static and thus predictable, while bitcoin fees are dynamic, and you can find out the price in your blockchain wallet after inputting the desired amount you want to send or exchange.
- CeFi – Platforms offer transactions at no extra cost due to the strict KYC and AML checks.
- DeFi – Platforms charge a transaction fee, though since DeFi operates stablecoins, the fee is almost always static and predictable.
Fiat Conversion Flexibility
Fiat currency is a type of government-issued money that isn't backed by gold or other commodities. An easy example is a modern paper-printed currency, such as the U.S. dollar.
- CeFi – Since fiat money is involved in the centralized finance model, it's easier to exchange such currency on CeFi platforms.
- DeFi – Doesn't provide conversion flexibility or even fiat-to-cryptocurrency exchange.
Centralized Finance vs. Decentralized Finance
The following image summarizes a concise recount of the key differences between centralized vs. decentralized finance, which will hopefully help you weigh your decision for your own product.
Conclusion
Both centralized and decentralized finance aim to achieve the same goal—making crypto trading popular and improving trading volume. However, the ways CeFi vs. DeFi ecosystems carry out their objectives are different.
While CeFi promises fund security and fair trade, DeFi aims to free the blockchain space from middlemen and intrusion, working over peer-to-peer networks. For example, DeFi protocols don't define the order of transaction execution, which provides more variables for market manipulation and, in turn, facilitates trading cryptos and innovation.
Are you in search of custom blockchain development services? Geniusee has a proven record of successful blockchain development for different industries with a deep immersion into business needs. Contact us to schedule a consultation or get a quote!





















