Outsourcing software development can be a smart business move, allowing companies to leverage the expertise of specialized development teams while reducing costs and improving efficiency. However, when outsourcing involves personal data processing activities, companies must ensure that they comply with relevant consumer data protection regulations and safeguard the privacy and security of their customers. All of the companies that start cooperating with outsourcing vendors need a DPA.
A legal basis instrument for ensuring safe and lawful personal data processing in outsourcing agreements is the data processing agreement (DPA). A data processing agreement must be signed between the business (the controller) and each third-party data processor to ensure that the data is stored properly and is not misused, sold, or vulnerable to attack. This is one of the most basic steps toward GDPR data processing agreement compliance. So let's take a closer look at what is a data processing agreement, who is the data controller and processor, what needs to be in data processing agreement, and much more!
In this article:
What is a data processing agreement
A data processing agreement (DPA) is a crucial, legally binding contract that establishes clear terms for the handling of personal information between two parties: the data controller and the data processor. The data controller is the one responsible for determining the reasons and methods of personal data processing, while the data processor performs the processing of personal information on behalf of the data controller. This written consent serves as a framework that outlines the responsibilities and obligations of both parties, ensuring the safe and lawful processing of personal information.
Ready to upgrade your tech?
Whether you need advice, system improvement, or a digital makeover, we have the expertise to create custom IT strategy that fit your specific requirements.
The DPA sets out the responsibilities and obligations of the software development company in relation to the processing of personal information. It includes requirements for security, confidentiality, and privacy, as well as outlining the specific processing activities that the data processor is authorized to perform. This ensures that the software development company processes data only in accordance with the controller's instructions.
It is important to tailor the DPA to the specific outsourcing agreement and personal data being processed. For example, if the software development company is located in a different country than the client, the DPA may need to include specific provisions regarding data transfers. It is recommended to work with legal professionals to ensure that the DPA meets all legal and regulatory requirements for software development outsourcing.
Who is a data controller and a data processor
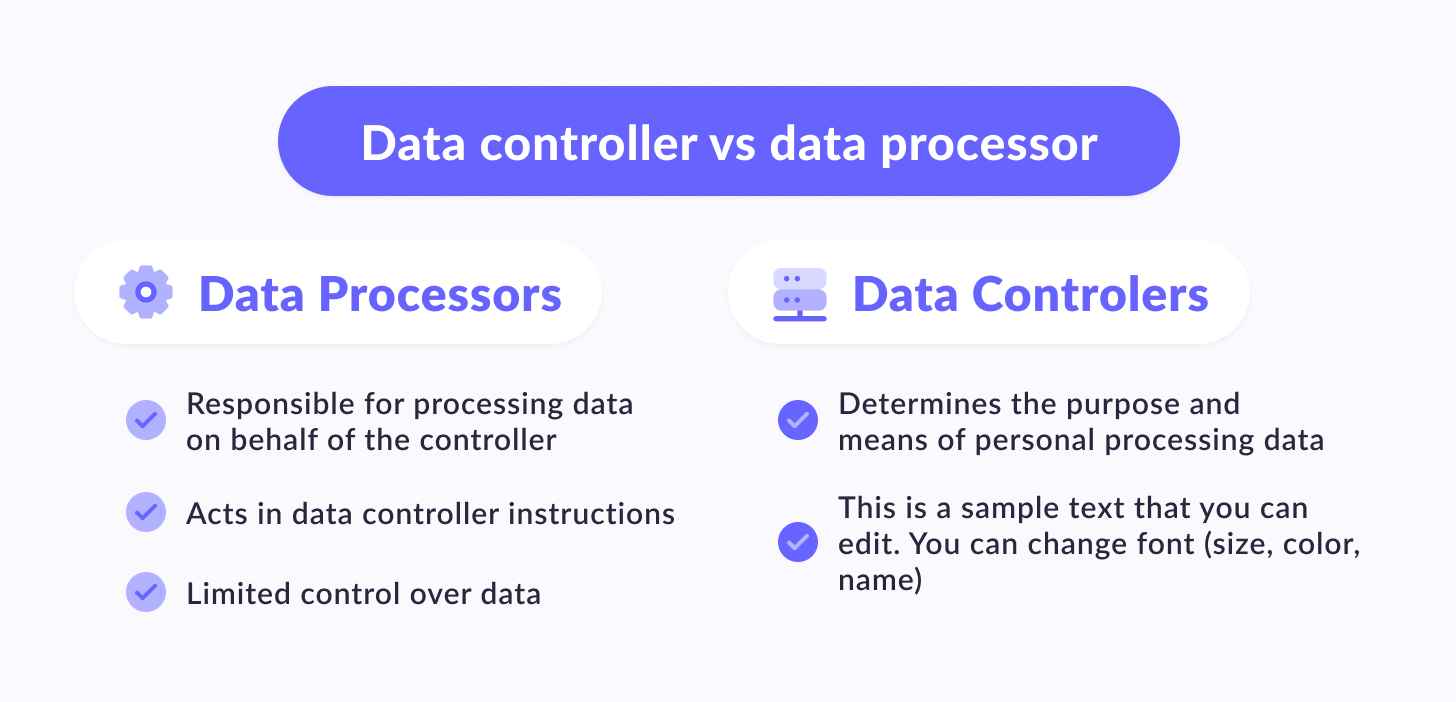
In the context of data protection and privacy, a data controller (data protection regulation DC) and a data processor (DP) are two distinct roles defined by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, but they are also used in other security laws and regulations around the world.
A data controller holds significant responsibility in determining the purposes and methods of processing personal data. Whether an individual or organization, DCs play a crucial role in collecting, using, sharing, and safeguarding personal information in accordance with data protection laws. They have legal obligations to ensure that personal data usage is processed lawfully, transparently, and fairly. Common examples of data controllers include businesses, government agencies, and non-profit organizations.
On the other hand, a data processor performs the actual processing of personal information on behalf of a data controller. DP may be third-party service providers that the DC contracts with for various purposes, such as cloud storage, payment processing, or software development. However, it's important to note that even though DP are not decision-makers in processing personal information, they still hold responsibilities and obligations under data protection laws. They must process personal information only for the purposes authorized by the DC and ensure data protection that proper security measures are in place. Common examples of DP include IT service providers, call centers, and marketing agencies.
What is GDPR
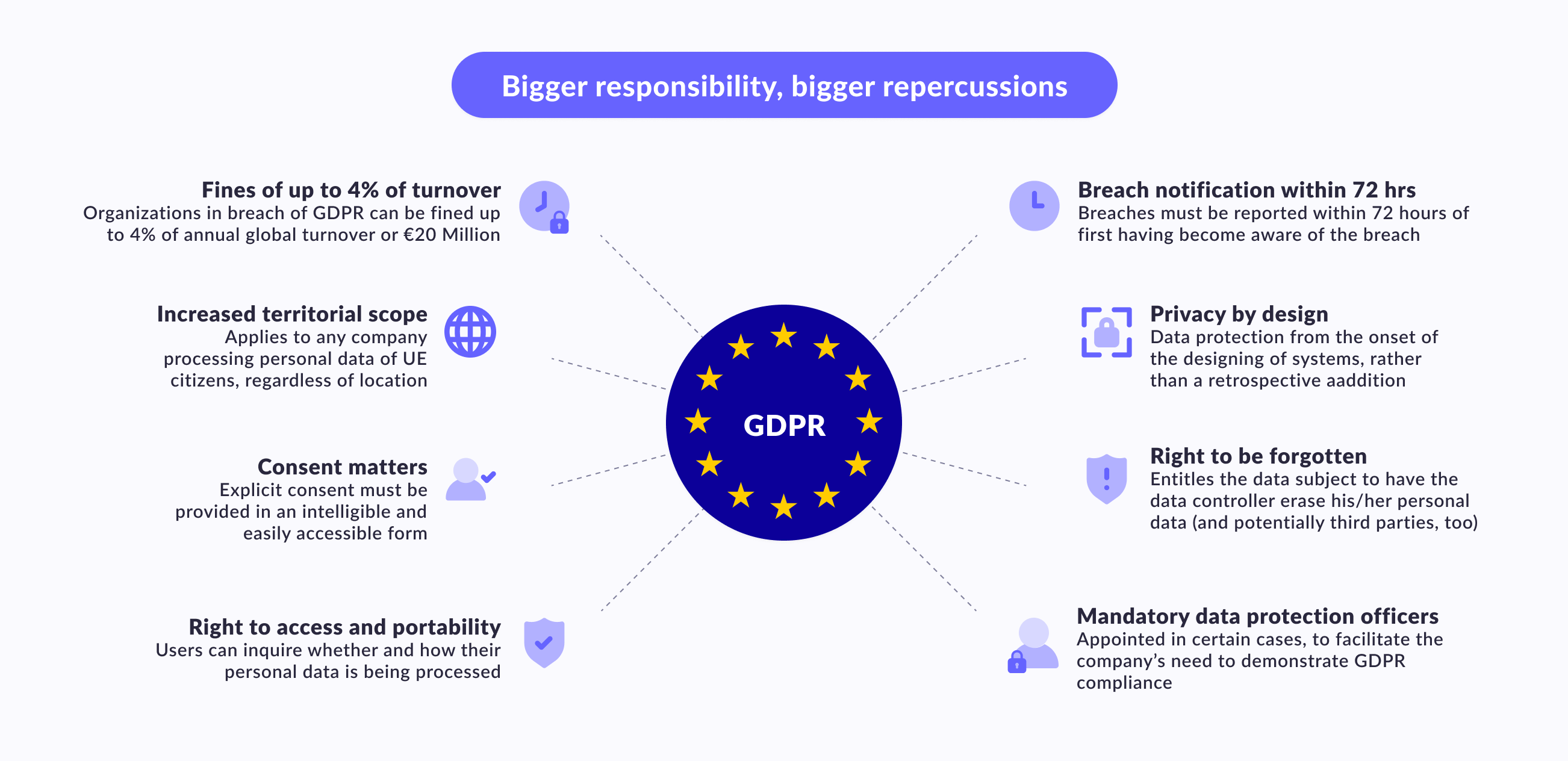
We have already shared the information about what data processing agreement is, and now let's talk about GDPR. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a wide-ranging data protection framework that was implemented in the European Union (EU) on May 25, 2018, with the intention of strengthening and harmonizing data protection laws across EU member states. This replaced the previous EU data protection directive, and it applies to all organizations that process the personal information of EU citizens, regardless of where the organization is based. This implies that organizations outside the EU must also comply with the GDPR compliance if they process the personal data of EU residents.
Personal information, under the GDPR, encompasses any data related to an identified or identifiable natural person. This can include name, address, email address, identification number, online identifiers, and much more.
The GDPR offers numerous rights to individuals regarding their personal information, such as the right to access, rectify, erase, and restrict the processing of their data. In addition, individuals have the right to data portability, meaning they can request a copy of their data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format.
Organizations that process personal data have significant responsibilities and obligations under the GDPR. For example, they must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal information, and they must inform supervisory authorities and affected individuals of any data breaches. Organizations must also designate a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if they process certain types of personal data or engage in certain types of processing activities.
Non-compliance with the GDPR carries severe consequences, including fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global revenue, whichever is higher. Each EU member state has a supervisory authority responsible for enforcing the GDPR, and they can investigate and sanction organizations that fail to comply with the regulation.


Thank you for Subscription!
What happens after you sign a DPA with the EU customer
After signing a Data Processing Agreement with an EU customer, there are several steps that you should take to ensure compliance with the terms of the agreement and with the General Data Protection Regulation:
- Review the DPA. It's important to review the data processing agreement carefully to ensure that you understand your responsibilities and obligations under the agreement.
- Implement appropriate security measures. You should implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal information, as required by the DPA and the GDPR.
- Train your employees. Your employees should be trained on the legal requirements of the DPA and GDPR compliance to ensure that they understand their responsibilities and obligations.
- Conduct regular risk assessments. You should conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential security risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks.
- Monitor compliance. You should monitor compliance with the DPA and the GDPR to ensure that you are meeting your obligations under the agreement and the law.
- Notify the customer of any breaches. If you experience a data breach that affects personal information covered by the DPA, you should notify the customer as required by the agreement and the GDPR.
- Cooperate with customer audits. The customer may conduct audits to ensure that you are complying with the terms of the DPA. You should cooperate with these audits and provide any information requested by the customer.
What needs to be in a DPA
The GDPR requires that certain provisions be included in a DPA to ensure that personal information is processed in accordance with the requirements of the regulation. Here are some of the key provisions that should be included in a DPA:
Scope and purpose
The DPA should clearly define the scope and purpose of the data processing activity, including the types of personal data being processed, the categories of data subjects, and the purposes of the processing.
Data security
This agreement should also specify the technical and organizational measures that the DP will implement to ensure the security of personal information.
Sub-processing
Suppose the DP intends to engage sub-processors to process data on behalf of the DC. In that case, the data processing agreements should require the customer data processor to enter into a separate sub-processing agreement with each sub-processor.
Data subject rights
The Data Processing Agreements should specify the data subject rights that the DP will facilitate, such as the right of access, rectification, erasure, and objection.
Data breaches
The DPA should also include DP obligations with respect to data breaches, including the obligation to notify the DC of any breaches without undue delay.

You may be interested
CTO as a service: grow your business with CaaS
Explore the benefits of tapping into top-tier CTO expertise without the full-time commitment, offering strategic guidance and innovation.
Continue readingData protection impact assessments
If the processing activity is likely to result in a high risk to the rights and freedoms of data subjects, the contract should require the DP to assist the data controller in conducting a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA).
Termination and return of data
The DPA document should contain conditions under which the agreement may be terminated and the information returned to the controller.
Liability and indemnification
It should specify the liability of the parties and any indemnification obligations.
Audit and compliance
Also, the agreement should mention the right of the DC to audit the data processor's compliance with the DPA and the GDPR.
Final thoughts
Data processing agreements are critical in software development outsourcing, particularly when working with EU customers. As a software development company, it's essential to understand who the DC and processor are, as well as the requirements of the GDPR Data Processing Agreement.
Once a DPA has been signed with an EU customer, it's important to ensure that all parties adhere to the agreement's terms and requirements. To create an effective data processing agreements, including specific clauses and provisions that align with GDPR compliance is essential. At Geniusee, we take customer data privacy seriously and have developed our Business DPA Agreement Template, which outlines our commitment to data protection authorities and compliance with GDPR.
By understanding the importance of DPAs and implementing effective measures, Geniusee maintains strong relationships with its customers and builds a reputation as a trustworthy and reliable partner!





















