The meaning of the abbreviation IT has expanded siginificantly beyond its original focus on information flow management and digital data processing. Today, IT employees are also responsible for setting up and operating computers and office equipment in an enterprise or office.
In general, this setup is fair and logical. However, as the responsibilities of IT specialists grow, the workload on IT department employees increases, leading to significantly more time spent on tasks and often resulting in delays and downtime in work processes.
How to properly assemble the efficient IT strategy of your tech department to get the best business results and amaze your customers?
There are two logical ways out of this situation. The first is to expand the IT department, which will entail additional material costs. The second is to properly organize the scheme of work of an existing department. Of course, the second option looks the most attractive (for the head of the department and the head of the organization) — we will consider it in more detail.
Types of IT department structure

An organizational chart plays a vital role in defining the IT department's success within any company. There are various types of IT department structures, and each structure has its own benefits and drawbacks. Let's take a closer look at 4 main IT team structures.
#1. Functional structure
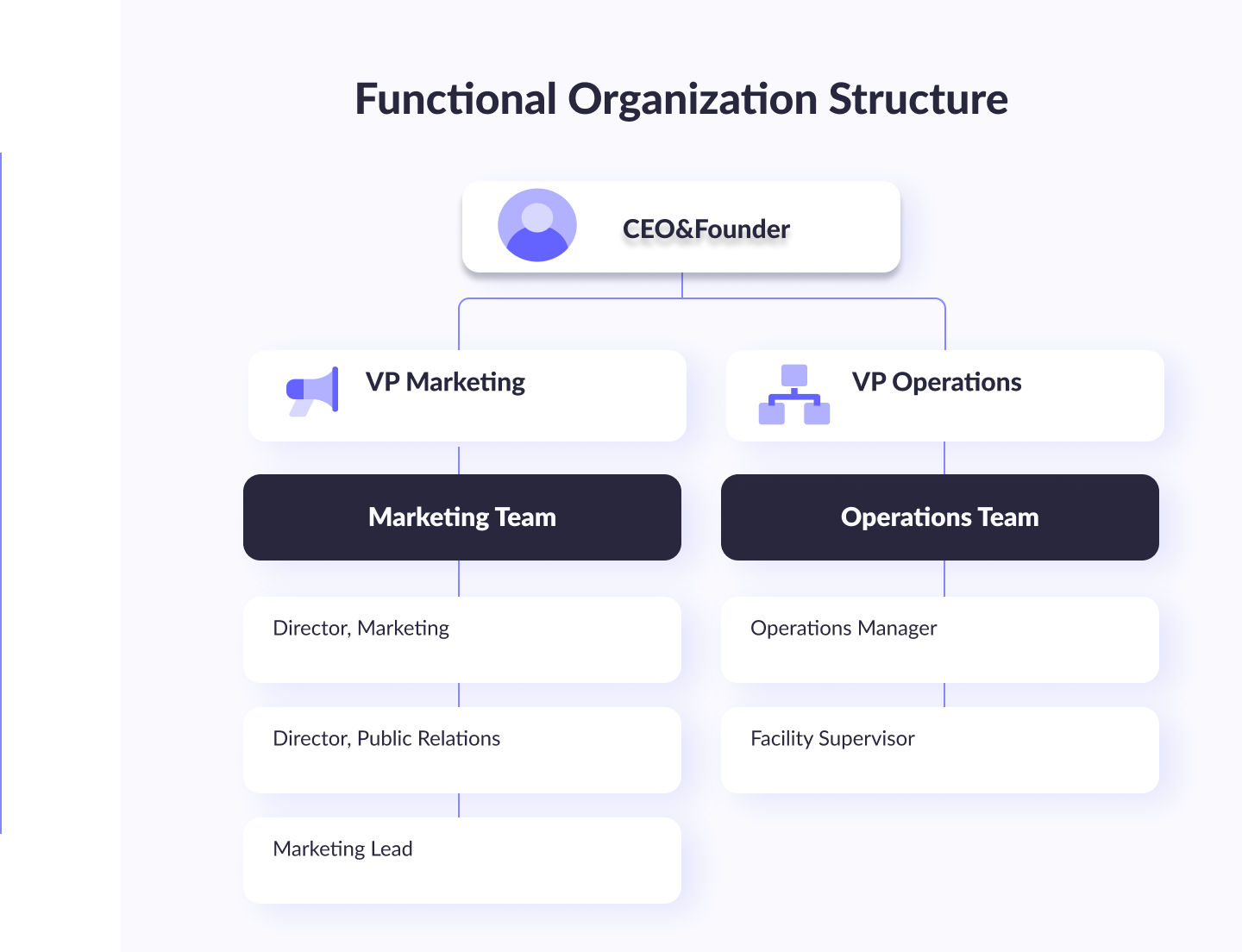
The functional IT organizational structure is a traditional hierarchical structure where the IT department with its own project manager leaders is divided into different functions such as networking, software development, infrastructure, and support. All functional teams are managed by a department head, who reports to the IT director or CTO. A functional model is suitable for large organizations where the IT department needs to handle a wide range of tasks.
#2. Divisional IT model
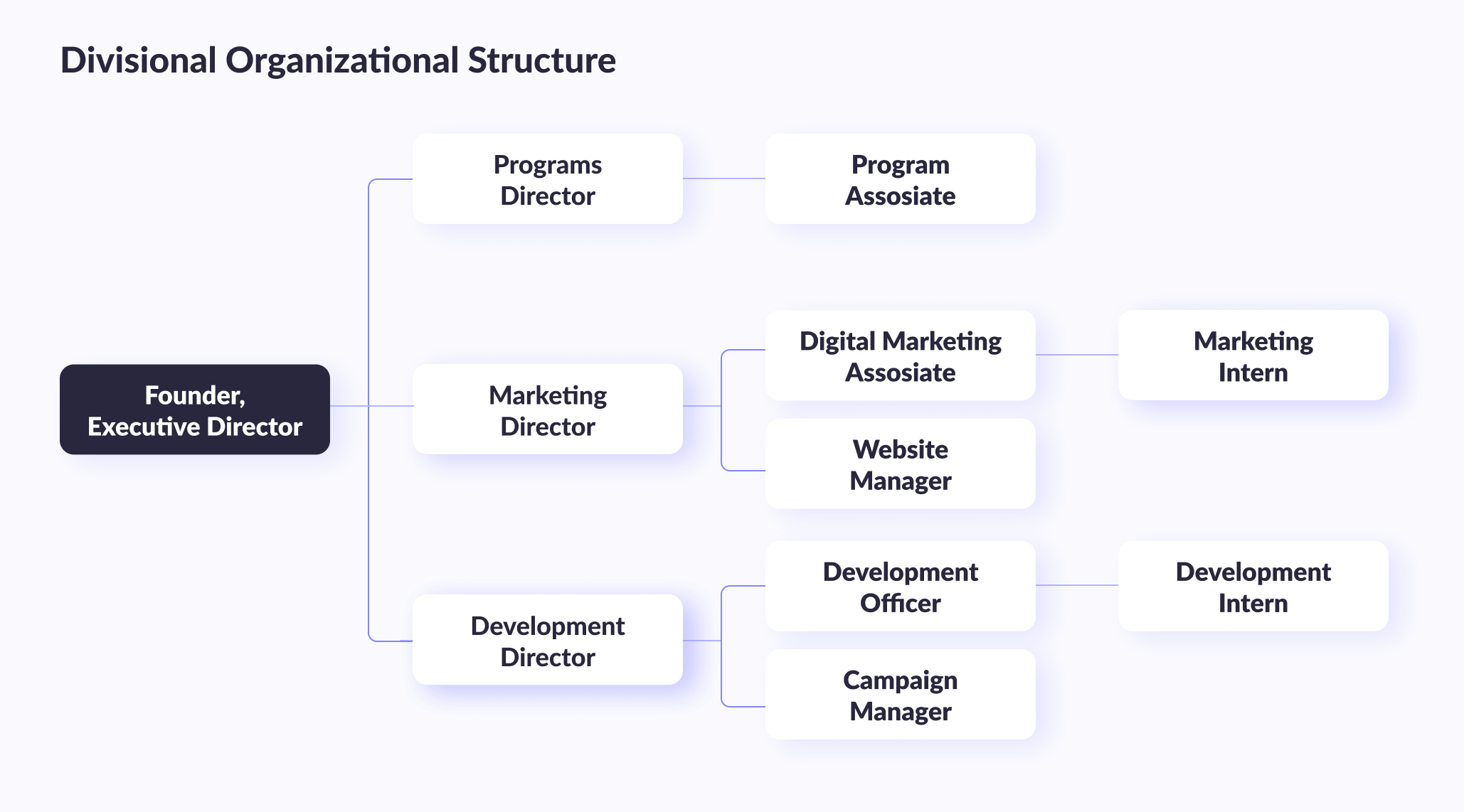
The divisional IT department organizational structure is used in organizations that have multiple business units or divisions. In this structure, the IT department is divided based on the business unit or division. Each division has its own IT department, which is responsible for the specific IT needs of that division. This management model allows for greater flexibility and customization to meet the needs of each business unit.
#3. Matrix IT structure
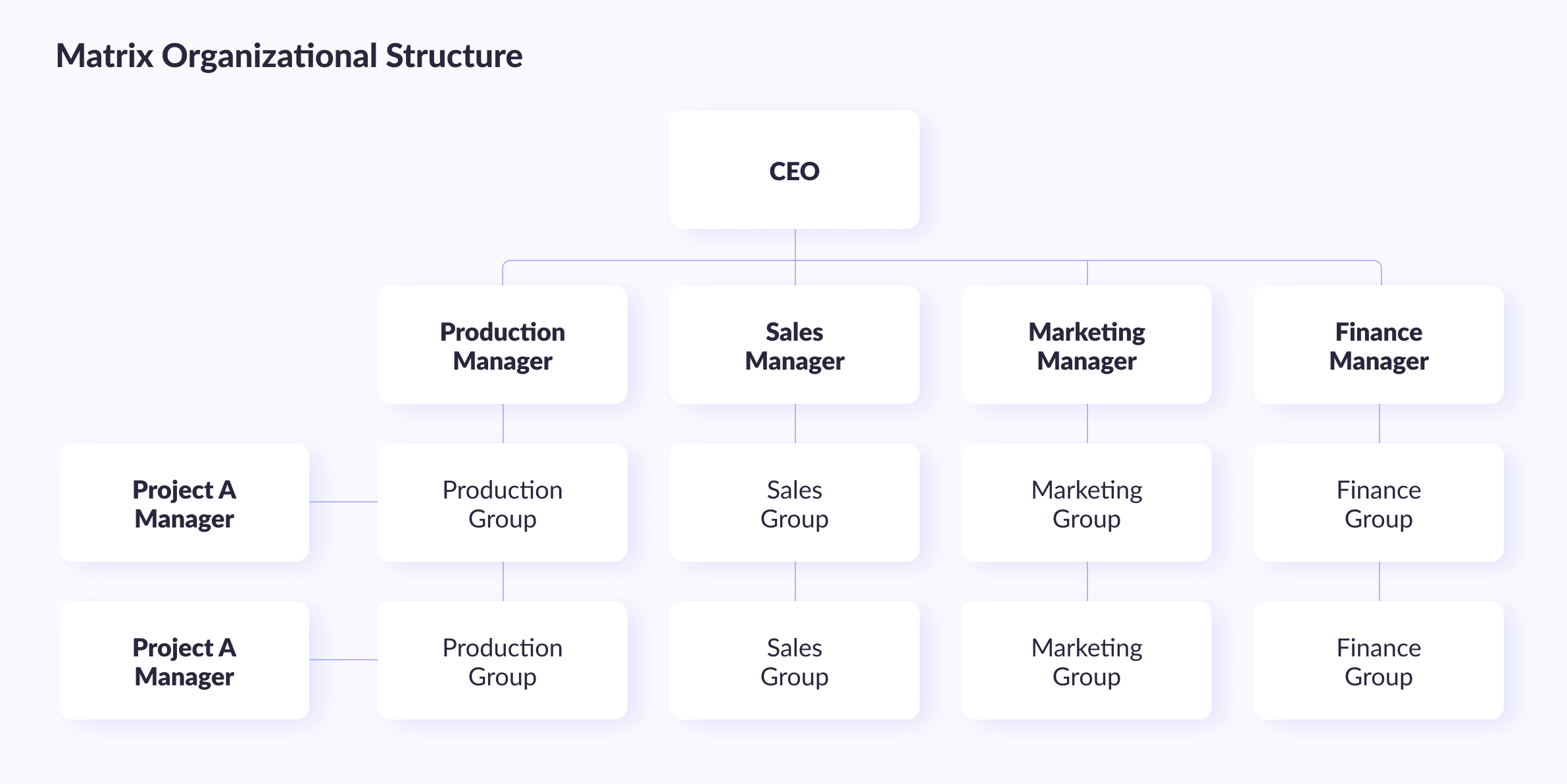
The matrix org chart is a combination of functional and divisional structures. In this management model, the IT department is divided into functional units, and each unit supports multiple business units or divisions. This structure allows for the efficient sharing of resources across the organization, and it provides greater flexibility to handle complex projects.
#4. Project-based IT organizational structure
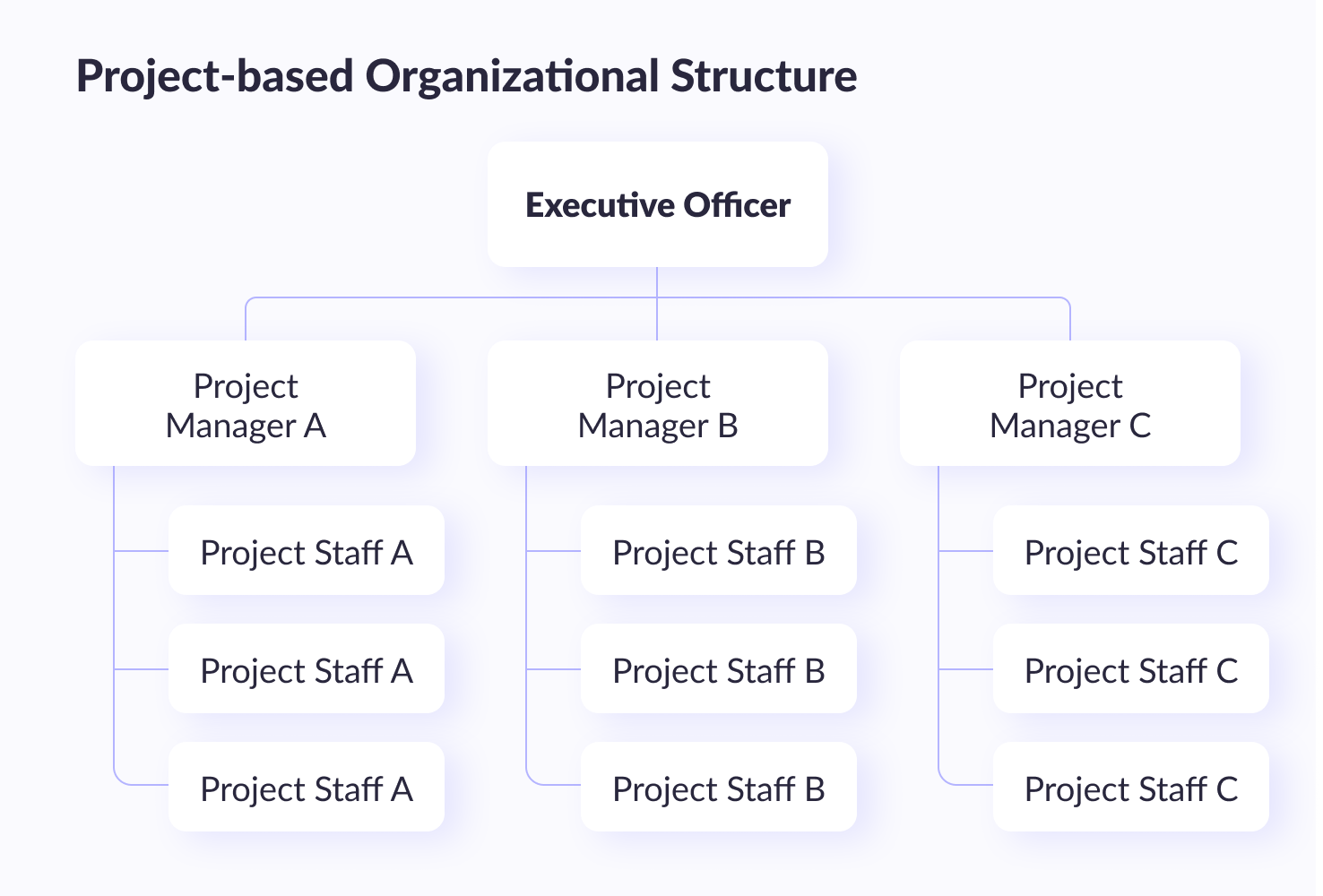
The project-based IT org chart is used by companies primarily focused on project delivery. In this structure, the IT department is organized around projects rather than business functions or units. Each project has its own IT manager who oversees the project team, which includes members from different information technology functions. This structure allows for greater collaboration and communication among team members.
If you’re unsure which IT structure fits best, conducting an IT audit can help clarify the organization’s needs and align IT resources accordingly. This step is essential for identifying gaps and ensuring that the chosen structure supports the company's overall strategic goals.
IT department structure and roles
Many companies, especially those on the path to digitalization, rely on the IT department for everything related to the smooth operation of the organization's computer networks. The IT department has three main areas of responsibility: managing the company's corporate systems, maintaining the infrastructure, and ensuring overall system functionality. In addition, IT specialists work with software and hardware in various areas that allow a business to succeed.
Each IT person in the department plays an important role in the company. Some are responsible for multiple areas, especially in smaller companies. In other cases, the company may have only one IT specialist. Here are the main responsibilities of the IT department:
Administration
Technical support
Communications
Programming
Company website
Application Development
Whether the IT team consists of 2 people or 20, it seems that there is always an endless list of tasks that need to be solved quickly. Many employees and business owners don't realize that the IT team is responsible for much more than just fixing computer problems or helping log in when an employee has forgotten their password.

Administration
IT administrators play an important role within a company and the IT department itself. They are approached when someone needs help with a technical problem or has just joined the company and needs help with new equipment. The duties of an administrator may overlap with those of other team members from time to time. For example, system and network administrators may have similar responsibilities but focus on different aspects of IT. Some general administrative duties include the following:
Support for the company's computer infrastructure
Help new users with computer and software problems
Create training programs for employees
Performing software updates
Renewal of licenses and other legal documents
Tracking current contracts with suppliers
Filling in organizational forms
Ensuring compliance with quality standards
Assessment of potential threats
Data storage control
Support
When people require access to computer systems or help with troubleshooting, they are usually looking for providing technical support. Technical support specialists are especially helpful in solving hardware and software issues, although their role in the company does not end there. Another big part of their work is educating people and answering questions about the technologies they use. Here is a list of duties that support staff performs:
Installing new software or hardware
Selection and purchase of IT equipment and consumables
Participation in asset management and IT inventory
Assistance in backing up and restoring digital assets
Troubleshooting the organization's computer network problems
Work logs creation
Process documentation
Setting up telephone lines
Ensuring documented processes
Installation of video and audio conferencing
Installation and configuration of printing, copying, and other equipment
Provision and installation of cloud applications/services
Equipment repair

On the topic
IT Support Levels: Level 1, Level 2, Level 3
What the technical support service is, the main support tiers, and the support structure.
Read moreCommunications
There are several instances in a business environment where the IT team helps make communication successful between all parties involved. Companies may need to communicate with potential or existing customers through a variety of technologies. Thus, with the development of digital technologies, meetings and interviews using the web are becoming more and more popular. The IT team is trained to assist in the event of technical failures at these important meetings. Here is a more detailed list of IT responsibilities related to communications:
Providing point-to-point telephone connections, as well as conference calls
Preparing for video and web conferences
Email maintenance and troubleshooting
Consultations for heads and employees of business departments
Coordination of network security systems, adding and deleting users
Providing end-user support for computer applications
Create backup copies of data sources
Loading new data into the system
Programming
The company's programming department has employees with the skills of web developers, programmers, and possibly other IT professionals involved in creating new programs. The latter often work with software developers and engineers to turn their projects into workable code. Here is a list of duties specific to this area:
Software development and improvement of business applications
Create new databases with productivity software
Convert printed and electronic documents to ASCII, HTML, PDF, and other formats
Using graphic applications to edit, copy, and save data
Spreading knowledge about application development languages
Programming in different languages such as Linux, Java, JavaScript, C++, Asp.net, C#, SQL, HTML, and PHP


Thank you for Subscription!
Company website
To create a successful and user-friendly website, you need to follow many steps. The IT team collaborates with different departments of the company to realize a shared vision of how the website should look and function. Most often, the marketing team provides copy and organizational design content for the site and then hands it over to the IT team for development. IT specialists work to write the code, test the functionality of web pages, and help resolve any user experience issues. Here is a list of duties that IT professionals perform on a website:
Website layout creation
Writing and implementation of site code
Website usability testing
Support for the company's internal network (intranet)
Application development
he IT team members may work to create computer programs or applications to facilitate business operations. Business applications are especially useful for content management, employee communication, customer relationship management, and enterprise resource planning. Developers put applications through a series of tests that ultimately lead to useful tools that employees and business owners can use. Here are some of the main responsibilities related to application development:
Turning a software concept into working code
Meetings with clients to discuss new specifications and features of the program
Creation of program code to perform tasks
Writing documentation to help users work with new programs
Mobile development with trustworthy vendor
The position of the IT department in the corporate structure
The IT department structure is also critical to ensure the proper business functioning. A poorly designed IT department hinders business, but a well-functioning one gives us a competitive edge in our industry. Properly strategic planning and setting up the defined structure of the IT department is an important step towards the success of our business.
In the early years of IT, computers were used exclusively in accounting. As a result, the IT department often falls automatically into the finance category. You may encounter this in some older companies. But usually, the IT department is a separate organization, for which the chief information officer (CIO) is responsible.
It’s critical that we have a good IT infrastructure in place to stay competitive and mitigate project risk. The CEO knows how to run his business, but the thought of organizing and structuring an IT department can be overwhelming. The size of our company plays a role in this. Are you small (less than 25 employees), medium (25-100 employees), or large (more than 100 employees)? Let's talk a little about the centralized structure of the IT department in different-sized companies.
The formation of an IT department is a key task that depends on the number of employees of the company/enterprise and the characteristics of the network infrastructure. And it cannot be decided separately from the identification of areas of responsibility — more on that below.
First, it’s determined how many IT specialists are needed to service the company's resources. In this case, "resources" is the number of working places involved, that is, places equipped with computer technology.
In world practice, it’s customary to use a ratio of at least two employees of the IT department per 100 users. At least two means that two people can handle the maintenance of the company quite well. Of course, nothing prevents hiring additional specialists sometimes, it’s even necessary, but it all depends on the configuration of the company's IT infrastructure and equipment, as well as on the level of training of IT department employees.
IT department structure in small organization
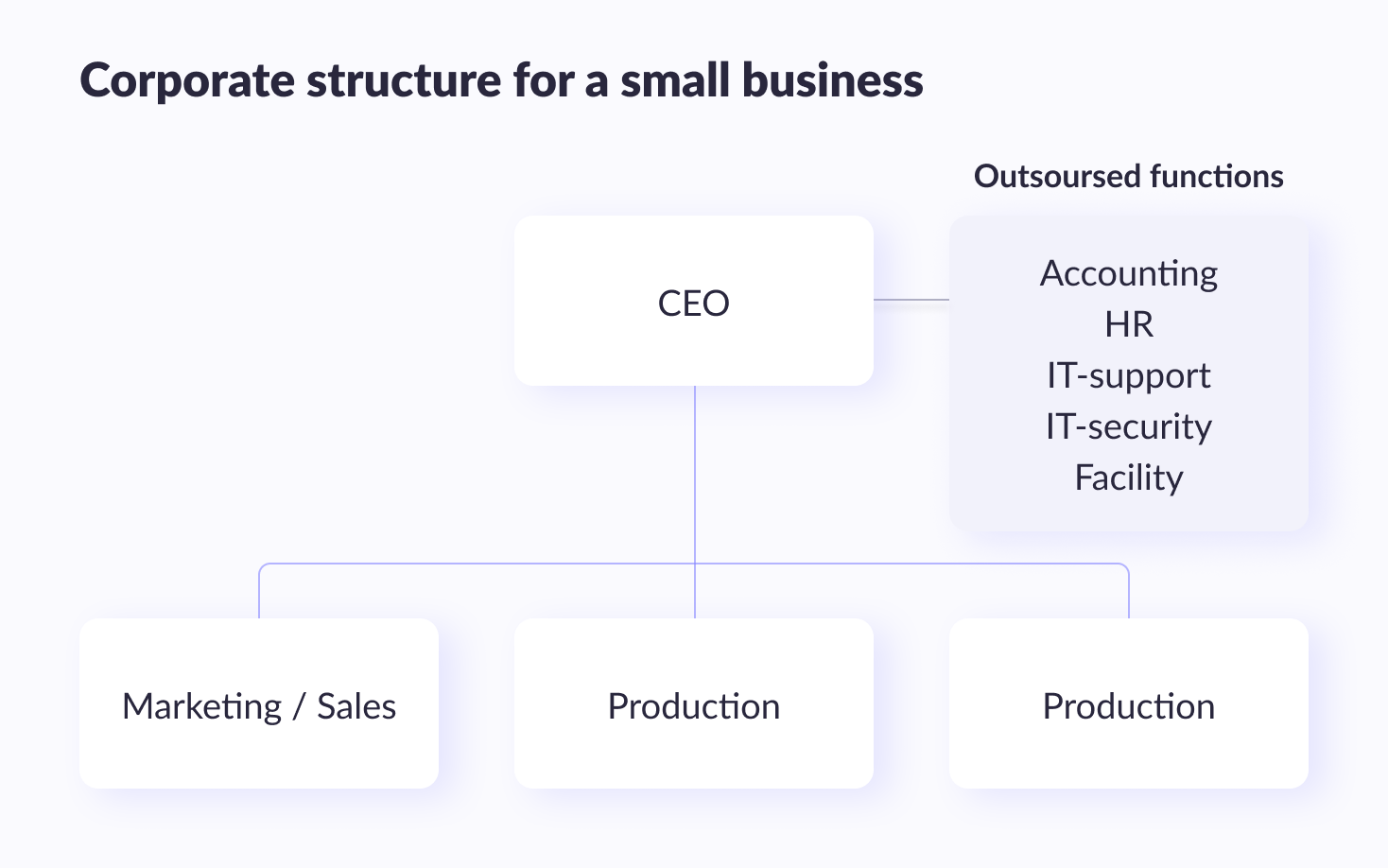
In a small business with fewer than 25 employees, it’s normal for each employee to perform multiple tasks. In this case, simple day-to-day IT issues fall to the person with the highest technical expertise in the organization (probably the chief technology officer). The people needed to provide an adequate level of asset protection and data security measures are usually hired from an outside consultant's office. IT and cybersecurity can provide a well-equipped managed service providers (MSP) or chief information security officer (CISO).
There is usually a SaaS application, so on-site technical support should not be minimal.
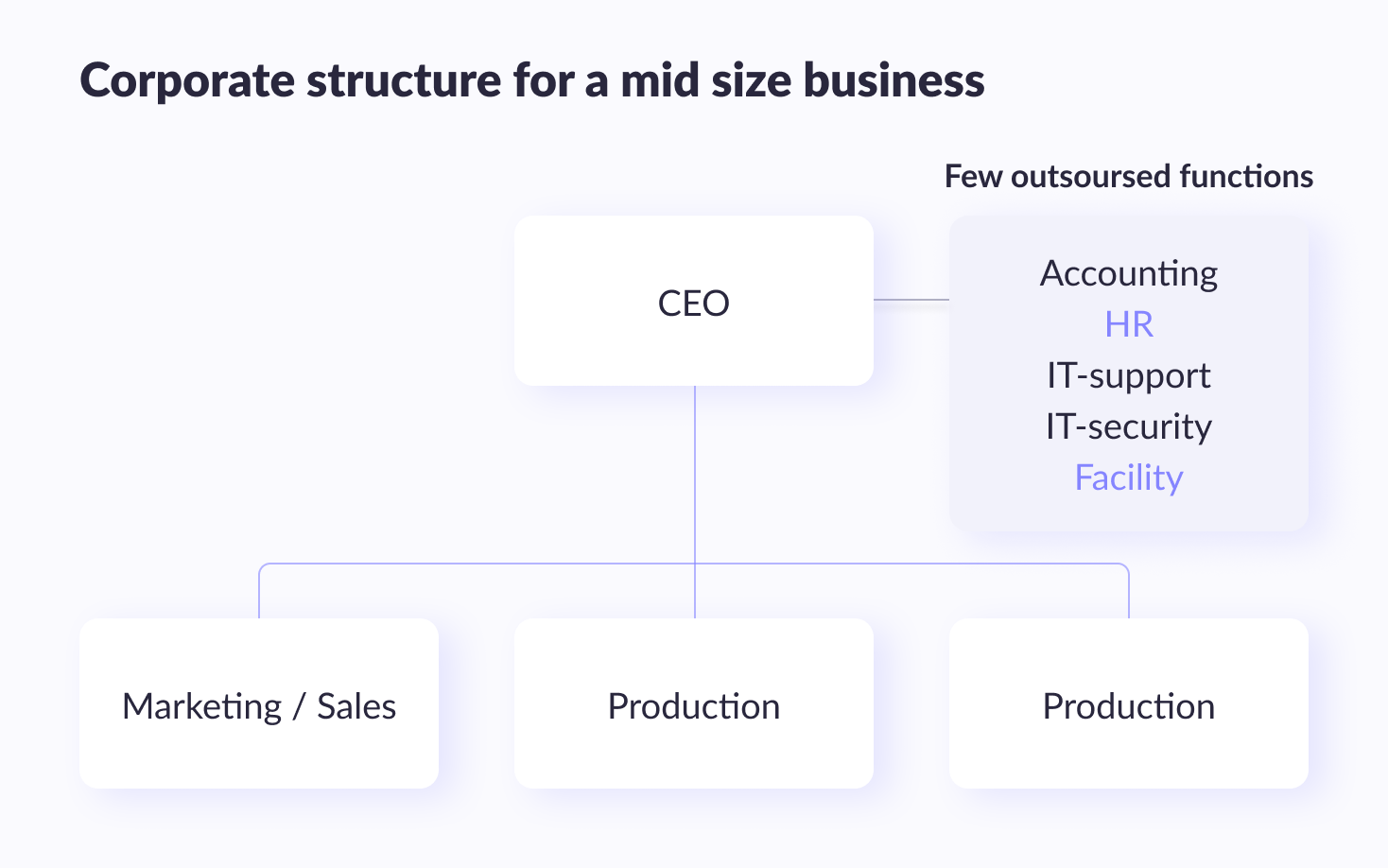
Structure of IT department for medium business
In medium businesses, it’s very common for someone to have the title of IT, but they also provide important support in providing services to their end customers. When weighing "Should I take care of the client or update IT security measures", working for the client almost always takes precedence. This IT professional is usually reactive rather than proactive. A company this size greatly benefits from a chief information security officer.
Structure of IT department for large business
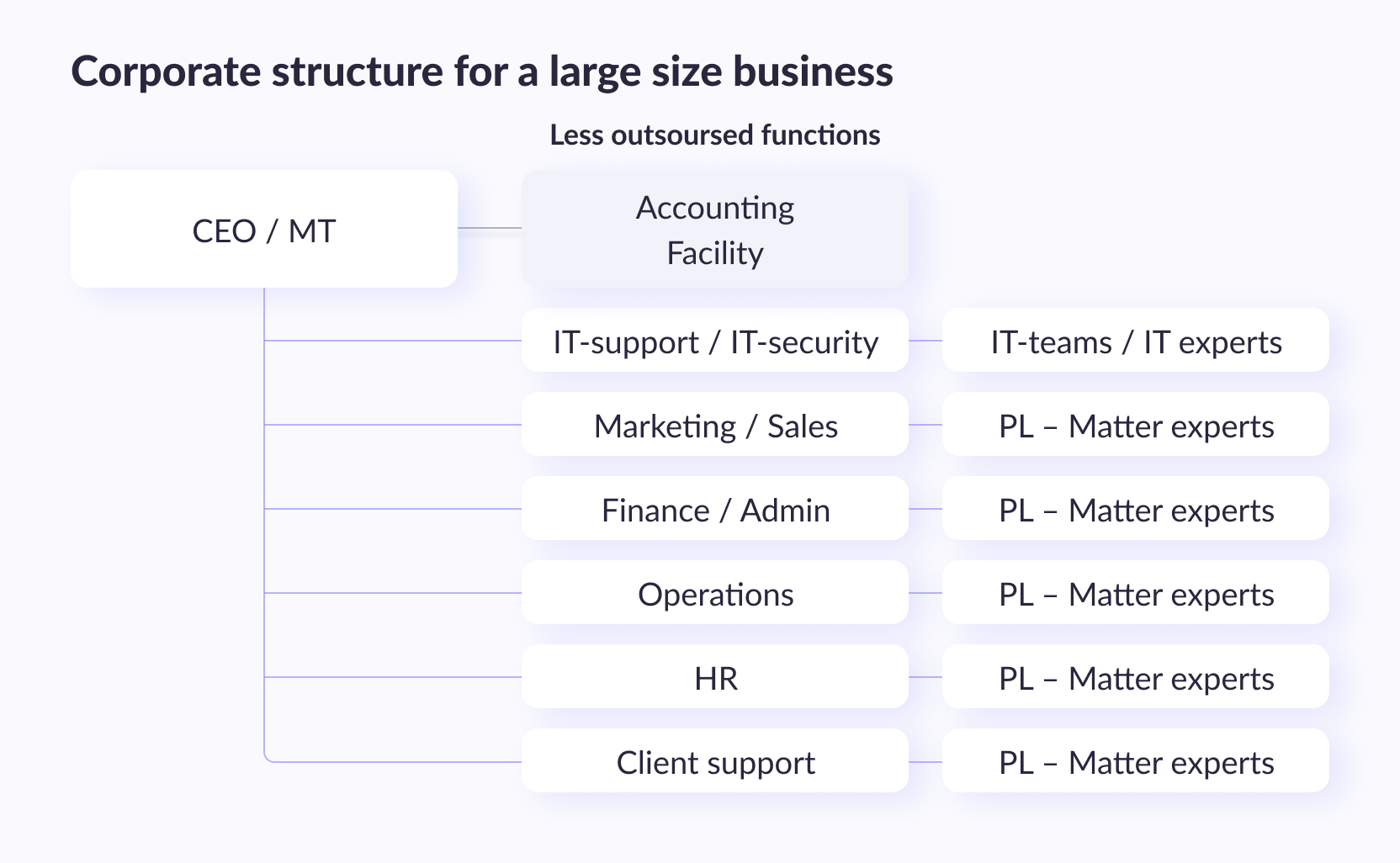
As the business grows, more people are needed to fill key positions and roles in the business. Be it employees or trusted freelancers. As a business grows, so does its dependence on IT. Businesses must remain productive, flexible, and secure. It’s critical to keep companies active, competitive, innovative, and ahead of the curve. Failure to perform IT can limit the growth or survival of a business.
For a correct interaction between IT specialists within the company, it’s recommended to keep a list of actions and settings performed by each of them individually.
To provide visibility, you can use an internal Web portal or forum to which ordinary users have access. In this case, over time, a knowledge base is formed, containing all the recommendations and instructions for using programs and equipment. In organizations with more than 200 employees, it’s more expedient to use a microblogging system that can display notifications to users on a computer screen — this makes it possible to promptly notify employees about server reboots, failure of any shared printer or copier, and other failures in the organization's public equipment.
Modern IT Department Structure Best Practices
1. Align IT department structure with business objectives
The IT department's structure should align with the business strategy of the organization. This includes understanding the organization's business objectives and how the IT department can support these goals. The IT department's structure should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the organization's strategy.
2. Establish clear roles and responsibilities
It’s crucial to define clear roles and responsibilities within the IT department to avoid confusion and improve efficiency. You need to develop job descriptions that outline the duties, expectations, and performance metrics for each IT person. It’s also important to communicate how each role contributes to the department's goals and how it supports the broader organizational strategy. This way, team members clearly understand their roles and responsibilities and can focus on delivering high-quality work that meets the department's objectives.
3. Promote collaboration
The IT department should promote a culture of continuous improvement that encourages innovation, experimentation, and learning. It means that you need to provide opportunities for team members to develop their skills and knowledge, fostering an environment that supports creativity and risk-taking, and encouraging the exploration of new ideas and technologies. By embracing a culture of continuous improvement, the IT department can stay ahead of emerging trends and technologies, improve its processes and operations, and deliver better value to the organization.
4. Strike a balance between centralized and decentralized structure
The centralized structure should find a balance between centralization and decentralization that aligns with the organization's goals and needs. Centralization can improve efficiency and reduce redundancy by consolidating IT resources and services, standardizing processes and policies, and establishing a single point of contact for IT issues. However, the decentralized structure can also offer benefits by providing local IT support and promoting innovation and flexibility. Finding the right balance can help the IT departments meet the organization's needs while optimizing its operations and resources.
5. Establish IT governance
Establishing IT governance is crucial for organizations to effectively manage their IT resources and ensure they are aligned with the overall organizational goals. This point includes the following actions - developing and implementing policies and procedures that govern IT investments, project management, and risk management. By doing so, IT investments can be evaluated against the organization's strategic objectives, prioritized and approved accordingly, and effectively managed throughout the project lifecycle.
Quick health check
Is your business analysis good enough? Check out how your company is operating
IT services outsourcing
IT outsourcing is the transfer of functions for the administration of the company's computer infrastructure. This includes maintenance of SCS (structured cabling systems), maintenance of computer equipment and peripherals, modernization, and software configuration; both remote project manager and visiting system administrator.
The widespread introduction of modern technologies into business intelligence has led to the need to create IT departments in companies with a developed computer infrastructure, which in turn has led to an increase in the cost of maintaining them. To a greater extent, financial difficulties fell on the shoulders of small businesses. As a result, as the practice has shown, it has become very profitable for small and medium-sized companies to use dedicated outsourcing teams rather than hiring administrators and IT engineers.
A typical set of computer park subscription services includes the following:
setting up and updating the hardware and software systems
creation and support of the system of data security and safety
periodic preventive and diagnostic measures in the hardware and software of the computer park in order to prevent emergency situations and identify "weak links"
repair or replacement of failed equipment or its modules
unlimited volume of telephone consultations
Practice shows that the transfer of computer park maintenance to outsourcing provides not only significant cost savings but also leads to an increase in productivity due to more qualified, high-quality, and efficient actions of the contractor than regular staff.
You can find actual prices on IT outsourcing in the article ''Outsource Developer Rates In 2022. How To Choose A Software Outsourcing Country.''
Custom software development services
Conclusions
Instead of a conclusion, I would like to draw an analogy between an IT system and a car. Good and timely service is necessary for any car, but, unfortunately, it will not make your car better. In order to improve its performance, you will have to turn to a tuning studio.
As for maintenance, here you need to decide whether it makes sense for you to create your own car service to service your car or if is it better to entrust this business to some specialized car service. You can be as skeptical as you like about outsourcing, but it has already become a reality. In almost any more or less large company, copiers and other peripherals are serviced by an external company.
Besides, you use telephony and the Internet provided by your telecommunications partner, don't you? The presence of e-mail, file servers, and other "infrastructural" things will not give you any competitive advantage. So it might be better to concentrate on creating your atelier for ''tailoring'' business systems for your company, leaving yourself the most creative, interesting, and responsible role — the role of a fashion designer, and give the sewing process ''outside.'' So you will be a trendsetter, and your competitors will only have the opportunity to repeat your style, which will already be outdated for you by that time.
Now more than ever, it’s important to have a ''perfect'' IT department that will be ready to meet the needs of the business and, in some ways, stay ahead of them. And if you need technology consulting services or help with building a proper IT department — book a 30-min free call with our specialists.





















