The modern economic model in the world directly depends on the level of technological progress. Technological progress not only forms new economic relations but also allows optimizing them. In this regard, banks are increasingly showing an increased interest in automated loan processing systems that would minimize the participation of experts and the influence of the human factor on decision-making.
In this article:
What is lending process automation?
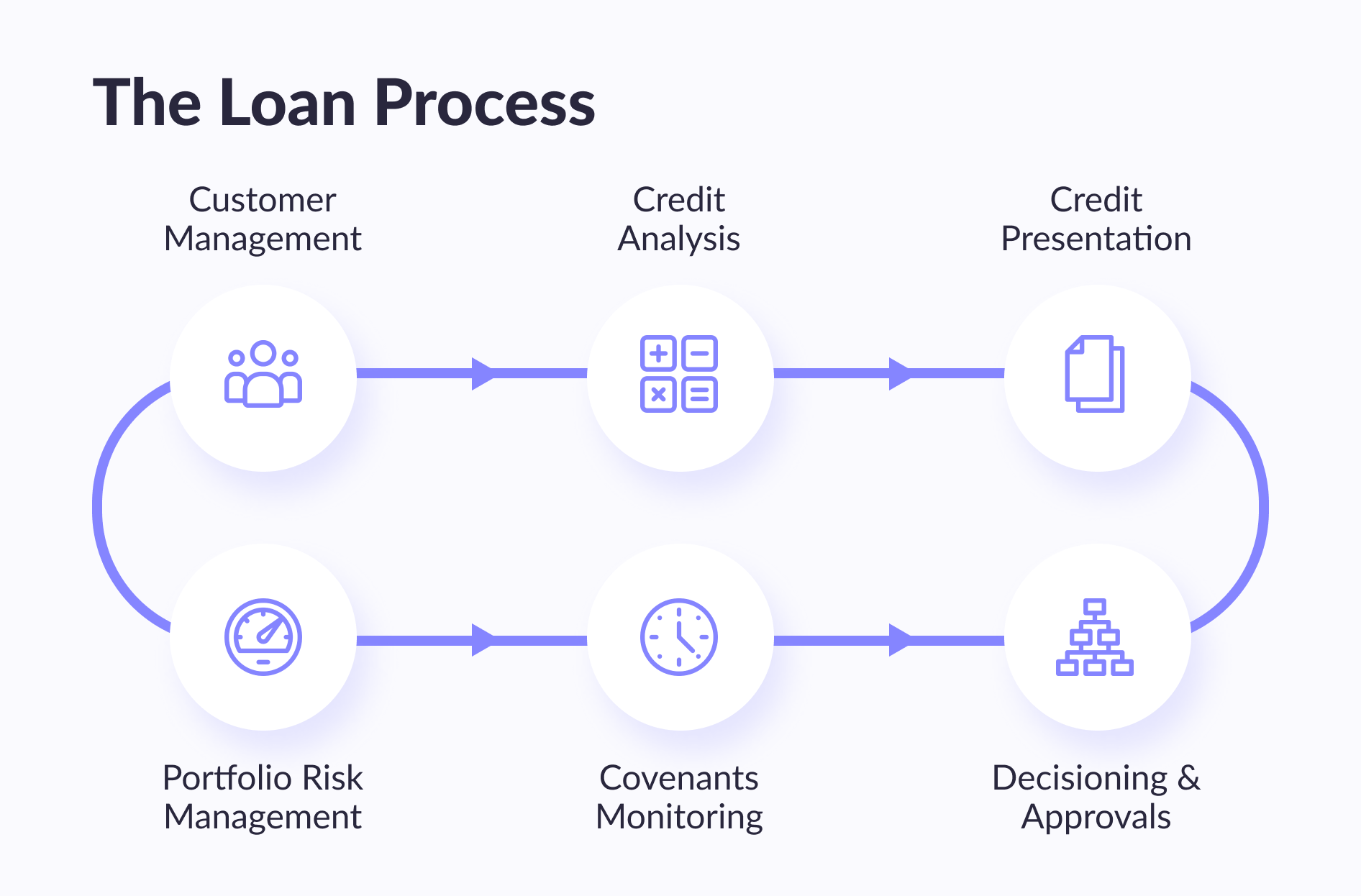
A competent assessment of the customers' creditworthiness ensures a high quality of the loan portfolio and a low level of default. Still, the bank must not only be sure that its borrowers will repay the loan: but it is equally important to know who should be offered certain individual conditions and organize the entire chain of work with clients quickly.
Therefore, the evaluation loan origination process needs to be automated. At its core, it is quite complex: for each individual, the loan applications contain a large amount of personal information, including income and credit history — more than two to three dozen parameters in total. The bank also collects information about the presence/absence of an individual on the black lists, etc., and other related data from external sources.
To unambiguously interpret the prepared parameters (after all, the parameter relationships are usually non-linear), banks previously relied on the accumulated subjective experience of expert employees, and the final lending decisions were made by credit committees, whose resources, of course, are limited.
The ability to quickly and efficiently serve a client is no longer an advantage, but a requirement for any bank that seeks to consolidate its position in the highly competitive financial services market. To get into the top leaders, it is necessary to introduce new services and products promptly and quickly respond to changing consumer needs. Automation in lending will be a game-changer in that regard.
Lending and underwriting process automation technology means a set of methods and automation tools for creating an automated risk management system through the implementation of software solutions. The technology is based on the search, and often the creation, of optimal ways of information exchange within the framework of accepted control schemes.
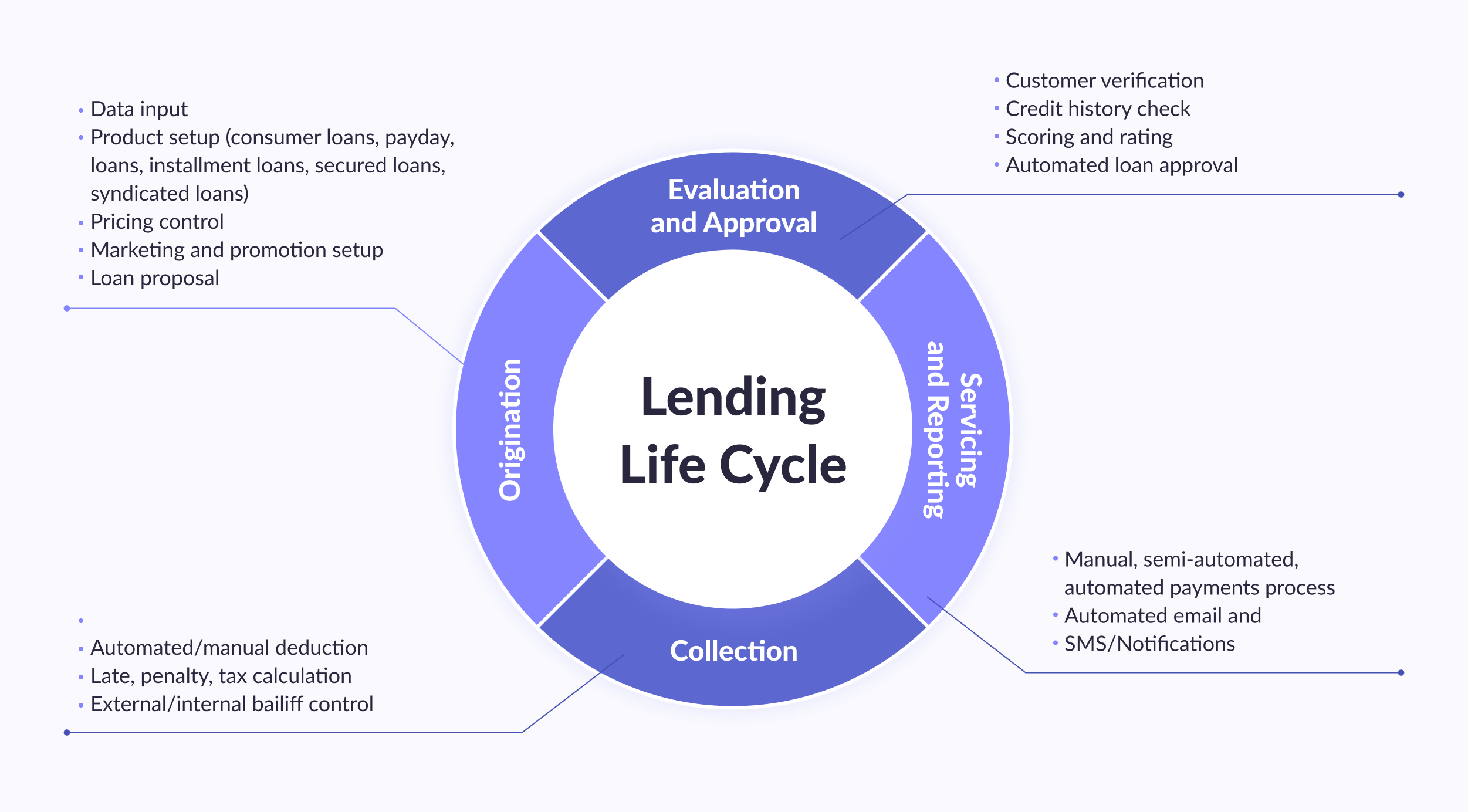
Why automate and integrate lending and underwriting?
Loan processing automation is aimed at achieving five goals:
- Transfer of transactions to automatic mode, which increases the speed of their processing;
- Creation of a single accounting center to track the activities of all offices and branches of the bank;
- Formation of a flexible product line that is suitable for customers in a particular region;
- Ensuring high speed and efficiency of decision-making on automated loan processing and competent portfolio risk assessment & risk management;
- Preventing fraud attempts among customers and bank employees.
Intelligent automation of the bank's operational work will make it possible to bring the procedure for registering products and providing services to a single standard. Thanks to this, customer service will be simplified and accelerated, positively affecting their loyalty to the bank. Reliable and fast operation of the bank, convenient creation, and development of products and services are ensured.
Lending operations that can be automated
Bank lending departments spend a significant amount of time processing loan applications, which forces the client to look for more productive banks for their needs. The human factor plays a key role in assessing the risks of issuing a loan, which can lead to an incorrect decision and worsen the bank’s loan portfolio.
So, what operations can be automated within the full-cycle lending process to avoid these risks?
Loan origination
Risk assessment
Application processing
Credit scoring and underwriting
Document verification and compliance checks
Loan documentation
Debt collection
Reporting
Supervision
Regulatory compliance
How loan automation improves credit servicing
Once the loan is approved and disbursed, loan servicing becomes an important aspect of the lending process. Traditionally, loan servicing involved manual tasks such as payment processing, account management, and customer support. However, loan automation is now improving servicing and overall customer experience.
Here's how loan automation is transforming loan servicing:
1. Online account access. Loan automation allows borrowers to access their loan accounts online, providing them with real-time information about their loan balance, payment schedule, and transaction history. This enables borrowers with greater control and visibility compared to their loans.
2. Automated payment processing. Instead of relying on manual payment processing, loan automation allows for seamless and efficient payment processing. Borrowers can create automatic recurring payments, reducing the risk of late or missed payments.
3. Personalized communication. Loan automation also allows traditional lenders to send personalized messages to borrowers, such as payment reminders or loan updates. This improves the customer experience by providing timely and relevant information.
4. Self-service options. Loan automation provides borrowers self-service options such as online loan modifications or deferment requests. This eliminates manual intervention and allows borrowers to manage their loans conveniently.
Lenders can use loan automation to provide borrowers with a seamless and personalized experience, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.

Do you know?
Fintech and Regtech in a nutshell: what’s the difference?
All the difference in one article, simply take it. Proven information by our CTO.
Let's seeAI & machine learning in lending and underwriting processes
Banks already use artificial intelligence to provide customer services and improve business processes. But the heyday of this technology may be yet to come. AI and machine learning in banking have accelerated access to products for many customers and automated some steps in internal processes, which also affected the speed of service.
Examples of using AI in banking & loan automation
Client credit scoring
Automated loan decisions on customer loan applications for loan origination process. Previously, loan applications from a large business were considered for two or three weeks, and this took the time and effort of many loan officers. Now, the loan automation by utilizing AI takes no more than seven minutes from the client's request to the receipt of money. Everything happens remotely, without paper documents, and the percentage of delays is reduced to almost zero.
Voice assistants and chatbots
They are used when a client contacts a call center or a bank chat to reduce service time and optimize employee work. Thanks to voice robots in call centers, customers receive an average consultation 40 seconds faster, and the bank saves over $2 million per month. As for the chatbot, it processes over 40% of client requests and saves the bank more than $10 million per month, through loan automation.
Anti-fraud and financial monitoring
AI is used to counter financial fraud by analyzing the atypical behavior of individuals and legal entities. Anti-fraud and financial monitoring play crucial roles in ensuring the integrity of the loan origination process. AI is employed to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, safeguarding the entire lending ecosystem from risks and ensuring a smooth & automated loan origination process.
Document processing
With the help of AI, it is possible to automatically process and enter customer data when opening commercial loans and performing banking operations where identity verification is required. Artificial intelligence recognizes more than 70 details from scans and photos of documents for each client in 2 seconds and performs about 15 automatic data checks.
Trends in lending and underwriting automation
In 2022-2023, lending process automation software trends involved lenders' focus on matching borrowers' expectations, leveraging omnichannel, and improving loan origination process efficiency. Let's take a closer look at the loan processing automation trends that will shape the lending industry in 2024.
1. End-to-end digitization
The most important trend in lending process automation will be increasing digitization. Digitization allows banks and financial institutions to streamline their operations. These operations include customer information collection, organization, and financial analysis. The switch does not happen instantly but will take place gradually.
Based on Accenture, over 50% of lending processes are still manually performed. By using technology, banks in North America can save more than 70 billion USD by 2025. Automation can assist existing employees and increase the efficiency of financial organizations. Tech companies will also delve deeper into financial services.
Automation platforms offer faster and more consistent loan approval processes. Automated loan origination process takes much less time by using digital lending platforms, and organizations can make loan decisioning faster.
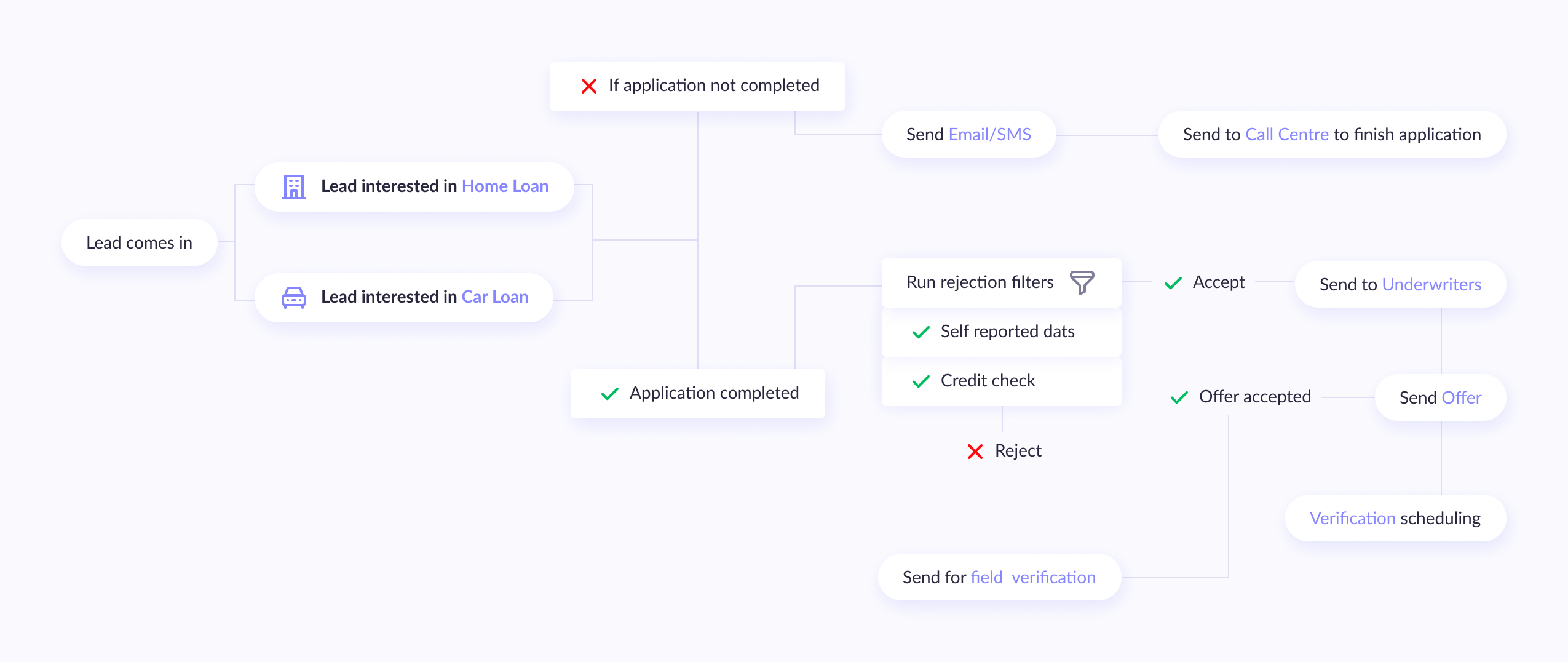
2. Switch to integrative microservices
Loan process control remains a paper-extensive process. Since accuracy is important in this business, a number of guides' hard work is going into verifying documents. All steps — from mortgage utility to disbursal and debt collection, contain guide work. The lending organizations that depend on those legacy structures want a further push to digitize their operations.
For customers, digitization will convey convenience. They can practice for a mortgage with some clicks. Lenders may even want to boost their reaction time by adopting automation. But loan processing automation won't constantly offer the favored outcome. In a few cases, creditors won't get the outcomes they want. The rush to update legacy structures may cost them extra in the lengthy run.
For this, the answer is to apply integrative microservices. It permits creditors to digitize their operations at their very own pace. The modern-day fashion is cloud-primarily based microservices. Companies can upload those offerings as modules one via way of means of one. This machine permits organizations to conform to regulatory adjustments too.
3. New enterprise models
Collaboration among banking and large tech has won traction recently. Banks had been partnering with Fintech for diverse offerings. For instance, NIBC financial institution uses the offerings of Oaknorth for credit score analysis. It is an instance of a collaborative version. Similarly, there exists a Point of Sale or POS transaction version. In this case, traders can be given cash through the usage of swipe machines. The aggregator version offers the purchaser all of the lending alternatives available. The peer-to-peer version permits purchasers to borrow from many creditors inclined to lend simultaneously.
4. Improved credit score structures
The credit score structures of conventional banks aren't appropriate for SMEs. There is a lot of overhead with traditional scoring structures. SMEs frequently no longer get admission to credit scores due to this system. Some troubles encompass huge documentation, high-hobby rates, and lengthy decision-making times. Now, Fintechs are supplying an opportunity scoring system. They use statistics-pushed fashions alongside financial institution details.
These statistics factors encompass:
Personal statistics, inclusive of age, name, touch details, financial institution credit score score;
Businesses' statistics like coin flows, financial institution account statements, economic statements, and POS transactions;
Behavioral statistics, inclusive of psychometric checks and spending patterns.
Fintech additionally makes use of different statistics factors, inclusive of schooling level, degrees, and occupation. These opportunity strategies enhance the accuracy of statistics-pushed automatic fashions. It finally reduces the time and fee of servicing a loan. Thus, quit clients can get a budget with minimum effort.
Conclusion
Computerization has expanded the effectiveness of various lending businesses around the world. Banking, including lending and loan underwriting, was, in numerous ways, an advancement pioneer. Still, the matter of starting an independent venture and business advances is as yet continued similarly as it was many years prior.
The scene for business loaning is currently evolving. Prodded on by the rise of more innovation-empowered contenders, numerous customary lenders are getting in on the demonstration by embracing mechanization strategies in their advanced beginning cycles. The contest is a long way from the main catalyst. Loan officers who perceive a should be more proficient, useful, and receptive to their clients, with more significant administration levels, also hope to carry out mechanical arrangements. These loan officers are additionally determined by the investment funds' cost and necessities to meet more tough administrative test guidelines. For other people, the capacity to assume back command over their information and to acquire more keen, more precise business experiences is the intention.
We see that barely any loan process specialists are incited to apply computerization to decrease human knowledge in the business loaning field. Rather, most see it as an empowering agent to hold the ability and draw in financiers' experience on things that matter, like gamble examination and client relationship with the board, rather than the organization.
At last, while mechanizing advanced guaranteeing automated loan processing systems can introduce a few difficulties, doing so can improve the establishment's brand as a pioneer and market pioneer among peers.


















