Should you keep your computing on-site or opt for a cloud-based solution? Many business owners face this dilemma. The question of cloud vs. on-premise solutions has led providers such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft to shift their focus to cloud delivery models. The COVID-19 pandemic also boosted the transition to the cloud due to the increase in remote work.
There are differences between the two models in security, accessibility, and price. If you are unsure which option is best for your business, read on to learn more about each service.
In This Article:
Cloud vs On-Premise Advantages and Disadvantages
Choosing between cloud and on-premise solutions can be complex. To make an informed decision, consider the pros and cons of both models. You can also review different use cases to see how businesses use on-premise and cloud computing.
Cloud Computing Basics
In simple terms, cloud computing means on-demand access to computing resources and data storage over the internet. Users get access to remote cloud servers in exchange for a monthly or usage-based fee. This means you don’t depend on a local in-house server to get access to all the apps, tools, and resources you need to operate your business.
The biggest providers of cloud-based services include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Azure, and Oracle. These providers serve businesses in a variety of industries by providing:
- Computing power to process your data
- Databases in the cloud
- Cloud storage (worldwide data hosting).
Benefits of Cloud Computing
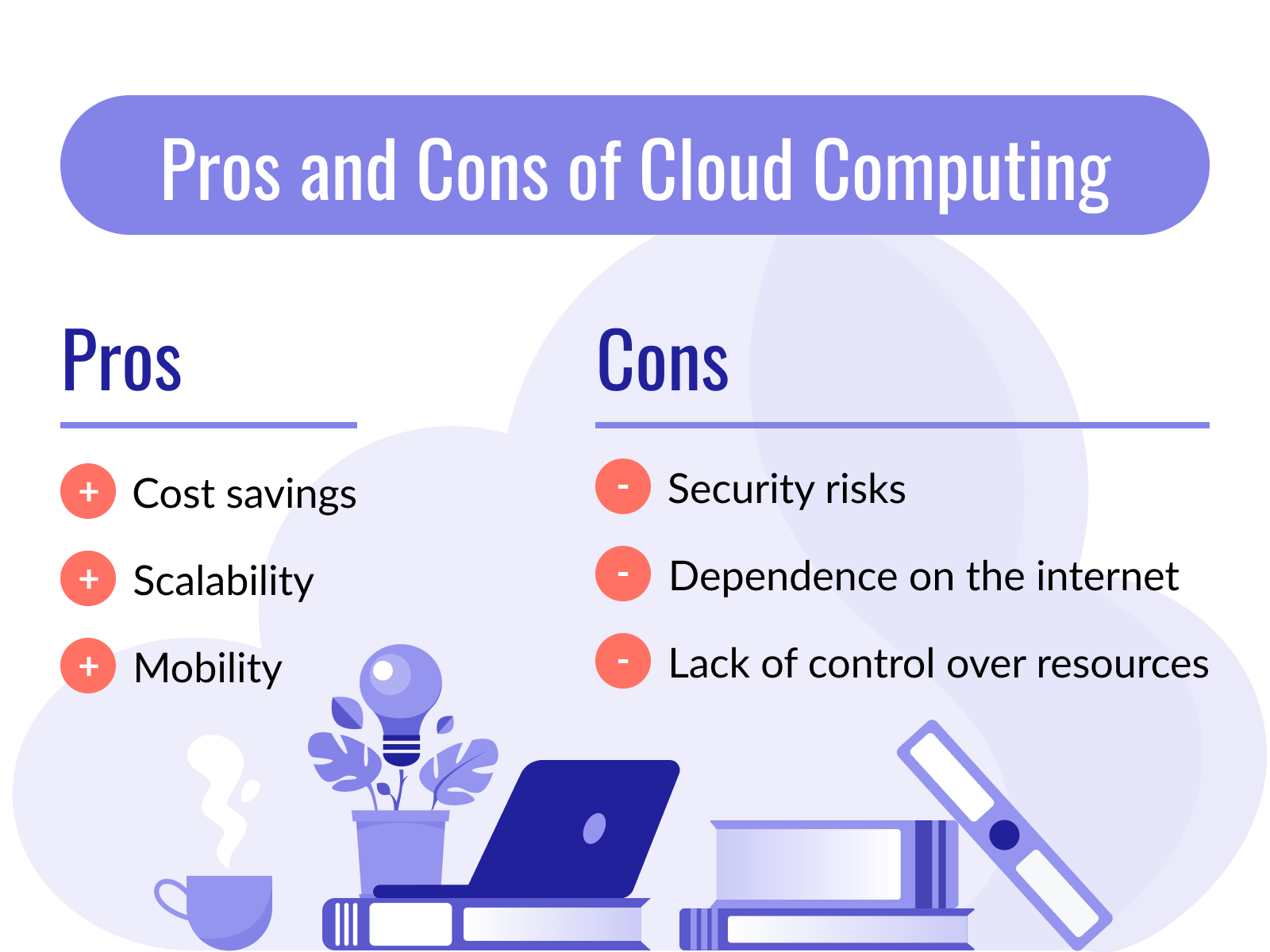
The cloud computing model offers several advantages, including:
- Cost savings. You don’t need to worry about the on-premise costs associated with ongoing maintenance and management of the servers. Business owners and managers can cut the costs of on-premise data centers. This makes cloud computing cheaper than its alternative.
- Scalability. You can manage exactly how many resources you need at any given time. The cloud-based solution allows you to scale up or down depending on your business processes and current needs.
- Mobility. You can access your data at any time from anywhere in the world. This allows you more time flexibility and doesn’t restrict access when you most need it.
More on the topic
What Is Cloud Infrastructure And Its Benefits For Early Stage Startups
Discover how cloud-based approaches level the playing field for businesses, offering cost-efficient and scalable IT solutions.
Read moreDrawbacks of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing services also come with certain disadvantages, such as:
- Security risks. The cloud service providers are responsible for the security of the cloud computing environment. This covers the servers, hardware, and IT infrastructure. However, it’s up to the clients to manage in-cloud security, meaning you need to control who has access to your resources and how they’re used. This is the shared responsibility model most cloud providers adhere to.
- Dependence on the internet. Obviously, you need a reliable internet connection to access your apps and data. So, during an internet service disruption, your hands will be tied.
- Lack of control over resources. The cloud service provider is in charge of managing the infrastructure of the cloud. So, your IT team will not have full control of all the resources if you are using public cloud services.
Cloud Computing Use Case — Digital Banking App
Using cloud systems for building and hosting apps is represented through interesting use cases. One of them is Zytara: Digital Banking App for Generation Z. This digital banking app is based on blockchain technology and hosting it on the cloud allows for scalability and security. The development team utilized an AWS stack that includes CloudFront, S3, Lambda, and ECS. The result is a gamified version of banking to educate Generation Z about finances while maintaining their privacy.
On-Premise Computing
As opposed to a cloud environment, on-premise systems include an in-house infrastructure. Also known as "on-prem" or "on-premises," this model means the local IT team manages physical hardware, hosting, and on-premises software solutions. It’s up to the business itself to secure the premises and equipment necessary to run its operations.
Benefits of On-Premise Computing
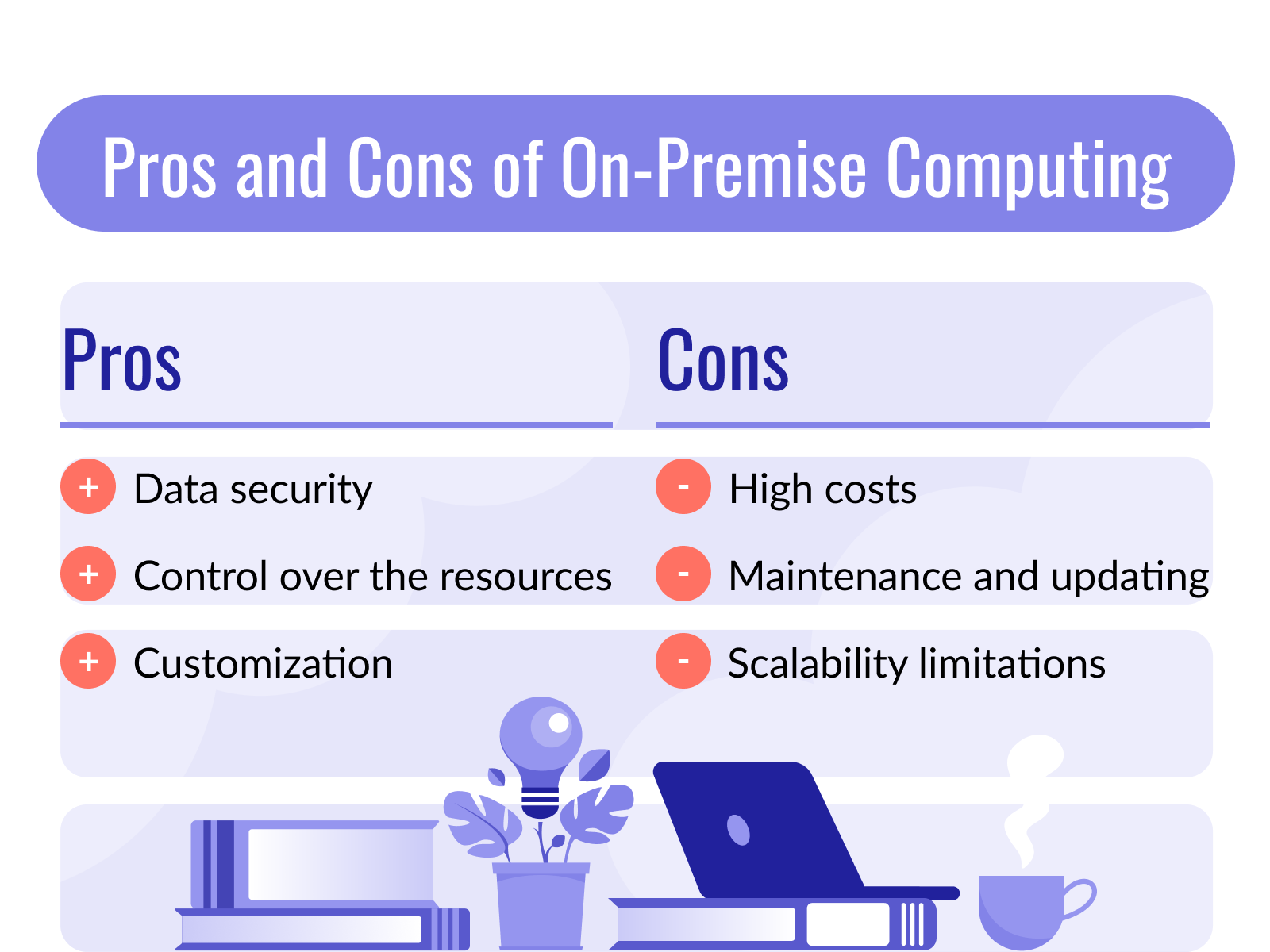
The key benefits of on-premise computing include:
- Data security. The in-house teams are completely responsible for data security. This removes intermediaries, external factors, and vulnerabilities. Any issues and risks are addressed by the company’s IT team.
- Control over the resources. As the server hardware is hosted in-house, a business can fully own its resources. This includes a higher degree of control over all the data and its use.
- Customization. As the business is managing its own infrastructure, there’s a higher degree of independence. Making adjustments and customizations as needed can be vital to ensure higher security and cost efficiency.


Thank you for Subscription!
Drawbacks of On-Premise Computing
Handling all your computing needs in-house can have its disadvantages, such as:
- High costs. Besides the initial capital investment into hardware and hosting, a suitable on-premise infrastructure comes with many expenses. The business will need to invest in maintenance, updates, periodic subscriptions, and a full-time IT team. Reliable on-premise infrastructure requires considerable investments: regular updating and maintenance costs, recurring subscription costs, plus the expense of an in-house IT team.
- Maintenance and updating. You may have invested substantial money into your on-premise computing, but your work is never over in this area. Equipment and technology are everchanging, and regular updates are a must.
- Scalability limitations. Unlike cloud-based services, upscaling and downscaling on-premise resources is not easy. It will take considerable time and additional investment.
On-Premise Computing Use Case — Microsoft Office
One of the most used on-premise software use cases is Microsoft Office. The business obtains a license and hosts the apps on its physical servers, and the users can access them in-house. This is a more secure option for companies that operate with sensitive or personal data.
Hybrid Infrastructure: Cloud and On-Premise
The hybrid infrastructure provides the best of both worlds—cloud and on-premise computing. The business, in this case, has its own infrastructure in-house and integrates a public or private cloud into its operations. Most companies do this to get complete control of their data centers and virtual machines, with added scalability.
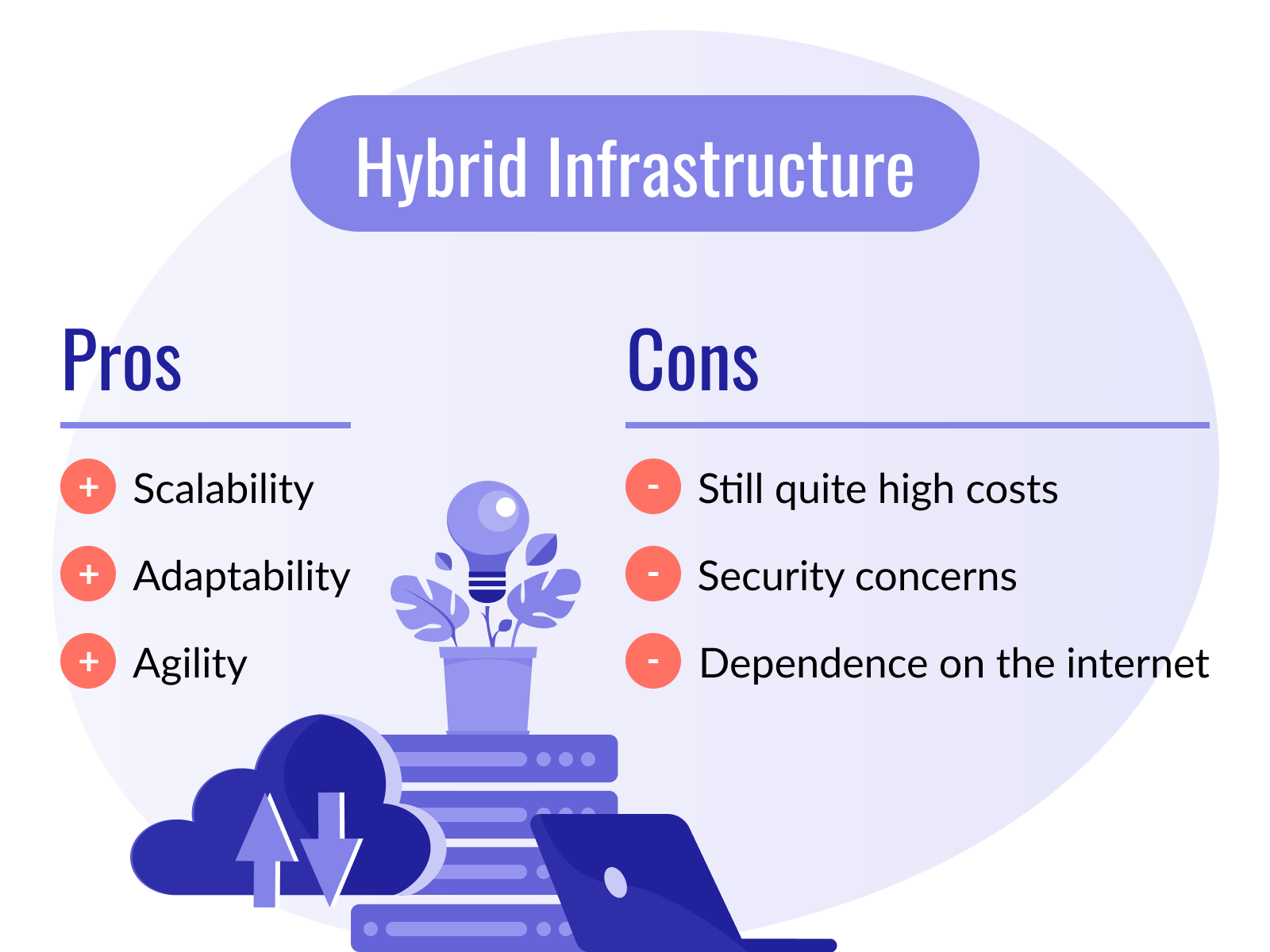
Hybrid cloud solutions come with several advantages, including:
- Scalability. The company can scale its computing up or down at any time according to changing needs.
- Adaptability. Companies can customize their systems for additional efficiency and security.
- Agility. Having greater control over the resources makes it easier for a business to react and respond to any issues that may arise.
Thanks to the cloud-based portion of computing, all its other benefits come to light. However, the hybrid model also has its disadvantages:
- Cost. In addition to having an on-premise IT team and resources, business owners and managers need to consider their cloud options. A public cloud is more affordable, while hybrid and private cloud solutions come at a higher price for their added security.
- Security. While a hybrid solution is more secure than a cloud-based solution, the company still has to rely on the third-party service provider and entrust them with sensitive data.
- Dependence on the internet. While a portion of the resources is entirely in-house and accessible to the business, access to databases and some services can be limited if the internet goes down.
Hybrid Infrastructure Use Case — My Tutor
The hybrid cloud infrastructure was put to use when developing the e-learning platform My Tutor. The infrastructure combines the client’s in-house data centers with Amazon services to ensure scalability. The result: a serverless microservice-based platform that reshapes school education in the US and the United Kingdom.
Need some advice?
Optimize your operations with our secure, scalable, and agile DevOps Services
Wrap Up
Choosing between cloud vs. on-premise computing will depend on your business needs and budget. Either option can work for providing the necessary infrastructure. However, for security and compliance, you should carefully consider the pros and cons of both models.
If you’re considering cloud solutions, one thing is certain. It’s better to opt for ready-made, reliable options such as Amazon Web Services than to try to build an infrastructure from scratch.





















