Probably the most pleasant thing during development is the moment when you realize how you can solve this or that problem. This moment happened to me when, while working on the development of a neobank application, I came to the conclusion that the fact that we are building a monolithic application on the frontend is not the best solution in this case. “We need micro frontends,” I heard distinctly in my head. I realized that I would need to convey to our clients what it is all about and why we should use micro frontends in our project. This is how the article, which is now in front of your eyes was born.
What are Micro Frontends: How and Where to Use them?
From my own experience I can say that all these years, the frontend developer has been writing monoliths in all the cases, although they understand that this is a bad habit. You divided your code into components, used require or import and defined npm packages in package.json, or spawned git repositories in your project, but nevertheless you still had to write a monolith.
It's time to change the situation.
In this article I will share what are micro frontends, what are main advantages of micro frontends, how micro frontends work, when to use micro frontends, what are the biggest challenges of using micro frontends.
Monolith Architecture.
Monolith is an ancient word for a huge block of stone. Although the term is widely used today, the presentation remains the same across all areas. In software engineering, a monolithic model refers to a single, indivisible unit. The concept of monolithic software is that the various components of an application are combined into one program on one platform. Typically, a monolithic application consists of a database, a client user interface, and a server application. All parts of the software are unified and all of its functions are managed in one place. Let's take a look at the structure of monolithic software in detail.
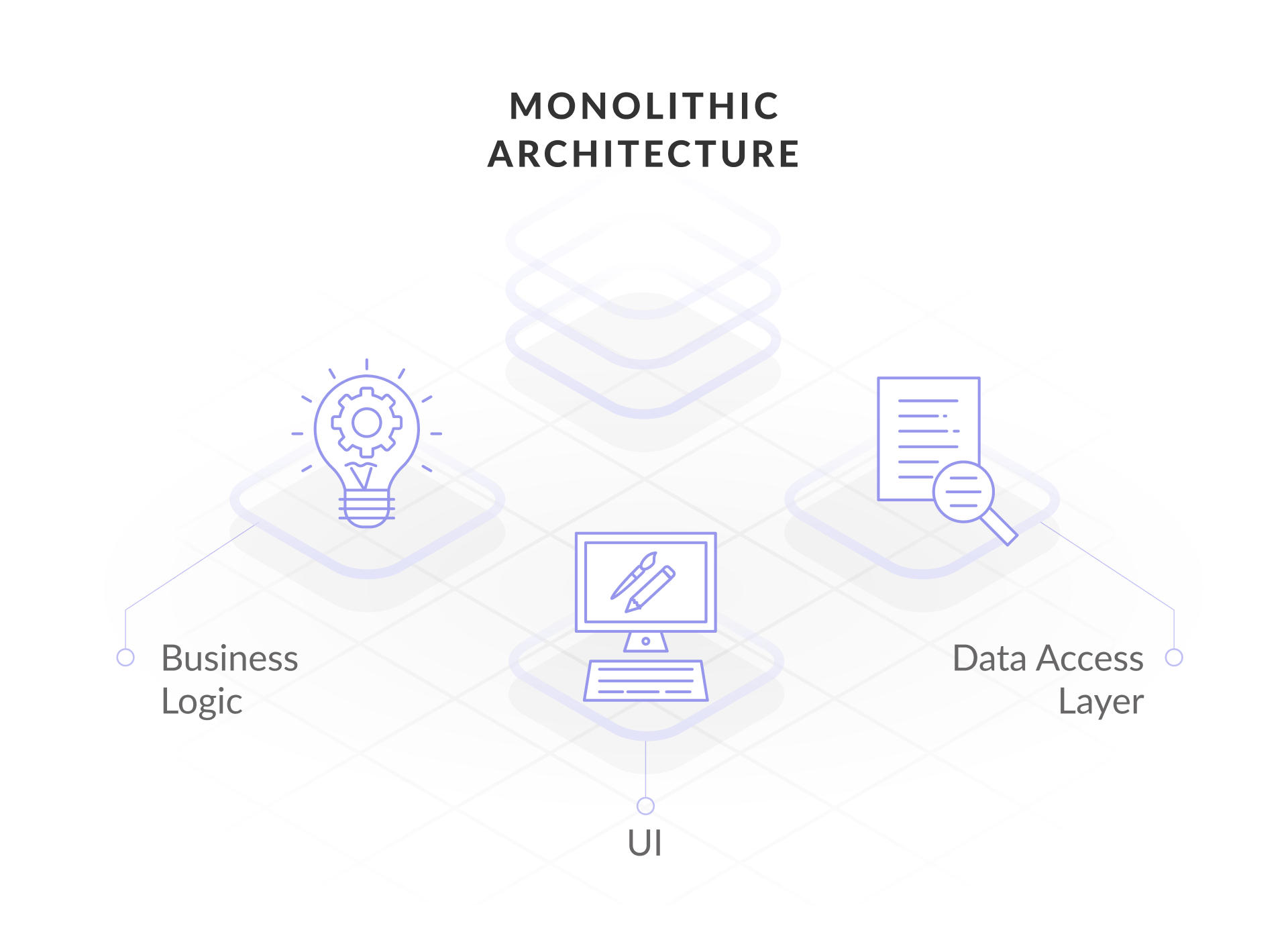
Monolithic architecture is convenient for small teams, which is why many startups take this approach when building an application. The components of monolithic software are interconnected and interdependent, which helps the software to be self-contained. This architecture is the traditional solution for building applications, but some developers consider it to be outdated.
Why is your code considered a monolith?
By their very nature, all frontend applications are monolithic - except for micro-frontend applications. The reason is that you are developing using the React library and there are two teams working on it. Both should use the same version of React and keep each other informed of updates, which means that they always resolve conflicts when merging their code. They are not completely independent from each other in the codebase. In fact, they probably use the same repository and the same build system. Front end microservices can save an application from being monolithic! But how can this be? After all, they are for the backend!
Disadvantages of a monolith.
1. Limited flexibility. Every small update requires a new deployment. Accordingly, if several teams are working on one project, they will have to wait.
2. Difficulty in introducing new technologies. Introducing a new technology into a monolith means rewriting the whole (large part) of the project.
3. Growing complexity. The more functionality the application has, the more functional blocks it consists of, the more connections between them there are, and accordingly, the more difficult it is to keep track of what is happening.
4. Organizational problems. The more teams work on a project, the more releases have to be implemented, which is fraught with the fact that each release can break an existing application (like a classic white screen). Each team member must use the same version of the libraries and notify everyone of any changes. There is also no complete independence from the codebase, developers would rather use one build system and one repository. It also creates problems for new team members, who will have to study the project before fixing a bug or creating a feature.
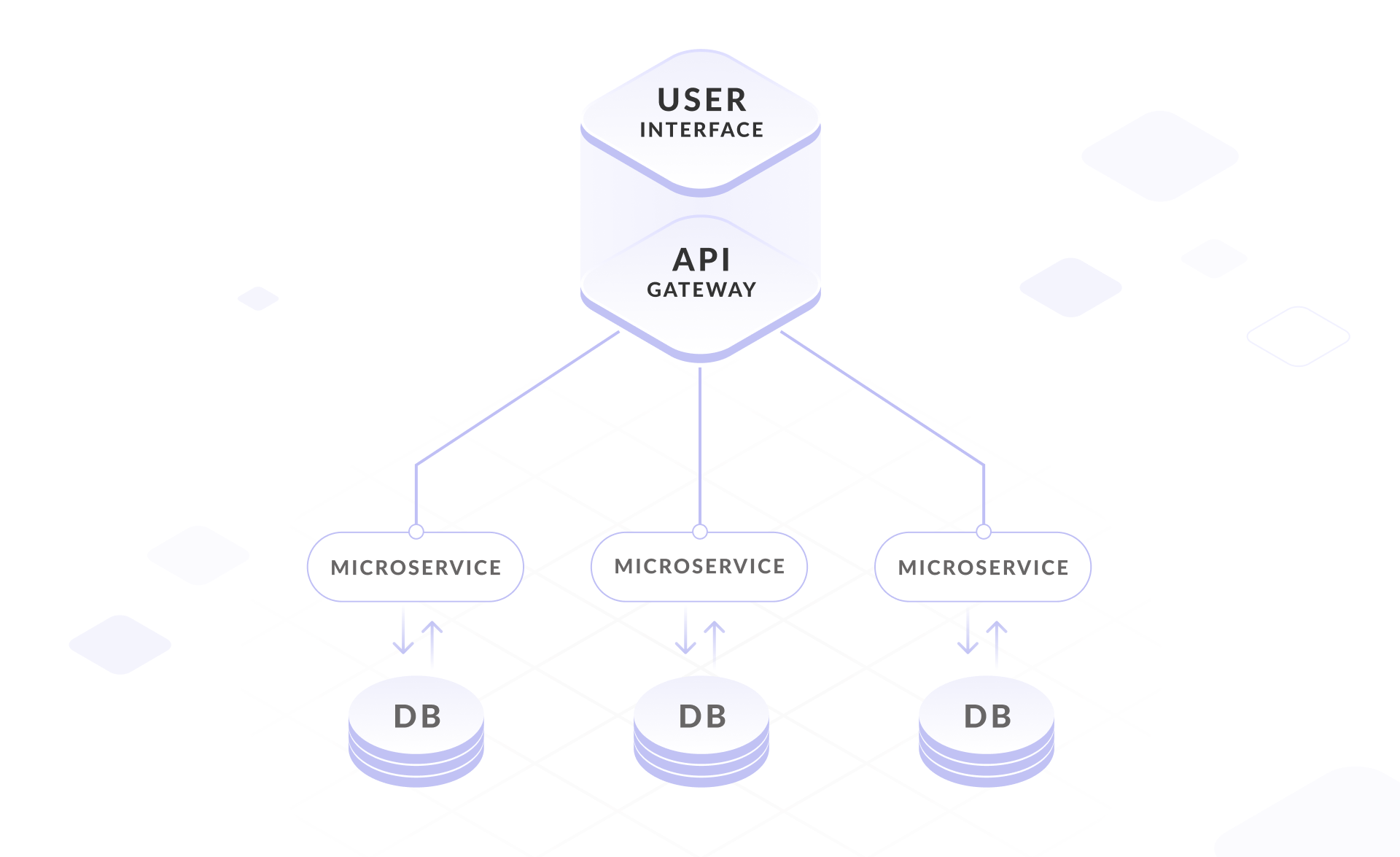
So What Are Micro Frontends?
All these problems are solved by microservice architecture. Microservices are a development technique that allows you to make independent deliveries of new functionality that cover their part of the platform. At the same time, the release of each microservice does not break the rest. Each microservice should perform one and only one business task. In the backend world, this approach has been used for a long time. But now many people have a question why not do the same in the front-end?
The principle of micro frontend is to make the presentation of a web application as a set of functions that independent teams will be responsible for. Microservice structures will look like a monolith, but for the user to interact with them as with one whole application, you need to create a "wrapper" for them. This level can be called connecting. But this approach is far from ideal and has several disadvantages.
Micro Frontends Cons
- You need to create a new layer in the application that will allow your micro frontends to interact with each other.
- Some constraints need to be added to the application to ensure compatibility.
- The deployment, assembly and configuration process for each micro frontend will be different, which of course will require additional effort.
- If different frameworks are used, then the size of the loaded bundles will be quite large.
Benefits of micro frontends
- Ability to use multiple frameworks in your application. You will have a choice of what to use for a particular task.
- Deployment independence. The assembly and delivery of your micro frontend will not affect the entire application as a whole, the changes will affect exactly that part of the business process that it has covered.
- It's easier to review the written code. By differentiating functionality, there is no longer a need to keep track of the entire application. The review is carried out only for the micro frontend, the functionality of which has been changed or expanded.
- Simplification in hiring employees. Now there is no need to look for an employee for the entire stack that appears in the project.
Micro frontend architecture.
The architecture of micro frontends looks pretty obvious, because similar principles have successfully been applied in the work on backend services for a long time to divide the monolithic frontend into small UI fragments. However, the UI is not exactly like services - it is the interface between the end user and the product, it must be thoughtful and systematic. Moreover, in the era of single page applications, entire applications are launched through a client-side browser. These are no longer simple HTML files, they are complex components that can contain various UI and business logic.
Imagine that I am dividing the structure of a monolithic application vertically, by business function. I will end up with several smaller applications with the same structure as the monolithic application. But if I add a dedicated application on top of these small monolithic applications, then users will interact with it. This added application, in its turn, will integrate the UI of those little apps. Let's call this layer a glue, because it takes the UI elements of each microservice and connects them into a single interface - this is the most direct implementation of the micro frontend.
Scheme of the application that uses the micro frontend approach:
1. There are N micro frontends.
2. We load each of them.
3. We initialize the micro frontends we need.
4. We mount the micro frontends where we need to.
5. Unmount when needed.
6. Each service will interact with the core.
Ways of setup micro frontends apps.
Unfortunately, there is no definite specification yet for building a micro frontend architecture. Here are perhaps the most affordable and simplest ways and techniques for building micro frontend applications:
- IFrames;
- Tailor.js library;
- single-spa framework.
Let's go through each of the listed approaches.
IFrames
IFrame is a long-standing technology that, despite all its irrelevance, makes it possible to build a micro frontend architecture. Using an IFrame, each individual widget can be placed in an IFrame that loads the desired application. With this approach, you are likely to run into the following problems:
- performance;
- complexity of support.
I do not recommend building a micro frontend architecture using IFrame. Today, there are other ways to make it easier and more effective.
Tailor.js library
Zalando has created an entire ecosystem for building a micro frontend architecture, and Tailor.js is part of the ecosystem. The peculiarity of Tailor.js is that it is a package for Node.js, and it is focused on building a micro-front-end architecture with server rendering.
For me, an additional feature of this package is the lack of documentation. I could find live examples of projects only in separate GitHub topics, where ordinary users ask for advice and attach links to their code repositories. If you need server rendering, then this library will definitely come in handy.
Single-spa
The main and, in my opinion, the best approach to building a micro frontend architecture is the single-spa framework. Here are the main reasons why I recommend choosing a single-spa:
- working examples using modern frameworks and libraries;
- good documentation;
- the ability to fumble the dependencies between individual widgets;
- support for independent deployments;
- building the application on the client side;
- a ready-made ecosystem of wrappers for the rapid integration of existing applications into the micro frontend architecture.
Single-spa is a framework that makes it possible to combine different applications, regardless of the library or framework used, into one whole. Under the hood of the single-spa is a set of existing tools along with its own solutions:
- SystemJS is a module loader that is needed to load individual applications asynchronously;
- Wrappers - single-spa provides separate wrappers for each framework, which creates a wrapper over the application needed to integrate and connect a separate application into a common single-spa;
- API - single-spa provides a set of tools that are needed for communication between individual applications, subscription to events, etc.
Communication between micro frontends.
Single-spa
Now I come to an interesting question - how do micro-frontends interact with each other?
To understand this, let's figure out what a core is and what functions it should perform.
In simple terms, the core is another application that brings our micro frontends together.
What is the core made of?
- Service loader;
- Router;
- Communication services.
The loader allows you to download our micro frontends and mount them in the place we need. To understand what is to be loaded, you can create JSON which will contain the data about the package you need to take.
bundles.json
{
"PaymentService": {
"version": 682, "enabled": true
},
"SalaryService": {
"version": 581, "enabled": true
},
"CheckPartnerService": {
"version": 65, "enabled": false
}
}
The router allows us to render our micro frontend depending on where we are now. The general scheme of the route looks like this:
1. Activating a new route;
2. Dismantling the micro frontend that was associated with the old route;
3. Installing a new micro frontend.
Communication between micro frontends can be done as you please. CORS approach can be used as an example.
In the case of SSR (Server-SIde-Rendering), all your microfronts should be turned into fragments and combined in the final HTML page.
When to use micro frontends.
Using this architectural approach in small projects and small teams presents more challenges and additional frontend development complexity than benefits. But large projects with distributed teams and huge number of requests, on the other hand, benefit more from building micro frontend applications. That is why today micro frontend architecture is already widely used by many large companies in their web applications:

Problems of micro service approach.
To make it clearer, below I will call each small monolithic application a micro application, since these are not just microservices, but stand-alone applications - each of them has UI elements and each of them represents a full-fledged business function. As you know, today's front-end ecosystem is very diverse and can be quite complex. And such simple, obvious solutions may turn out to be inappropriate during the implementation of the product.
Challenge # 1: Achieve cohesive and consistent UI behavior when we have a lot of completely standalone micro applications.
There is no panacea, but there is an idea to create a common UI library, which would also be an independent micro-application. In this case, all other micro-applications will need to depend on this UI library.
Another option is to create generic CSS variables at the root level. The advantage of this solution is that we get a global custom theme for all applications.
Alternatively, we can make SASS variables and mixins common to all commands. The disadvantages of this approach will be repeated implementation of UI elements and the need to constantly check the design of similar elements in all micro applications.
Challenge # 2: Make sure one team doesn't interfere with another team's CSS.
First, it is possible to limit the scope of the CSS using selectors formed by the name of the micro application. By placing this constraint on the middle tier, you can reduce the overall frontend development time, but at the same time increase the responsibility of the middle tier.
Second, you can force each micro application to become a custom web component. The advantage of this approach is that the browser is responsible for the limitation. However, everything has a price: with Shadow DOM, it is nearly impossible to do server-side rendering. Besides, custom elements are not 100% supported by browsers - especially if you need IE support.
Challenge # 3: make global information common to different micro applications
This problem is one of the most common, but it can be solved quite easily. HTML5 is powerful enough to be largely unexplored by most front-end developers. One such feature is custom events, which allows you to share information across micro applications.
Also the pub-sub or T39 implementation can help you. If you need a more subtle global state handler, you can implement a small generic Redux - thus a more reactive architecture.
Challenge# 4: If all micro applications are autonomous, how do you do client-side routing?
The solution to the problem is implementation dependent. All major modern frameworks have powerful client-side routing mechanisms using browser history state. The problem is which application is responsible for the current route and when.
My pragmatic approach is to create a generic client router that is only responsible for the top-level routes, and the rest is left to the appropriate micro-applications. Let's say we have a route definition / content /: id. The shared router will resolve the c / content part and the resolved route will be passed to ContentMicroApp. ContentMicroApp is a stand-alone server that will only be called with /: id.
Challenge # 5: Orchestrate the client side so that you don't have to reload the page every time
The bonding layer solves problems on the client side, but not on the server side. On the client side, after loading a single HTML, we cannot load individual parts when changing the URL. Hence, we need a mechanism that downloads the fragments asynchronously. The problem is that these fragments can have dependencies, and there should be a possibility for these dependencies to be resolved on the client side. This means that a micro frontend solution must offer a mechanism for loading micro applications and dependency injection.
Conclusion
As a result, having studied all the possible information about micro frontends available on the Internet (and as I mentioned above, the micro frontend is still a problem with the documentation), I was able to convey the correctness of this approach in the case of developing a sufficiently large application for a neobank.
Remember, if you have a regular company website and a small project with a small team working on it, then most likely you don’t need a micro frontend concept. If you have several teams on your project and several interacting views on different domains, then it makes sense to consider this approach. First of all, you need to evaluate the benefits that you will receive in return for the effort and time spent, whether it is worth it or not.
Good luck with micro frontends!





















