Manufacturing has become one of the main areas of AI application technologies. However, these are not only AI solutions but also the Internet of Things, Big Data, and Augmented Reality. Machine learning will also play a connecting role here.
Today, AI algorithms solve a whole pool of problems in enterprises. For example, computer vision monitors whether employees are using personal protective equipment. Such solutions are in demand in hazardous and food manufacturing. According to the Journal of Advanced Manufacturing & Processing, the global smart manufacturing market will grow to $238.8 billion in 2028.
Neural networks increase production processes' efficiency, help control product quality, and manage warehouses. So, what else can you expect from a new AI solution as a manufacturing business owner?
This article will discuss the various AI solutions for manufacturing, the benefits they can offer for your businesses, and how the Geniusee team can help you develop AI-powered manufacturing solutions.
Benefits of AI for manufacturing
What additional opportunities does the integration of AI into the industry provide? Why would manufacturers use tools like machine learning and computer vision? Before we determine their main advantages, let’s take a look at some challenges that companies usually face:
Challenge | Description |
Inefficient production cycles | In traditional manufacturing environments, workflow cycles tend to be very slow due to low automation levels and human intervention. |
High costs | Delays, random breakdowns, or production flaws cause sharp increases in maintenance and waste disposal costs. |
Inconsistent product quality | Visual inspections can hardly detect defects, resulting in claims, customer complaints, and poor company reputation. |
Difficulty with market trends | Delays in adapting to consumers’ requirements or incorporating new materials lead to manufacturing harmful products and losing business opportunities. |
Safety risks for workers | Many accidents occur in high-risk workplaces, which have profound repercussions on time lost, insurance expenditures, and general output. |
Bad customer service and product personalization | Manual customer support and standard products lead to clients’ dissatisfaction caused by high response time and non-targeted approach. |
Increased efficiency and productivity
If you integrate AI, you will shorten the production cycle and deeply automate repetitive tasks such as assembly, quality control, packaging, and product transportation. For instance, Siemens applied AI in robotic systems in its factories, and they gained 20% cycle time performance. Their Amberg factory, known as the ‘factory of the future, is fully automated at 75%, with a 99.99885% quality rate.
Minimizing costs and risks
AI helps prevent equipment failure and reduce scrap and production waste, making it more environmentally friendly. General Electric (GE) applies AI to maintain industrial machinery, especially for predictive maintenance. By introducing these systems, GE reduced unexpected engine breakage by 25% and saved more than $1 billion annually.
Improving product quality and innovation
Machine learning tools help develop products considering new market requirements and consumer preferences. They also simplify the introduction of new materials and technologies into production. AI is a tool that allows Toyota to test and adopt new materials. It advances the company’s shift toward lighter and more environmentally friendly car parts.
Production optimization
AI manufacturing algorithms can analyze data sets and determine the best solutions for production problems. They also allow the creation of forecasts and simulation scenarios that help optimize any manufacturing operation and adapt to market conditions. Nestle decreased operational costs by 14-20% and enhanced inventory systems. They use AI to simulate production lines and adjust to changes during the year, such as holiday chocolates.
Reducing human error and increasing safety
AI allows you to reduce the risks associated with human involvement in the production process (errors, negligence, etc.). AI tools can also eliminate the need for humans to work in hazardous environments and help monitor safety compliance. Rio Tinto mining firm employs automated trucks and drills to eliminate the chances of suffering losses from the many dangers. This reduced workplace injury and massively increased productivity.
New quality of service
Automating customer service and support using AI significantly improves the quality of service: It allows you to process consumer requests faster, provide them with more relevant information, and offer personalized offers and products. Amazon and its Alexa devices help and quickly respond to users' questions, improving user satisfaction.
Therefore, the role of AI in production can hardly be overestimated; in times of fierce consumer competition, it can become one of the main factors of success.
Use of AI technologies in manufacturing
The scope of production is vast: high-tech mechanical engineering, agricultural production, and the production of consumer goods. Therefore, there is room for all available AI technologies in manufacturing. Let's name the main ones among them.
Machine learning (ML)
This term refers to a mechanism that allows a computer to learn from structured data and adjust its algorithms without explicit human programming. There are many types of machine learning. The rationale for learning, the data type, the range of use, and the kind of learning model (supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning) differentiate them. Typical ML examples are voice recognition, text sentiment detection, and medical and technical diagnostics.
Deep learning (DL)
It is a type of ML that uses neural networks to process large amounts of unstructured data. A neural network is a whole system of algorithms that comprehensively interprets data at several levels. Deep learning is used, in particular, in machine translation of texts, search engines, image analysis, etc.
Generative AI
This AI system can recognize and analyze data and generate new content based on this analysis: textual, visual, and multimedia. Generative AI is very close to creating a full-fledged creative product: ChatGPT can generate texts, DALL-E and Stable Diffusion models create images, etc.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This is the direction of AI's development, based on machine and deep learning methods to interpret, process, and determine the meaning of human-written text by machines. NLP methods and large language models allow AI to interact with a person in the format of regular correspondence, process documents, etc.
Speech recognition
Compared to NLP, this technology has another level of complexity — recognition of human spoken speech for conversion into text, further analysis, and processing. Modern voice assistants of any complexity are built on AI speech recognition technologies.
Computer vision
This development uses machine learning and neural networks to analyze visual data — videos, images, camera broadcasts, etc. Its goal is to teach AI to perceive visual information flexibly as humans do. Using computer vision, you can implement a facial recognition system, environmental monitoring, or visual control of product quality.
The future of AI’s decisive technologies and industry roles is unclear. However, its practical applications are promising. Let's look at them below.
.


Thank you for Subscription!
AI use cases in the manufacturing industry
Employing artificial intelligence on a grand scale is changing the way we live and work. Developments in generative AI and ML algorithms are transforming industries across the board. From art to medicine to supply chain management, AI systems are slowly creeping into every aspect of our lives. Similarly, AI adoption is impacting the manufacturing industry.
Are you wondering, “How is AI used in manufacturing?” Then, examine our breakdown of the technologies and their potential benefits for manufacturing businesses.
AI technology | How it’s used |
Predictive analytics | Predictive maintenance (equipment); Optimize assembly line processes; Demand forecasting (resources, inventory, order management) |
Computer vision | Detect product defects (quality control) |
Robots and mechanical arms | Perform tasks that demand precision or heavy lifting |
Digital twins | Create simulations to predict and improve outcomes on the shop floor |
Robotic process automation | Automate processes to save time for manufacturing engineers and workers |
Now that you have an idea about the use cases of AI in manufacturing, it’s time to dive deeper.
Predictive maintenance
Did you know inefficient equipment maintenance can decrease production capacity by up to 20%? Simultaneously, predictive maintenance costs 5-10% less and increases uptime by 10-20%.
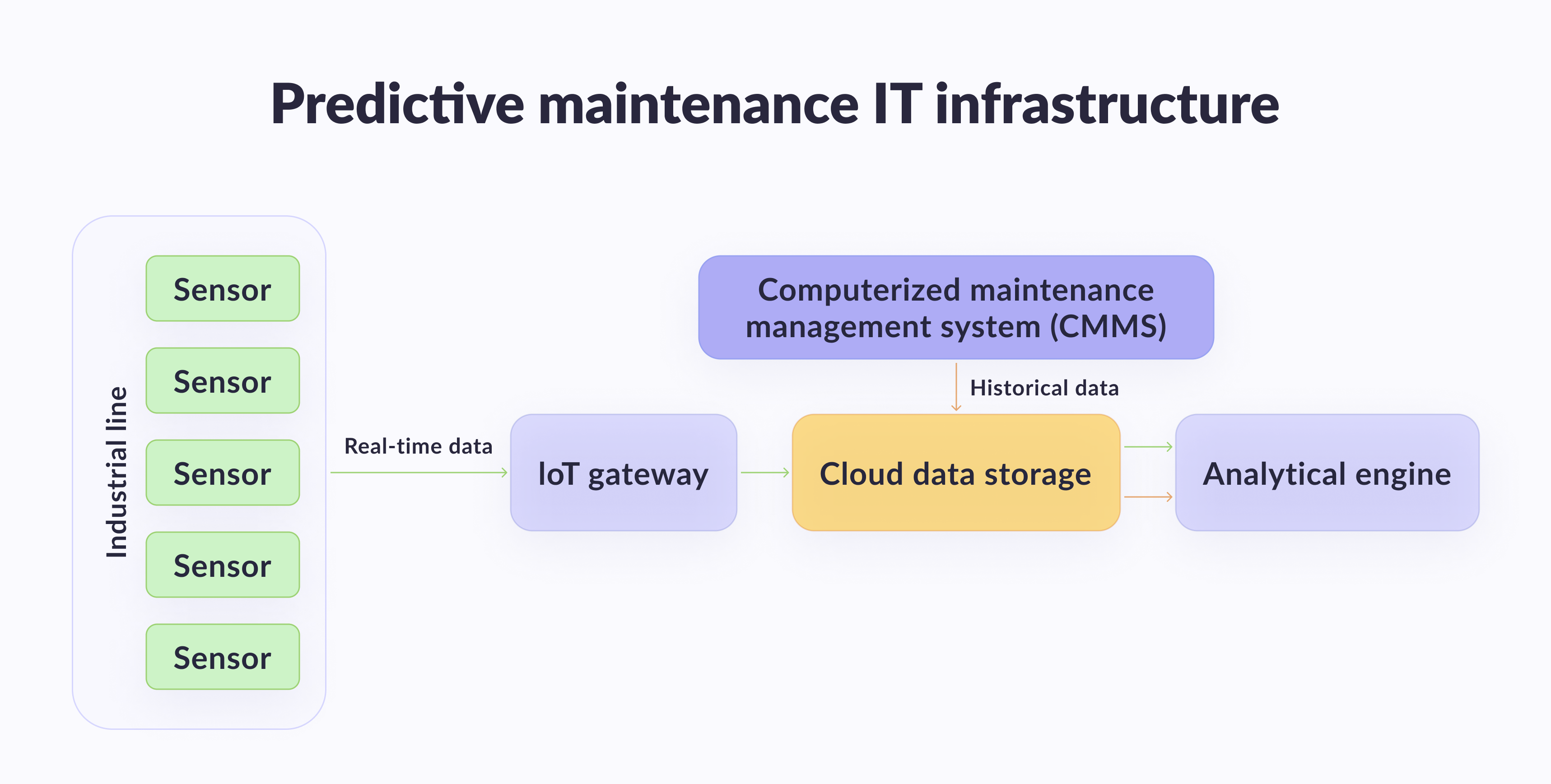
Predicting equipment malfunction
Using AI and ML models will keep your shop floor operations going. AI analyses sensor data to create maintenance schedules that prevent expensive failures and delays.
Yet, how does it work? First, you need to set up equipment sensors. These sensors should feed real-time data, including weather conditions, into the system. Then, the AI models analyze data based on past performance and several parameters. As a result, you will get an evaluation of current performance, potential breakdown estimates, and actionable recommendations.
Benefits of AI-powered predictive analytics
The benefits of these AI algorithms in manufacturing plants are numerous:
Decreased equipment downtime,
Extended equipment life,
Reduced maintenance time and cost,
Increased productivity,
Improved workplace safety,
Better quality control.
These benefits make it easy to see how AI use in manufacturing drives profitability.
Airbus uses AI-powered analytics in aircraft production
Many companies like Airbus use AI in manufacturing and aviation. In addition to real-time aircraft performance monitoring, they use smart sensors in their manufacturing processes.
Sensors monitor conditions such as temperature and pressure to forecast assembly line problems. If parameters breach limits, the machines halt and redistribute workloads to minimize time and resources. The result: machine life increases by 20-40%, saving the company millions of dollars.
Visual inspection with AI
Visual inspection is a vital part of quality control in manufacturing. However, human workers might miss such things because of distractions or fatigue. AI-powered computer vision powers some success stories, which can detect the slightest changes on the assembly line.
Inspecting products for defects
While utilizing AI and machine learning to detect anomalies does require an initial investment, the results are compelling. Feeding manufacturing data into deep learning algorithms trains the system to recognize even the subtlest surface defects and deformations in production. The more data you feed into the system, the better it gets.
Advantages of AI-powered inspections in smart manufacturing
Here are some of the benefits manufacturers get from AI-powered computer vision:
95% defect detection rate,
99% less false positives,
25-90% reduction in inspection time,
30-80% increase in inspection accuracy,
10-30% reduction in labor cost.
Sounds almost too good to be true? Artificial intelligence in manufacturing inspections works because machines don’t tire or miss details. An AI model that understands shapes and surfaces quickly compares that data to training one to catch inconsistencies and produce accurate results.
Example: Flex uses computer vision to boost operational efficiency by 30%
Flex manufactures printed circuit boards for electronic devices. These intricate parts need thorough inspection and are in high demand. The company started implementing AI and machine learning in defect detection to improve production speed and battle quality issues. And it paid off. Replacing traditional quality control inspections with automated systems increased operational efficiency by 30% and product yield by 97%.

More from our blog:
Nonfunctional requirements in synthetic speech generation
Explore how to make AI audio generative systems effectively to improve your business operations.
Read nowProcess optimization with AI-driven analytics
AI analytics are a powerful tool in the manufacturing industry. They can optimize each part of the product development process, from material sourcing to order management.
Identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks
Predictive maintenance with AI-enabled sensors allows you to prevent equipment malfunctions, saving you from one of the most inefficient sources — equipment malfunctions. When you find inefficiencies, you can use targeted solutions to improve productivity.
Another common issue is defective products, which waste materials, time, and customer trust. AI algorithms watch for defects, trace their source (raw materials, faulty equipment, or human error), and then propose data-driven solutions. Digital twins allow you to simulate scenarios to test materials and processes without going through them.
Optimizing scheduling and resource use
Once you know what problems you have in your manufacturing process, you can tackle them with thoughtful planning. For example, AI can schedule maintenance to avoid disruptions during low-demand periods. Digital twins can also be used to check your production capacity to see if it can take on increased demand.
Furthermore, AI-powered analytics can help with resource allocation:
AI can track inventory, supplies, and the workforce involved in the manufacturing process.
Then, you can plan orders, track them through supply chains, and automate processes as needed.
Manufacturing AI aims to accelerate production and reduce costs via data-driven insights. These tools analyze data across production, quality, and supply chains, including generative AI, digital twins, and AI-powered robots. This level of analysis is beyond what any human can do: it enables manufacturers to react to risks and seize opportunities in real time.
Condals’ AI-driven analytics reduce scrap by 45%
Condals Group Foundry is a leading iron and steel casting provider in Spain and Slovakia.
However, producing massive amounts of iron casting also led to high scrap rates in their manufacturing processes. To tackle this challenge, they partnered with Data Prophet. The first step was employing AI in manufacturing to collect and analyze production environment data. Then, the algorithm could detect issues and suggest improvements. By getting an overview of operations and tracking their resources, Condals reached a 45% decrease in scrap. By saving resources and minimizing rework, they also improved their profitability.
Demand forecasting and supply chain management
One of the most impactful uses of AI in manufacturing could be accurate demand forecasting. While internal analysis of product development processes is useful, it means nothing if you can’t meet external demand, which is where big data comes into play.
Predicting product demand
Market trends and demand fluctuations determine when to scale up and down manufacturing. During downtime, you can plan maintenance, train employees, and run simulations to prepare for higher demand. So, how do you predict demand and get there before the competition? The advantage comes from pairing the AI-powered system with external data sources.
With the simplification of unstructured information, AI propels manufacturing forward. AI analyzes past data, seasonal trends, sales, and customer inquiries to forecast the production needs that are made and adapted to them.
Optimizing inventory levels and supply chain efficiency
New research has shown that using a particular material or process leads to a longer product lifespan, and the media is buzzing about it. You use that material or process in developing your products.
AI will detect the increased interest, analyze the supply and demand, and help you prepare for the demand surge. It can:
predict how your sales will increase and how much stock you should have
warn supply chain management issues beforehand
suggest equipment maintenance schedules that can help prevent production delays and missed deliveries.
Danone uses AI-powered supply chain optimization to reduce lost sales
Danone is a multinational food-products corporation based in France. It showcases one of the stellar uses of AI in manufacturing. So, what did they do? They used artificial intelligence to predict market demand shifts and optimize inventory management. Through data-based planning, they reduced lost sales and product obsolescence by 30%.
We’re here to support you if you want to start using AI in manufacturing but aren’t sure how. Our team of versatile experts can help guide your digital transformation. Whether you’re interested in generative design or predictive maintenance or want to streamline processes, Geniusee can develop a customized solution tailored to your needs. To navigate you a little, we would like to show some of our case studies and use cases:
Forethought
We developed an innovative web app to meet interfacing requirements and boost customers’ experiences. Our team made a Chrome extension in the React JS category and an AI control panel. Below, you can see what it features:
Customized activity monitoring that can determine the level of satisfaction with customer interactions in real time.
Foresees customers’ requirements based on past and present information.
Creates interactive responses to improve specific customer questions.
AI-Driven Manufacturing (PM & QC)
We developed AI solutions for a manufacturing company to optimize its functioning. Features:
Predict equipment failures before they occur so that potential loss of time is minimized.
Robots' picture and voice recognition reveal defects that the human eye cannot identify.
Nimble.ai
We collaborated with a robotics firm to build data pipelines and incorporate more autonomous behavior in the robots. Here’s what Nimble.ai can do:
Allows robots to sense problems with their performance and enhance the tasks they are handling.
Enhances the robot control policies’ functionality through interaction as well as learning.
Conclusion
It is impossible to ignore the topic of using AI and ML in manufacturing because, in the next decade, artificial intelligence will become one of the main drivers of labor productivity growth.
We don't yet have all the comprehensive data on how AI impacts manufacturing. Its tools already provide businesses with many competitive advantages: deep automation, precise quality control, increased security, and new opportunities in design, marketing, service, etc.
AI use cases in manufacturing range from predicting equipment breakdowns to quality inspections and process improvement to inventory and supply chain management, but that’s not all.
AI capabilities can also improve the manufacturing sector through:
Generative design and additive manufacturing using generative AI
Robotic process automation for repetitive tasks
Digital twin technology for simulations
Robotic workers and collaborative robots (co-bots)
Of course, not every manufacturer has all the necessary resources and competencies to implement AI programs. However, you can secure long-term development prospects and get help from our external IT team with all the essential technologies, specialists, and experience.





















