Tired of unknown words like ‘Internet of Things (IoT),’ ‘IoT products,’ ‘IoT project,’ ‘IoT devices,’ ‘ IoT apps,’ and many more? Just guessing. If so, dive into it to finally understand what means such strange terms as IoT services.
In this article:
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a game changer. You should’ve heard that. But what does the term — ‘Internet of Things’ really mean?
IoT — a general definition for physical objects (devices, e.g.) that owe embedded software, sensors, etc., and may exchange data, retrieve and analyze information, make decisions, and many more. Does it sound as if this whole IoT project thing is soon to be a base for the rising of machines in the world of digital transformation? Not so fast.
IoT solutions are designed to enable and simplify connection and interaction between human beings and devices. So-called smart objects and embedded devices with enhanced data analytics capabilities.
IoT initiatives tend to make our lives easier and improve their quality.
Smart shelves, remote patient monitoring, connected vehicles, smart lighting, smart homes, industrial IoT in inventory tracking, asset tracking, vehicle tracking, energy management, especially energy consumption, or supply chain management are a lot of IoT examples and even more dormant or not opportunities among both industrial applications and consumer devices.
Opportunities and challenges
The Internet of Things (IoT) is constantly evolving, so challenges and opportunities keep emerging. Let’s get through the most common nowadays.
Opportunities of the Internet of Things:
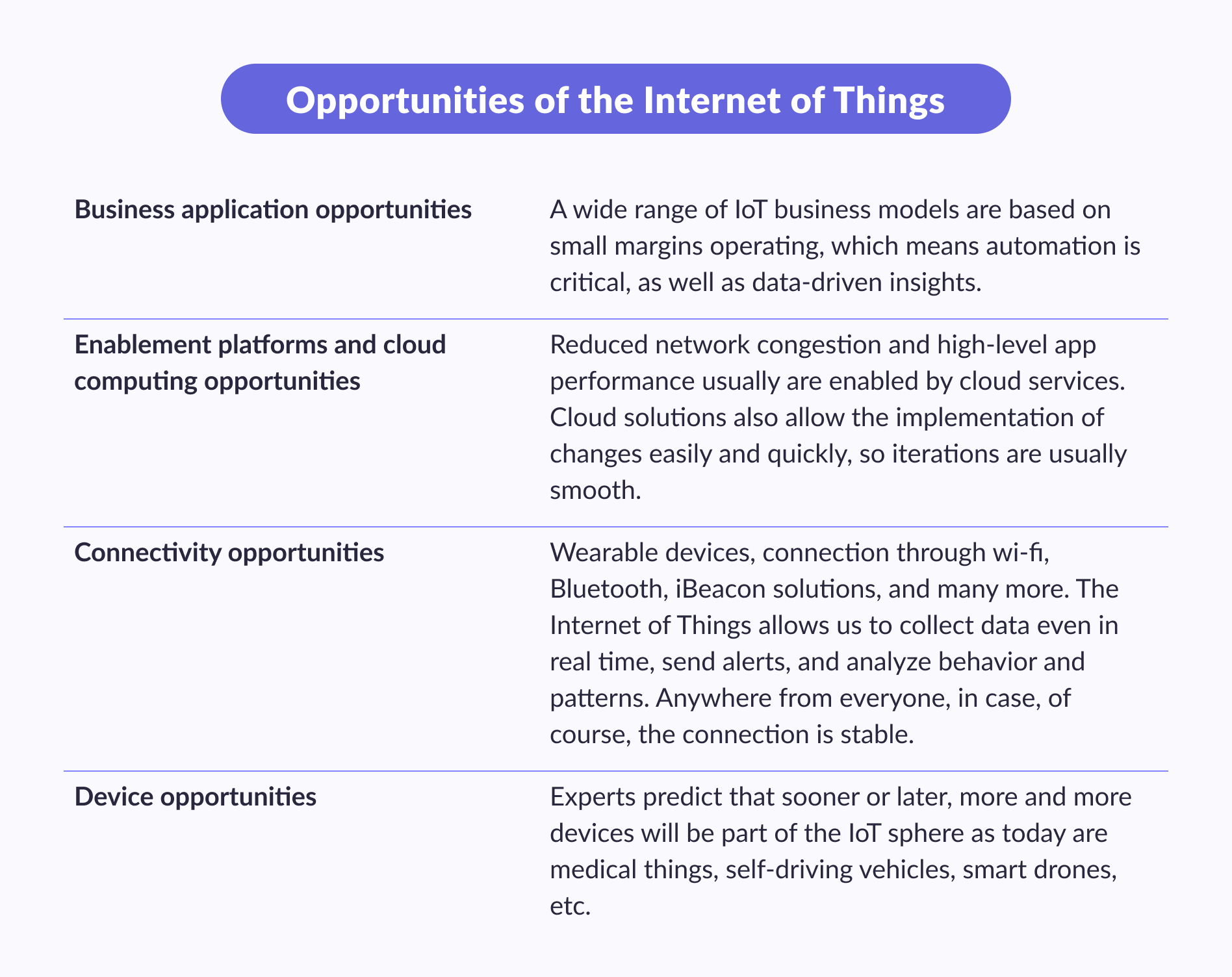
Challenges of the Internet of Things:

How does IoT work?
It is only possible to understand the basics of IoT by realizing how IoT works.
When we talk about IoT systems, we define four basic components:
- Sensors
- Connectivity
- Data Processing
- User Interface
Embedded sensors in devices emit data through a common network to the main storage or application for data processing (collection, storing, transmitting, analyzing, etc.). The user interface obviously is needed to provide interaction between the end customer and the IoT application.
By the way
Are you ready to give custom IoT a try? Well then, Geniusee is ready to become your reliable IoT development partner!
Advantages of IoT
We may determine IoT basics as a combination of two main features: connectivity and automation. What do we mean by it?
Automation
IoT technology is determined to automate processes, especially communication between computing devices connected to the Internet through a wireless network.
Connectivity
As IoT applications allow us to collect and exchange data from different sources (devices) anywhere in the world through IoT networks, it scales the accessibility drastically.
So, as we may see, the main benefits of IoT are pledged into its core. Yet, there are much more of them.
Efficiency
We’ve already mentioned that IoT allows automating a lot of things, such as collecting data, analyzing it, transferring, and exchanging, so manual tasks for your employees are minimized, and they can apply some creativity to your company’s internal systems, saving you time and money.
- Assets and resources efficiency
- Labor productivity
- Operation management improvement
- Raise cost efficiency
Safety
It is both about companies and individuals. The protection and welfare of employees are important, not only from the perspective of law requirements but also from the point of view of the socially responsible brand. As many IoT solutions are designed for MedTech, for example, connected medical devices or heart rate monitors, hospitals and insurance companies may benefit significantly from retrieved data. Andwe will, knowing that our close-knit community is safe.
- Health monitoring
- Regulatory compliance
- Access by biometric data
Customer satisfaction
You could autonomously retrieve data, gigabytes, and terabytes of it, studying and analyzing your customer to assure the best service, needs fulfillment, and increase in retention rate. Isn’t it a dream?
Not so easy, of course, but IoT services absolutely allow understanding the specific needs and behavior of end-user until, of course, you keep up with data privacy, compliance, and regulatory requirements.
- Better customer experience
- New competitive advantages
- Data-based customer-centric solutions
Business potential
As IoT systems automate some parts of work, guarantee safety and protection to your employees, save your resources, and help increase customer satisfaction rate, we may state without hesitations that it boosts your business immensely.
- Improve business models
- Assure assets and energy efficiency
- Find new business opportunities
- Outstand competitors
- Expand your market presence
Quick health check
Is your business analysis good enough? Are you sure? Check out how your company is doing
Social responsibility
Not necessarily, but IoT solutions could easily be used for increasing life level. You may say that smart cities, electronic toll collection systems, or smart public transport are solutions for governmental organizations only. Truth, yet, what about industrial or individual tools for ameliorating environmental impact like smart heating to assure energy efficiency? Plus, it influences your brand positively.
- Improve your input for society
- Influence the environment considerably
- Create a trustworthy image
- Enhance your brand with CSR
We should mention the disadvantages as well. IoT for beginners could be s challenging task, so we may mention it too. Indeed, so is any other technology, so we rather concentrate on other aspects:
- Data storage
- Security and privacy concerns
- Data leaks
- Lack of standardization
- Complexity
- Connection dependence
- Unemployment rate raise
- Reduction of interpersonal communication
As we may see, most ‘detrimental’ basics of the Internet of Things correlate with those in other ‘modern fields’. That is why we feel it acceptable to call them ‘bearable’.
IoT across industries
Could you ever imagine that drones will be used not just by state forces or videomakers but also by farmers to collect agricultural data? A trendy bracelet that turns out to be a healthcare device collecting patient data? Here we listed the most well-known examples of IoT in different industries.
Disclaimer: This is definitely NOT a full list of all possible IoT applications, connected devices, and industries using IoT solutions. To our belief, any domain may benefit from IoT applications and services, and sooner or later, electronic appliances will become a part of our everyday lives.
Smart Healthcare
- Remote patient monitoring
- Modernized patient assistance
- Drug management
- Smart beds
- Remote surgery
Utilities and Energy
- Resources monitoring and controls
- Residential demand response
- Storage monitoring
- Poles monitoring
- Field operations
- Smart meters
- Smart thermostats
Gas and Oil
- Acoustic operations monitoring
- Digital twins for assets and projects
- Predictive and preventive maintenance
- Seismic exploration sensors
- Sensor-based tank monitoring
- Asset tracking and management
Manufacturing
- Remote production control
- Predictive maintenance
- Connected operations
- Asset tracking
- Compliance monitoring
Real Estate
- Predictive maintenance
- Smart security
- Digital signage
- Environment monitoring
- Waste management
- Smart homes
Inventory Management Logistics
- Fleet management
- Smart inventory management
- Predictive maintenance
- Supply chain management
Government and Public Sector
- Road traffic management
- Infrastructure monitoring control
- Digital signage
- Public transportation
- Disaster prevention
- Waste management
- Parking management
Military and Defense
- Smart drones
- Proactive health surveillance
- Battlefield monitoring systems
- Fleet management
- Inventory tracking
- Smart target recognition
- Autonomous reconnaissance
- AR training systems
Automotive
- Fleet management and monitoring
- Connected vehicles
- Remote vehicle diagnostics
- Vehicle tracking
Agriculture
- Agro-drones for monitoring
- Crop management
- Greenhouse automation
- Livestock tracking and monitoring
- Precision farming
- Observing climate conditions
Retail
- Retail supply chain
- Smart shelves
- Delivery operations
- Warehouse automation
- Connected POS machines
IoT hardware
What do we call ‘IoT hardware’?
Devices and physical components of IoT systems that respond and capture data, following programmed instructions. Let’s analyze them by category:
1. Chips
Electronic appliances implanted in machines, smart objects, or things to transmit collected data through the wireless network
- Microcontrollers
- Chips
- Integrated circuits
- Systems for radio frequency identification
- Others
2. Sensors
The base component of IoT architecture that measures and senses programmed information, providing usable output.
- Power management modules
- Sensing modules
- Energy modules
3. Actuators
Energy into motion if we’re taking it simply. Actuators take an electrical signal and combine it with an energy source to provide motion to the data assembling system.
- Hydraulic actuators
- Pneumatic actuators
- Electrical actuators
- Thermal actuators
- Magnetic actuators
- Relay actuators
4. Standard devices
Devices we are all used to using.
- Tablets
- Watches
- Smartphones
- Switches
- Routers
- Others


Thank you for Subscription!
IoT software
Here we will be talking about programs that enable IoT devices to do their job, for example, operating systems, applications, firmware, middleware, and others.
1. Data processing
- Collection
- Retrieval
- Transmission
- Storage
2. Device integration
- Limitations management
- Protocols control
- Applications communication
3. Real-time analytics
- Automation of manual tasks
- Interactive analytical dashboards
- AI and ML-based models
- Big data analytics
4. Application and process extension
- Processes provision
- Procedures enhancement
- Accentuation of built-in scenarios
Risks of IoT
Most IoT risks refer to security and cyber threats.
1. Lack of physical hardening
Most IoT devices remotely connect to an intermediary network location, so in case hackers gain access to the physical devices or their part as a memory card, it may become a danger.
2. Insecure data storage and transfer
Lack of encryption and access controls in cross-communication increases potential breaches and compromising risks.
3. Lack of visibility and device management
Improper management of monitoring and tracking systems may lead to a lack of visibility of potential risks or already-in-a-system malicious bugs.
4. Botnets
These internet-connected devices are designed for compromising networks, stealing data, or sending spam. Their malware allows hackers to gain access to IoT devices and infiltrate the network.
5. Weak passcodes
This risk is common not only for IoT applications and platforms but for any other service, and the problem is usually easily solved by the usage of password creation and saving apps and proper password hygiene.
6. Insecure ecosystem interfaces
API and third-party services used for communication between devices may lead to breaches and leaks by attackers.
7. AI-based attacks
AI attacks have been with us for almost 15 years, yet the modern threats they present have risen significantly. As cybersecurity specialists invent new ways to protect systems, hackers try to break them again and again.
How to fight those attacks and prevent risks?
- Information hygiene
- Cybersecurity services
- Security compliance
- Constant tracking and monitoring
Easy and simple. We believe that you can do that!

If we mentioned security
How to implement Zero Trust security model: full guide
Have you ever wonder how to make a solid basis for security system in your organization? We have some tips
Let's seeMajor examples
Smart Home
- Smart heating
- Smart gardening
- Video doorbells
- Smart door locks
- Personal assistants
Smart city
- Smart parking lots
- Smart waste management
- Smart traffic control systems
- Smart street lighting
- Smart utility meters
Smart factory
- Predictive maintenance
- Fleet management
- Remote production control
- Asset and inventory tracking
- Compliance monitoring
IoT architecture and technologies
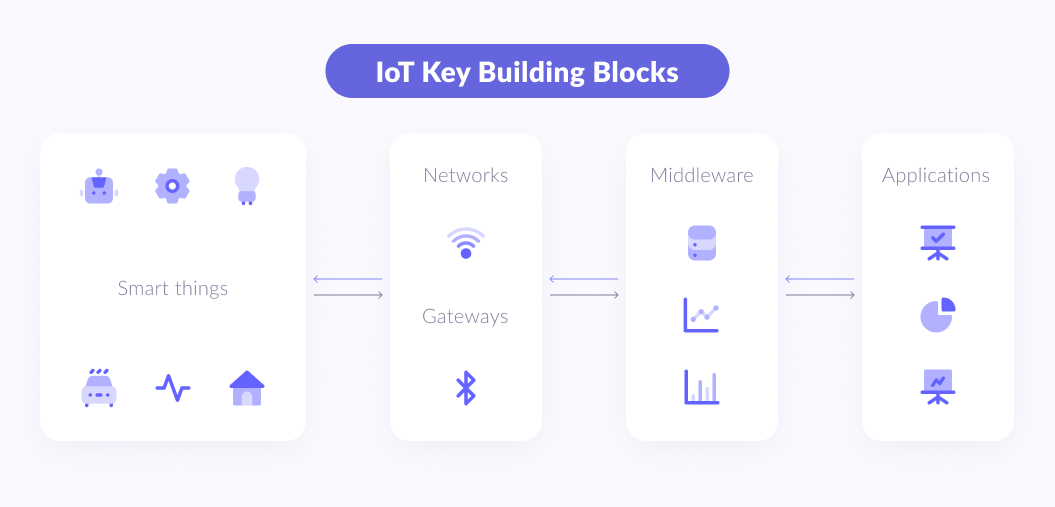
Understanding IoT basics is inseparable from technical details. Let’s discuss the architecture IoT solutions are based on and the technologies used to make them work.
We may divide the Internet of Things solution architecture into three levels:
Device level
IoT sensors, radio frequency identification (RFD), GPS tags, and other hardware solutions that provide data collection and transmit it to the next level.
IoT gateway
Computer science nowadays brings data analysis to the next level, making IoT devices’ existence possible. Data collected by hardware is stored in data lakes and control apps, then sent to data warehouses, where they are structured for further data analytics. Algorithms, enlightened by unusual IoT data patterns and trends and with the help of machine learning, scan all possible ways of problem-solving by the AI and ML models.
IoT platform
The results of IoT data analytics are sent and processed on this level, authorizing the end customers to communicate with IoT devices or solutions via user apps with real-time IoT-generated reports and data.
When we talk about IoT technologies, we simply mean the tech stack that is used to create IoT solutions; it may sound like a child's game. Yet it’s not just picking the right set of technologies and putting them together. The thing here is to lead the process securely, accurately, and cost-effectively.
The main recent tech trends in IoT:
- Cloud-based solutions
- Artificial intelligence
- Code containers
- IoT-based streaming analytics
- Machine learning
- Real-time databases
- Low-code and no-code solutions
- Function-as-a-Service
- Deep learning
- Digital twins
- 2-way BMI (Brain Machine Interface)
- Data ecosystems
- AI&ML based analytics
Importance of related services in IoT
IoT development is only possible with synergy with other services and technologies. Some of them are even inseparable from each other. Let’s see what services are the most critical for the Internet of Things.
Blockchain:
Blockchain allows us to transfer data from IoT devices without a central control system and management.
ML and MLOPs:
Based on past user behavior, the ML model seeks patterns, analyzes data, and learns to predict future digital interactions.
AI:
Collect data, transmit data, store data, run through data analytics applications, and much more. AI ensures intelligent decision-making based on experience and future predictions.
Big Data:
Big data simplify the analysis and storage of processed data. Speed, volume, and variety as core stones of Big Data empower your insights.
Geniusee IoT for the best business decisions
When choosing an Internet of Things software development company, check its portfolio first. IoT application development services are hard to build without solid practice and expertise. Geniusee development teams tailored over 100 projects, and more than 15% percent of those in our portfolio are completely centered on the Internet of Things product development. Both industrial IoT and consumer IoT, yet most of our projects contain side custom IoT solutions that are a supportive part of the main solution.
Look through our cases to check our IoT expertise!





















