More than half of banking transactions in America are carried out via the Internet. At the same time, along with the growth of online transactions, the activity of fraudsters has also increased. According to experts in FinTech software development services, global financial losses due to cybercrime amounted to more than 6 trillion dollars in 2022. Statistics show that almost 2 million cyber crimes were registered worldwide in 2021, which is 16% more than the same period in 2020. At the same time, 500,000 of them are classified as serious and especially serious.
Online payments' security becomes even more important due to this. So let's discuss how to avoid online payment security concerns and protect yourself and your customers.
In this article:
What is online payment?
Despite the fact that the forms of electronic payments can be different (payment using a bank card, Internet banking system, payment terminal, SMS, etc.), from the point of view of US law, all this is the same operation: money transfer funds. Money transfer services are provided by an operator — a bank, an owner of payment terminals, etc. The operator, in turn, uses the services of one of the online payment systems — Visa, MasterCard, PayPal, etc.
The principle of operation of electronic payment systems is the same. In one way or another, the payer deposits funds into his account. As a result, a balance is formed on his account, within which the payment can be made. Then, using the operator-provided interface, the payer specifies how much should be transferred and who should receive it.
As a result, a payment order is formed, with the help of which the operator instructs the payment processor to make a non-cash money transfer. The main problem of electronic payments: how to make sure that the payment order was made by the payer and not by someone pretending to be him?
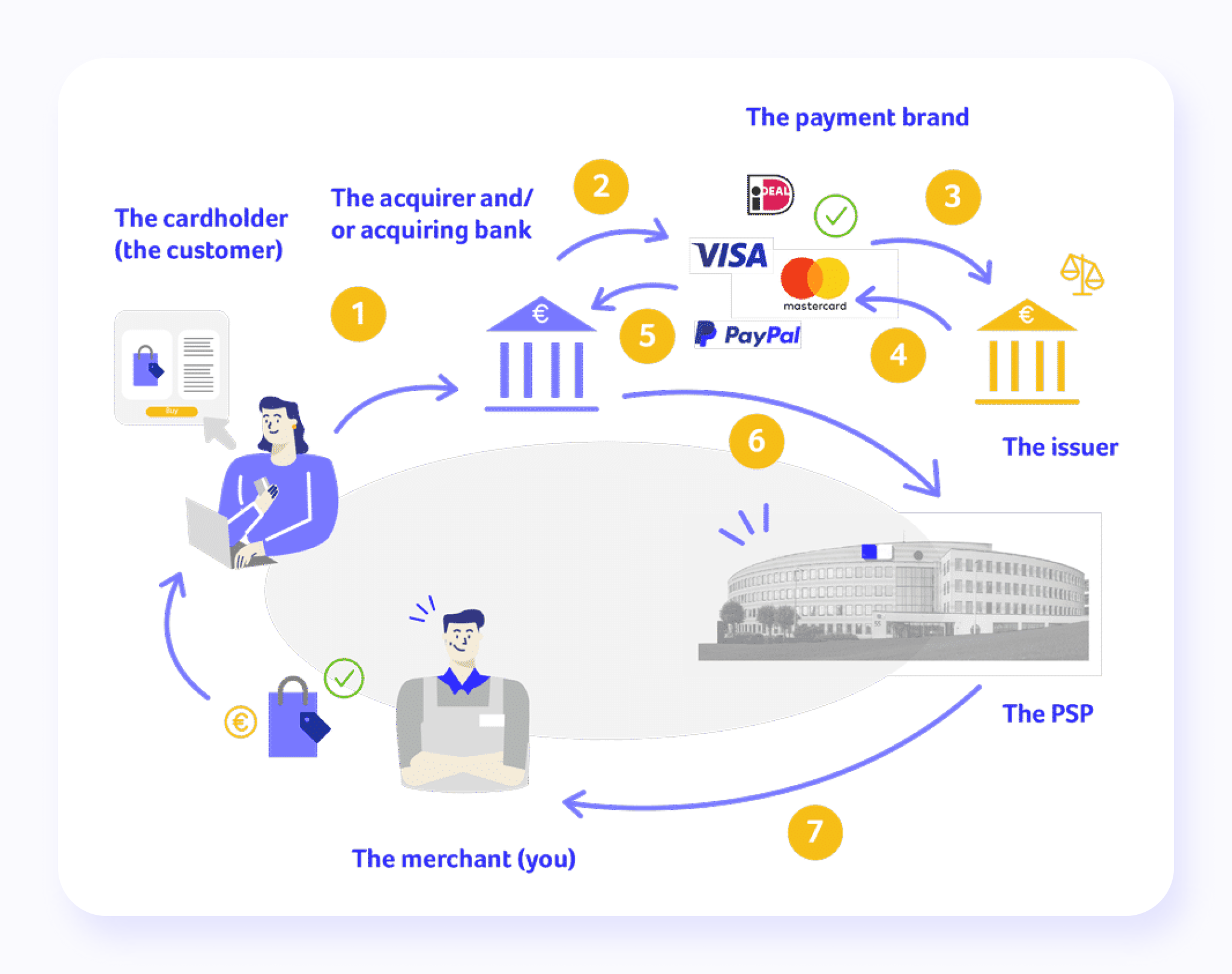
Different forms of digital payments have their nuances. When using a bank card, the payer transfers funds from his bank account. The card is the “key” to gaining access to the bank account and can be used for payment in two ways: using a special terminal (at an ATM or cash desk of a store) and using a website. When paying through the terminal, the identity of the payer is confirmed by themselves, and the card (more precisely, the financial information recorded on its magnetic stripe or chip) and the PIN code, which no one knows except the payer.
When paying through the website, payment confirmation is the information imprinted on the card (card number, holder name, expiration date, and CVC/CVV confirmation code), which the payer must enter in the appropriate fields of the web form. In this case, the CVC/CVV code is a password that no one but the payer should know.
In remote banking systems (RBS), different forms of payments are available to the client:
- one-time payments;
- template payments (the client fills out the template form once, indicating the details of the recipient, in the future, it is necessary to indicate only the amount of the payment);
- automatic payments (template payments that are automatically made with a certain frequency — for example, monthly).
In addition to payments, the RBS system provides the client with other banking operations, depending on the bank and the set of services for which the agreement between the client and the bank provides.
An alternative to paying with a bank card is payment using the Internet banking system (in banking terminology — remote banking systems, RBS). As a rule, this is a website that provides users with direct access to their bank account and allows them to find various banking details and perform different operations (including non-cash payments).
To access the account, the user must enter a name and password. Unlike mobile payments using a bank card, the RBS system can use several levels of identity theft protection, for example, confirmation of transactions using one-time strong passwords sent to the client via SMS messages or the use of an electronic signature.
Payment via the Internet using an electronic wallet is the movement of virtual money with a real equivalent. Electronic wallets, along with bank cards, are also used to pay for goods and services over the Internet. Users can replenish them in various ways: through a bank card, a special prepaid card, or a payment terminal.
The only and main difference between e-wallets and a bank account is that their operator, as a rule, is not a bank. This removes from the payer a number of restrictions imposed by banking legislation but also deprives him of several guarantees that the legislation provides to bank customers.
Another way to pay online is to use e-wallets. Funds deposited to the account are converted into virtual currency, which can be used for mobile payments between the operator's clients and money transfers to other payment systems. As a rule, in order to access transactions with their wallet on the operator's website, the payer must enter a name and password. Technically, working with an electronic wallet is no different from RBS, and the same additional degrees of identity theft protection can be used in the system.


Thank you for Subscription!
Top 9 digital payment security risks
Let's discuss online security issues in the e-payment system — at least the most common ones. Our experts gathered 9 major online payment security concerns so you can be ready to ensure digital payment security.
Security of personal data
Many companies do not comply with the rules for storing sensitive data of employees and customers, which is why they are leaked. The problem exists with small online stores and services that cannot provide the proper level of personal financial information security. Leaked databases of customers of large retailers, social networks, government employees, etc., are found on the Web almost every day. At the same time, companies suffer large reputational losses and legal liability in the event of personal data leakage.
In order to protect personal payment information in an organization, it is necessary to use data leakage control (DLP) systems and, of course, event monitoring and incident detection tools. Companies can choose an internal system or order outsourcing services from specialized providers.
Cyber attacks on online stores
Since the beginning of the pandemic, many online retailers have faced DDoS attacks and hacks. Cybercriminals have become more active due to the growing popularity of online shopping. To break into user accounts, attackers often use smart bots that can bypass traditional protection schemes. Often, hackers seek to obtain users' personal data in order to resell it on the black market.
To protect your company against DDOS attacks and assure processing payment security, you can use specialized services offered by large hosting companies. A good practice to prevent cyberattacks is to conduct regular digital payment security analysis. This helps eliminate vulnerabilities in critical systems and infrastructure in general.
3-D Secure payment confirmation page
One of the new trends is the social engineering method associated with 3-D Secure technology. 3-D Secure payment confirmation pages have always been considered the most effective security measure for bank card data. The 3-D Secure protocol implies two-factor user authentication when transacting via the Internet.
However, nothing is perfect, including secure payment methods. Scammers have learned to fake a payment verification page. First, the user visits the fake online store page and is taken to a fake payment confirmation page. On the resource of scammers, users enter card details, as well as a code from an SMS message to confirm the payment.
At the same time, the server of the attackers initiates an appeal to the real 3-D Secure server, so for the bank, the operation looks like a transfer of funds from the card to the card at the user's initiative. It can be difficult for the latter to recognize fake pages since they contain the logos of Visa and Mastercard digital payment systems, which do not raise doubts about the authenticity of the resource.
To protect yourself from scammers, it is essential to check the online store — its reputation and reviews of other buyers. Experts believe that in the future, 3DS 2.0 technology will be used to prevent such cybercrime, which involves authentication not only by SMS code but also by biometric data. This could become a revolution in online payment security.

More on the topic
How to choose an online payment system?
Have you ever wondered how to choose one payment system forever, not for a year or two? Check our article to find out some useful tips.
Tell me''Twins'' of banking sites
Another way by which criminals steal money from users' bank accounts is by using the "mirror" sites of banks. A fake site is difficult to distinguish from the original: it is similar in design and name. If a person goes to such a “mirror” online resource and enters a username and password, then scammers can get into their personal account on the real site. Among other things, they connect the mobile banking service to their number.
It is not recommended to go to the bank's website from third-party Internet resources to secure online payments, bank accounts, and all personal data you gave to the bank. At the same time, before entering the login and password on the online banking site, you should check the page address — it must match the one indicated on the bank card.
Requirements to pay a commission
In several cases, attackers send letters to victims on behalf of the regulator, stating that they allegedly have accounts with a large sum of money opened in foreign credit institutions, so a commission must be paid.
If a person has received fake emails about the receipt of a large amount of money from an unknown organization and is asked to pay a commission, tax, or insurance to receive it, we recommend that you do not respond to such messages and, in no case, transfer money.
Fake passports
In 2021, scammers began posting ads for selling real estate, cars, and medical masks on popular online platforms. Before concluding a ''deal'', they asked to confirm their solvency, which required transferring a small amount of money to friends or relatives through special payment systems and presenting a payment receipt. In this way, they lured out the personal data of the recipients of the transfers and made fake passports in their names, after which they visited bank branches and stole money from the accounts.
When purchasing via the Internet, it is worth checking the seller's reputation and also not making transfers even to familiar accounts if you have to use an unfamiliar payment system for this.
Phishing scams
There are many scenarios for phishing scams, from collecting sensitive data to sophisticated attacks on computer networks. All these scenarios boil down to one goal — criminals force the user to pay for a certain product or service, after which they simply disappear.
For example, scammers can create fake online stores that allegedly sell various products at very attractive prices. These can be either copies of well-known trading platforms or “original” sites, but in any case, the scheme of deception will be the same — receive payment and not send the goods. At the same time, your credit card details, along with any other information that you leave on the fake site, also fall into the clutches of attackers.
Links to such sites may be distributed, for example, through advertising mailings in instant messengers or by email. But you can also get caught on a phishing site in search results.
Malware
There's no way to safely use a computer that's infected with malicious software, especially when browsing websites or making digital payments. Some Trojans can steal passwords and other sensitive data, including bank card details. Malware can also lead users to sites that contain phishing scams, manipulate browser search results, or even replace real websites with fake ones.
For instance, a Trojan from public Wi-Fi might alter the system's “hosts” file, redirecting the user to a phishing site instead of a legitimate online store or bank. The browser's address bar would still show the correct domain, making it hard for the user to realize something's off.
Other security threats include malicious scripts embedded in web pages or browser extensions. These scripts execute actions planned by attackers, often redirecting users to dangerous sites. This makes it easy for cybercriminals to mislead users, especially those unfamiliar with online security.
It's crucial to recognize that any website can be vulnerable to attacks. Malicious actors can inject malicious code into a site's pages, setting up chains of redirects that steer users towards phishing scams or fake payment pages. With the range of malware out there, there are countless ways these scenarios can unfold.
Data breaches
Typically, data breaches from the databases of financial institutions or other companies are not enough to steal money without your knowledge. However, personal data in the public domain attracts scammers. Using social engineering, they try to get the missing information that allows them to get to your savings. Fraudsters rely on the card and account owners to provide the data they need.
Fraudsters call and introduce themselves as bank security officers and send messages about blocking the card.
They can also write an email that “you are entitled to compensation; you just need to pay a small commission to transfer it to your account.”
Sometimes, they even knock on the door and offer to “get tested for coronavirus” because “the neighbors tested positive.”
The methods of suspicious activity are very different, but the task is always the same: scammers play on emotions so that people voluntarily transfer their savings to them or provide secret data that will allow them to write off money from bank cards. In the event of a face-to-face meeting, they can simply ransack an apartment.
You can’t completely prevent data breaches, but you can reduce the risk of losing money to a minimum. It is important to always follow financial security measures (especially beware of connecting to public Wi-Fi and remember to install regular software updates).
Safest online payment methods

Paypal
One of the most popular electronic payment systems in Europe and the USA. Its peculiarity is that it requires binding an international bank card, with which you can replenish your wallet.
Paypal is a kind of passport for making international financial payments. And you should enter all the data very carefully. The slightest discrepancy can cause questions from the security service and the suspension of your account.
Visa and MasterCard
The most popular and convenient for paying for purchases in foreign and domestic online stores are, of course, Visa and MasterCard plastic cards.
It is advisable to have a separate virtual card for online purchases, Visa Virtual or MasterCard Virtual. It is linked to your main payment card and additional Internet payment protection systems. You simply transfer from the main card to the virtual one a certain amount you plan to spend, and from it, you make payments in online stores worldwide.
Digital wallets
Many large online stores and services accept payments from electronic wallets. You can create an e-wallet specifically for secure online payments on the Internet and put the required amount on it right before transferring it to the seller. It is much safer than paying with a payroll or credit card with a large limit.
You do not have to indicate your card number, expiration date, or secret code. This means that even if you get to a phishing site, scammers will not be able to access your bank account.
You can be offered to link a bank card to an electronic wallet. At the same time, secrecy will not decrease: card details are not used when paying; they will remain a secret for the seller.
Your way through Fintech
Everything you need to know about FinTech collected in one guide presented by top Geniusee experts
Crypto wallets
In virtual wallets, unlike their classical counterparts, money is not actually stored. The crypto wallet contains a private key for controlling virtual funds and tokens for making transactions. At the same time, the security of user funds is more dependent on the reliability of the underlying code. That is why developers combine security with ease of use, privacy, and other popular features when creating such wallets.
How to protect yourself from scammers
There are a number of signs by which unreliable credit and debit cards and electronic wallets can be calculated. These include many payees and payers — more than 10 per day and more than 50 per month. Banks should pay attention to the unusually high level of transactions for crediting or debiting non-cash funds by individuals, in particular, more than 30 fraudulent transactions per day. Finally, banks should be wary of transaction volumes over $5,000 per day and over $50,000 per month.

Another criterion for a suspicious account is a low balance at the end of the trading day, which does not exceed 10% of the average daily volume of transactions. In addition to passport data, users need to protect access to a mobile device since one-time transaction confirmation codes are sent to it. Two-factor authentication can be enabled in the security section or the user profile settings on many platforms.
It is worth disabling all payment options if they are not necessary. For example, if you do not use payment applications for social networks or cell phones, disable the ability to use them.
The development of schemes used by fraudsters, in turn, helps to make security patches to the systems of financial institutions. Large banks use advanced anti-fraud platforms using artificial intelligence-based algorithms.
Now, we'd love to share with you four best practices for online payment security.
1. Two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication is a method of identifying a user in a service (usually on the Internet) by requesting two different types of authentication data, which provides a two-layer, and therefore more effective account protection against unauthorized entry. In practice, it usually looks like this: the first frontier is a login and password, and the second is a special code that comes via SMS or email. This is one of the most popular ways to assure online payment security.
2. Tokenize customer card data
Tokenization is a type of encryption for secure storage of data. In online transactions, it is used to protect cardholder data. For example, when you want to pay in a selected online store or pay a utility bill, enter your credit card number, expiration date, and CVV in the space provided. At this point, you report information about the map to a third-party resource that can store it. Even worse, keeping sensitive information not well protected is bad for you and good for attackers.
However, tokenization technology increases the number of secure digital payments in the Internet environment. It protects user data during online financial transactions, whether it is payment by card or smartphone.

Important issue
How to implement Zero Trust security: practical steps
Zero Trust security model is one of the best ways to start with if you want to build a well-protected system.
Tell me more
3. Get an SSL certificate
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is one of the standard security solutions for establishing an encrypted connection between a web server and a client (web browser). SSL is used to secure online financial transactions and ensure that sensitive information (such as credit card information, user login credentials, and personal data) is encrypted and transmitted securely. To secure your resource with SSL, you must obtain an SSL certificate from a CA (certificate authority) and install it on your server. An SSL-secured website starts with HTTPS, not HTTP. That may seem uncomfortable in the beginning, yet is reasonable if you genuinely seek online payment security.
4. Use a personal verification system
Digital identity verification methods such as biometric verification, facial recognition, and digital ID verification can help companies, governments, and financial institutions verify a person's online identity.
A personal verification system can be used when the person and their identity document are not physically present. Digital identity verification can also be used to speed up identity verification, such as using electronic gates to scan passports at airports.
Digital identity verification is key to opening an account and attracting a client. Once the applicant's identity is verified, financial institutions may conduct background checks to ensure that the applicant is not a criminal attempting to commit a scam.
A developer is your best friend
A weak IT department is a real problem for any modern, especially online business. Is it worth talking about companies where the owner is also an accountant, marketer, and salesman, and in all these worries, he is not at all up to the development staff? But accepting payments is a financial and technological story in equal measure; the need for technical specialists appears already at the stage of preparation for connecting online payments.
We are talking about the requirements for the site, which are established by international payment systems, and without compliance with them, the road to the world of online payments is closed. For example, the site must implement the functionality of the basket, publish the procedure for payment, delivery, and return of goods, and provide a privacy policy and sensitive information about the seller.
Many businesses create websites on website builders or use templates for CMS and can handle the preparation on their own. But when it comes to integrating with a payment gateway, you need serious back-end development knowledge, and any mistake can hurt your wallet and online payment security.
You need to assess your technical resources when choosing a payment partner critically. If there are no full-time developers, it is better to abandon the idea of direct cooperation with banks.
The lack of technical support and the lengthy procedure for resolving emerging security issues of the electronic payment system — and questions will arise almost daily — will play against the company.





















