Geniusee team decided to write this article to provide business leaders with an understanding of the evolving COVID-19 situation and what awaits their business. The virus emerged suddenly and has been moving quickly, and some of the perspectives that we are going to speak about may fall rapidly out of date.
7 Important Tips to Save Your Business During COVID-19
Fears of an economic crisis because of COVID-19 are growing. Estonia has already stated that it has entered the crisis phase. Other countries are aware that the economic crisis and restructuring is on their doorstep. The size of future losses depends on how long the epidemic will last.
Three scenarios
As can be expected of any forecasting, three courses of events scenarios are modelled: optimistic, plausible and pessimistic. Let's talk about each of them.
According to the first, optimistic one , epidemic control in other countries will be established as quickly as in China. New cases of the disease are being recorded, but adults continue to go to work,as well as children to school. In this case, the global economy may be limited mainly to China’s losses - its GDP growth may slow down from 6% to 4.7% and the global GDP could drop from previously projected 2.5% to 2%. At the same time, China is likely to resume most of its production by the end of the first quarter 2021.
In the second scenario, a more plausible one at the moment, the global growth is going to slow down because the countries that have encountered coronavirus are not able to achieve the same rapid control over its spread as China has done. According to this scenario, small and medium-sized businesses and developing countries as a whole will feel bigger pressure. Air and travel companies will miss the start of the summer vacation season. But by May-June the virus will have disappeared and demand will have recovered. Oil prices will be under pressure until the third quarter. The world economic growth will slow down to 1-1.5%.
Both of these scenarios suggest that coronavirus is seasonal, which is still not certain. If the virus continues to spread actively with the onset of spring in the northern hemisphere, a global recession will begin. It will be felt throughout the year. This is the third scenario, the worst one. In this case, the global GDP growth will slow down to 1.5-0.5%.
Companies that navigate disruptions better often succeed because they invest in their core customer segments and anticipate their behaviors.
Supply problems
Undoubtedly, the supply chain should be addressed specifically. Analysts say the impact of the virus outbreak in China on its production has a slowed-down effect on the European economy. Although many Chinese plants have resumed production and have been operating at more than 90% capacity since the beginning of March, other companies dependent on Chinese imports are only now facing the consequences. They are experiencing delays in deliveries by an average of 8-10 days, and the unpredictability of the timing and scale of demand recovery is very high.
7 tips how to react on COVID-19
1. Protect employees. Provide clear information about the coronavirus and provide autonomy to local managers to respond to changes quickly and accurately.
2. Create a cross-functional response team that will monitor the status of employees, the financial condition of the company, supply chain, marketing and communications in the context of the spread of coronavirus. Speed is important: each subgroup sets specific goals for the next 48 hours.
3. Make sure you have enough liquidity (Financial stress-testing and contingency plan). Companies must model their financial performance in each of the three scenarios and identify triggers that can significantly reduce liquidity.
4. Stabilize supply chain. Prevent increased consumer demand for certain products when they begin to stockpile.
5. Stay close to your customer. Those companies that anticipate the behavior of their customers will better tolerate failures. For example, in China, online shopping and food and grocery delivery have grown when the people were told to isolate themselves. Investing in online deliveries now seems to be a win-win business option.
Immediate stabilization (inventory planning, near-term pricing changes, discounts)
Medium/longer-term stabilization (investment and microtargeting for priority segments with long-term growth)
6. Create a plan and behaviors for different scenarios and follow them.
7. Respond to challenges. The business should remember that it is a part of the community. Be ready to support people with money, equipment, expertise. There are examples of companies that have switched to the production of medical masks and clothing ‘cause it was a necessity.
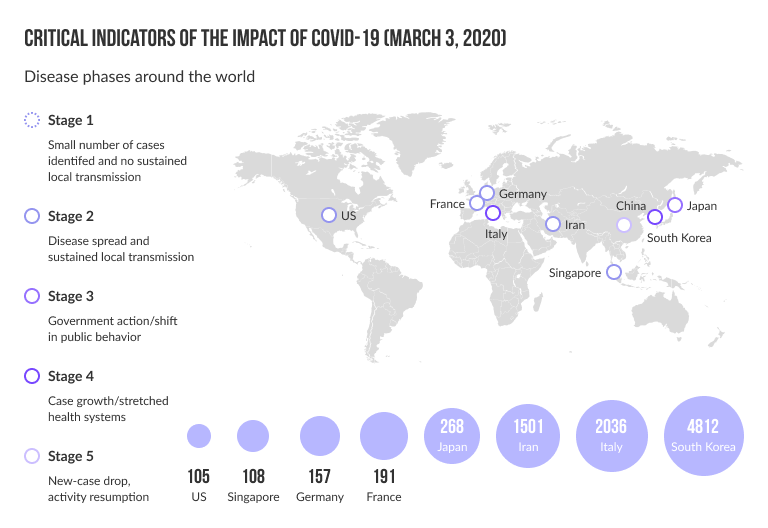
Source: CNBC; Economist; EgyptAir; International Air Transport Association; Johns Hopkins Center for Systems Science and Engineering; New York Times; OAG Aviation Worldwide; Reuters; World Health Organization situation reports.
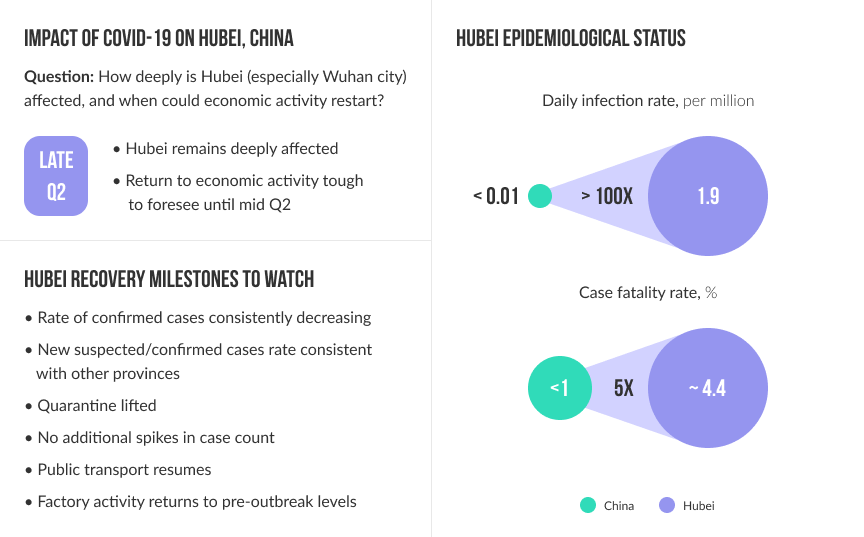
Source: Baidu QianXi; Centers for Disease Control; Columbia University; Economist; EgyptAir; Jakarta Post; Johns Hopkins Center for Systems Science and Engineering; London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine; National Bureau of Statistics of China; New York Times; OAG Aviation Worldwide; Organisation for Economic Co-operation Development; Peking University HSBC Business School; Reuters; TomTom Trac Index; World Health Organization situation reports; Xian Jiaotong University; McKinsey Global Institute
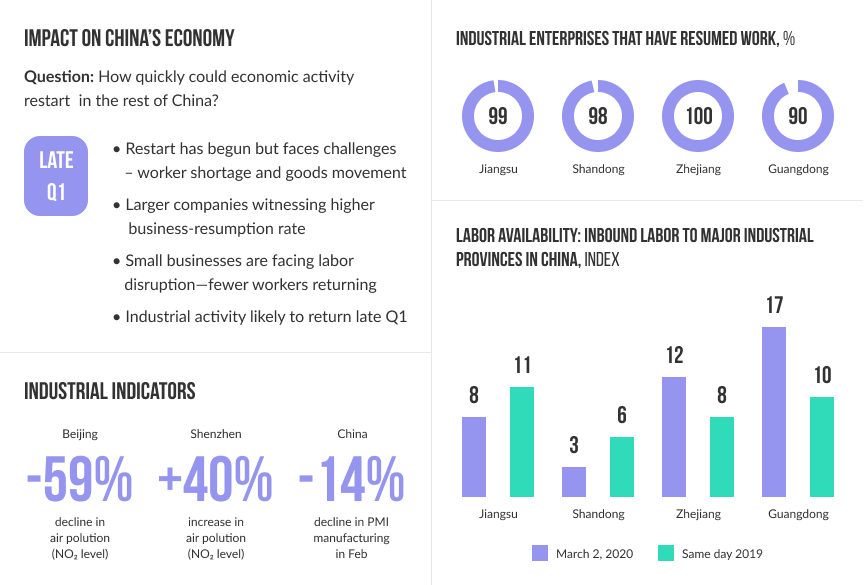
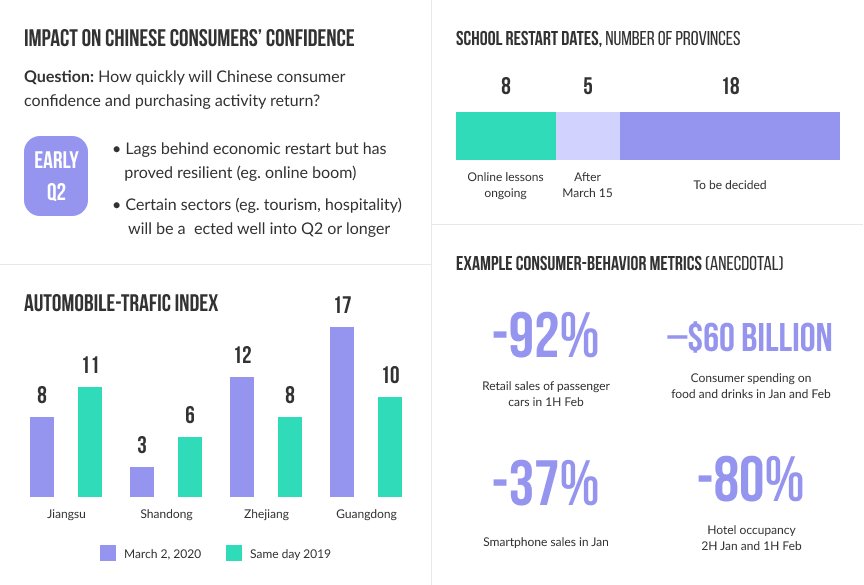
The COVID-19 crisis is a story with an unknown ending and the way it might end depends hugely on how each of us acts. So take care of your loved ones and your business.
You can get more info here.





















